Biology - Chapter 10
... 13. division of the cytoplasm during cell division 14. second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up acorss the center of the cell ...
... 13. division of the cytoplasm during cell division 14. second phase of mitosis, during which the chromosomes line up acorss the center of the cell ...
The Cell Theory - Ursuline High School
... structure and function in an organism. 3. Cells come only from existing cells. ...
... structure and function in an organism. 3. Cells come only from existing cells. ...
Cells: form fits function - Science-Hinz
... 5. Look at the shape of the plant root epidermis (p613). Its main job is to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Describe the shape of these cells and explain how its shape would help it to do its job. ...
... 5. Look at the shape of the plant root epidermis (p613). Its main job is to absorb water and minerals from the soil. Describe the shape of these cells and explain how its shape would help it to do its job. ...
LIFE SCIENCE UNIT 1 TEST REVIEW, CHAPTERS 1 AND 2
... 22. PLANT HAVE TUBES THAT TRANSPORT FOOD AND WATER TO ALL CELLS 23. REDI SHOWED THAT MAGGOTS HATCHED FROM EGGS LAYED ON MEAT, NOT FROM THE MEAT ITSELF. 24. LIST THE STEPS (7) OF THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD a. STATE PROBLEM, GATHER RESEARCH, MAKE A HYPOTHESIS, TEST HYPOTHESIS, ANALYZE DATA, DRAW CONCLUSION ...
... 22. PLANT HAVE TUBES THAT TRANSPORT FOOD AND WATER TO ALL CELLS 23. REDI SHOWED THAT MAGGOTS HATCHED FROM EGGS LAYED ON MEAT, NOT FROM THE MEAT ITSELF. 24. LIST THE STEPS (7) OF THE SCIENTIFIC METHOD a. STATE PROBLEM, GATHER RESEARCH, MAKE A HYPOTHESIS, TEST HYPOTHESIS, ANALYZE DATA, DRAW CONCLUSION ...
human derived tissues 3D vascular networks for
... 1.University of California, Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA ...
... 1.University of California, Irvine, Irvine, CA, USA ...
Unit C Key Terms C31-The Range of Disease
... Cell membrane-part of ALL cells that separates the cell from the environment and controls what moves in and out of the cell ...
... Cell membrane-part of ALL cells that separates the cell from the environment and controls what moves in and out of the cell ...
The Cell Theory
... a monastery) to describe the honeycomb shape and structure of a thin slice of cork he observed under a primitive microscope. Robert Hooke Neglected Hooke Anton Van Leeuenhoek, 1674 An Unlikely Scientist, made microcsopes and observed blood cells, bacteria and single celled organisms. Robert Brown, 1 ...
... a monastery) to describe the honeycomb shape and structure of a thin slice of cork he observed under a primitive microscope. Robert Hooke Neglected Hooke Anton Van Leeuenhoek, 1674 An Unlikely Scientist, made microcsopes and observed blood cells, bacteria and single celled organisms. Robert Brown, 1 ...
Cell Theory Section A1.1
... Metabolism- the sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism ...
... Metabolism- the sum of the physical and chemical processes in an organism ...
bio_ch05
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
Power Point
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
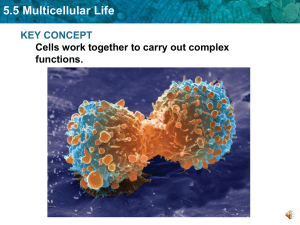
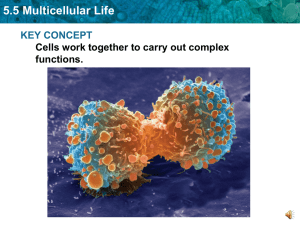
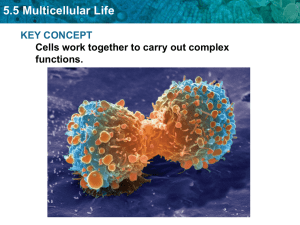
5.5 Multicellular Life KEY CONCEPT Cells work together to carry out complex functions.
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
Specialised Cells
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
... and animals consist of many cells and so are known as multicellular They contain many different types of cells. Each type of cell is designed to carry out a particular job or function. This is known as cell specialism Not all cells look the same. Some cells have a special shape and feature ...
7th Grade Review for Benchmark
... All body systems work together to make the organism function within an environment. The endocrine system in an organism is the system responsible for producing chemicals in the body such as insulin, sex hormones and adrenaline. Animal Adaptations Over time, as an environment changes, organisms must ...
... All body systems work together to make the organism function within an environment. The endocrine system in an organism is the system responsible for producing chemicals in the body such as insulin, sex hormones and adrenaline. Animal Adaptations Over time, as an environment changes, organisms must ...
Stem Cells
... Pluripotent – inside blastocyst; can develop into most types of cells (not the tissue around embryo) ...
... Pluripotent – inside blastocyst; can develop into most types of cells (not the tissue around embryo) ...
Cell Structure (Organelles)
... a. may or may not be the same element b. example – Oxygen (O2), Salt (NaCl) 3. compound – two or more different elements combined a. all compounds are molecules, not all molecules are compounds b. example – Carbon dioxide (CO2), Water (H2O) 4. atom- the smallest and most basic unit of matter 5. cata ...
... a. may or may not be the same element b. example – Oxygen (O2), Salt (NaCl) 3. compound – two or more different elements combined a. all compounds are molecules, not all molecules are compounds b. example – Carbon dioxide (CO2), Water (H2O) 4. atom- the smallest and most basic unit of matter 5. cata ...
ESRC Stem Cell Initiative: Capacity Building and Awareness
... of ‘outcome’ over longer period of time than normal? ...
... of ‘outcome’ over longer period of time than normal? ...
Honors Biology Midterm Chapters and Topics 2014
... Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Types of microscopes and why they are used Prokaryotes verses Eukaryotes Comparing plant and animal cells Cell structures and functions Chapter 5 The Working Cell Plasma membrane structure and function Passive transport o Diffusion o Facilitated diffusion o Osmosis: hypo ...
... Chapter 4 A Tour of the Cell Types of microscopes and why they are used Prokaryotes verses Eukaryotes Comparing plant and animal cells Cell structures and functions Chapter 5 The Working Cell Plasma membrane structure and function Passive transport o Diffusion o Facilitated diffusion o Osmosis: hypo ...
Membrane Transport Lab
... Learning Targets “I Can…” -Define “selective permeability.” -Model a living cell by using dialysis tubing in a liquid medium. - Predict the results of an experiment that involves animal cells rather than plant cells. ...
... Learning Targets “I Can…” -Define “selective permeability.” -Model a living cell by using dialysis tubing in a liquid medium. - Predict the results of an experiment that involves animal cells rather than plant cells. ...
INTRODUCTION TO THE CELL NOTES
... 7. Compare the two basic types of cells by indicating with a check which of the following are characteristics of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells: ...
... 7. Compare the two basic types of cells by indicating with a check which of the following are characteristics of prokaryotic or eukaryotic cells: ...
Directions for Cell Review in Class Specialized Cells-
... Use the information below to complete the matching activity with specialized animal cells and answer the questions about specialized plant cells. Souce: Cell Types (From CK-12 Life Science Concepts for Middle School) ...
... Use the information below to complete the matching activity with specialized animal cells and answer the questions about specialized plant cells. Souce: Cell Types (From CK-12 Life Science Concepts for Middle School) ...
How Does a Cell Spend Most of it`s Life
... Introduction: Please discuss the stages of mitosis (including interphase). Be sure to describe what happens during each phase. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ...
... Introduction: Please discuss the stages of mitosis (including interphase). Be sure to describe what happens during each phase. _________________________________________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________ ...
Cells
... The CELL THEORY: – All living things are made of cells. – Cells come from pre-existing cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. ...
... The CELL THEORY: – All living things are made of cells. – Cells come from pre-existing cells. – Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in all living organisms. ...
Tissue engineering

Tissue engineering is the use of a combination of cells, engineering and materials methods, and suitable biochemical and physicochemical factors to improve or replace biological functions. While it was once categorized as a sub-field of biomaterials, having grown in scope and importance it can be considered as a field in its own right.While most definitions of tissue engineering cover a broad range of applications, in practice the term is closely associated with applications that repair or replace portions of or whole tissues (i.e., bone, cartilage, blood vessels, bladder, skin, muscle etc.). Often, the tissues involved require certain mechanical and structural properties for proper functioning. The term has also been applied to efforts to perform specific biochemical functions using cells within an artificially-created support system (e.g. an artificial pancreas, or a bio artificial liver). The term regenerative medicine is often used synonymously with tissue engineering, although those involved in regenerative medicine place more emphasis on the use of stem cells or progenitor cells to produce tissues.