The Way Things Actually Are!!!
... Terms To Know • Prokaryote: – Simple cells that have no nucleus ...
... Terms To Know • Prokaryote: – Simple cells that have no nucleus ...
Cells - hdueck
... contains genetic code that controls cell made of DNA & proteins (deoxyribonucleic acid) ...
... contains genetic code that controls cell made of DNA & proteins (deoxyribonucleic acid) ...
Cell Growth and Division
... ____________________ is the process by which new cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Each “daughter” cell gets an ______________ copy of the DNA and half of the cytoplasm and organelles. Cell Reproduction--Prokaryotes In ___________________, cell division takes the form of BINARY FISSION ...
... ____________________ is the process by which new cells are produced from pre-existing cells. Each “daughter” cell gets an ______________ copy of the DNA and half of the cytoplasm and organelles. Cell Reproduction--Prokaryotes In ___________________, cell division takes the form of BINARY FISSION ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell - Foothill Technology High School
... “pulling” forces) Makes up microvilli core, contracts muscles, causes cytoplasmic streaming and pseudopod extensions in cells ...
... “pulling” forces) Makes up microvilli core, contracts muscles, causes cytoplasmic streaming and pseudopod extensions in cells ...
Plant Cell Mitosis
... DNA molecules, but between S phase and mitosis, replicated chromosomes are double DNA molecules. ...
... DNA molecules, but between S phase and mitosis, replicated chromosomes are double DNA molecules. ...
THE CELL – STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION All living things are
... All living things are composed of cells. Although individual cells may be modified to perform specific functions, most animal and plant cells share many basic structures. Important cellular terms: 1. PROKARYOTE: a cell without a true nucleus ex. bacteria 2. EUKARYOTE: a cell with a true nucleus and ...
... All living things are composed of cells. Although individual cells may be modified to perform specific functions, most animal and plant cells share many basic structures. Important cellular terms: 1. PROKARYOTE: a cell without a true nucleus ex. bacteria 2. EUKARYOTE: a cell with a true nucleus and ...
What to know Chap 11
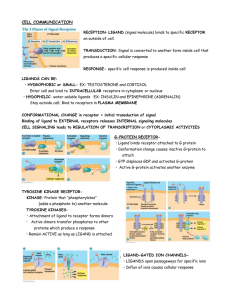
... Enter cell and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in cytoplasm or nucleus • HYDOPHILIC- water-soluble ligands EX: INSULIN and EPINEPHRINE (ADRENALIN) Stay outside cell; Bind to receptors in PLASMA MEMBRANE CONFORMATIONAL CHANGE in receptor = initial transduction of signal Binding of ligand to EXTERNAL ...
... Enter cell and bind to INTRACELLULAR receptors in cytoplasm or nucleus • HYDOPHILIC- water-soluble ligands EX: INSULIN and EPINEPHRINE (ADRENALIN) Stay outside cell; Bind to receptors in PLASMA MEMBRANE CONFORMATIONAL CHANGE in receptor = initial transduction of signal Binding of ligand to EXTERNAL ...
2.3: EUKARYOTIC CELLS
... • Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell • Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. • Identify named structures in an electron micrograph of liver cells. • Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
... • Draw and label a diagram of the ultrastructure of a liver cell as an example of an animal cell • Annotate the diagram with the functions of each named structure. • Identify named structures in an electron micrograph of liver cells. • Compare prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. ...
Biology I Cell Test Review- Answer Key List the 3 parts of the cell
... e. cell wall- support and protection for cell, usually made of tough fibers like cellulose and other carbohydrates f. ribosome-makes proteins, many structures interact to synthesize and transport. g. rough ER-ribosomes attached, transports molecules to other parts of the cell h. Golgi apparatus-help ...
... e. cell wall- support and protection for cell, usually made of tough fibers like cellulose and other carbohydrates f. ribosome-makes proteins, many structures interact to synthesize and transport. g. rough ER-ribosomes attached, transports molecules to other parts of the cell h. Golgi apparatus-help ...
Plant Cell Mitosis
... DNA molecules, but between S phase and mitosis, replicated chromosomes are double DNA molecules. ...
... DNA molecules, but between S phase and mitosis, replicated chromosomes are double DNA molecules. ...
Cell Organelle Notes - Beachwood City Schools
... Prokaryotic cells (cells without a nucleus) are very simple. The majority of cell jobs occur in the center of the cell with no organization. There are a few areas, but not many that have specific jobs. Prokaryotic cells are bacteria. Eukaryotic cells (cells with a nucleus) have compartments called o ...
... Prokaryotic cells (cells without a nucleus) are very simple. The majority of cell jobs occur in the center of the cell with no organization. There are a few areas, but not many that have specific jobs. Prokaryotic cells are bacteria. Eukaryotic cells (cells with a nucleus) have compartments called o ...
Cell Organelle Powerpoint
... ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Network of membranes and sacs Types: 1. Rough ER: ribosomes on surface Function: package proteins for secretion, send transport vesicles to Golgi, make replacement membrane 2. Smooth ER: no ribosomes on surface Function: synthesize lipids, metabolize ...
... ENDOPLASMIC RETICULUM (ER) Network of membranes and sacs Types: 1. Rough ER: ribosomes on surface Function: package proteins for secretion, send transport vesicles to Golgi, make replacement membrane 2. Smooth ER: no ribosomes on surface Function: synthesize lipids, metabolize ...
Cell Division Jeopardy Cheat Sheet
... of the cell during metaphase, and “pull” them apart during anaphase. What is the cell cycle? It is the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells. What events occur in the G1 phase? The cell increases in size. The cell doubles th ...
... of the cell during metaphase, and “pull” them apart during anaphase. What is the cell cycle? It is the life of a cell from the time it is first formed from a dividing parent cell until its own division into two cells. What events occur in the G1 phase? The cell increases in size. The cell doubles th ...
BMT+Treatment+of+Infectious+Diseasespost
... Human cells do not contain this machinery, so they are unaffected. ...
... Human cells do not contain this machinery, so they are unaffected. ...
Cells Alive Activity
... How to get onto the website: 1. Open up your browser and type in this address: http://cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm 2. Read through this first webpage in order to answer questions 1-2 on this worksheet. 3. Click on the green “TAKE ME TO THE ANIMATION” link. 4. Choose the “Animal Cell” link. 5. Use ...
... How to get onto the website: 1. Open up your browser and type in this address: http://cellsalive.com/cells/3dcell.htm 2. Read through this first webpage in order to answer questions 1-2 on this worksheet. 3. Click on the green “TAKE ME TO THE ANIMATION” link. 4. Choose the “Animal Cell” link. 5. Use ...
Media Release
... process are still a mystery, but in a study published August 22 in Developmental Cell, a research team reports one protein responsible for giving a cell's nucleus its durable, deformable nature. These results, the authors say, may explain the invasiveness of certain cancer cells. "The nucleus is the ...
... process are still a mystery, but in a study published August 22 in Developmental Cell, a research team reports one protein responsible for giving a cell's nucleus its durable, deformable nature. These results, the authors say, may explain the invasiveness of certain cancer cells. "The nucleus is the ...
Chapter Eight - Danes. . .Back to Basics!!!
... Throughout this presentation, please answer all questions in complete sentences and complete mini assignments where requested. ...
... Throughout this presentation, please answer all questions in complete sentences and complete mini assignments where requested. ...
Bacterial growth
... the inner of which is thin and firm composed of cellulose. The outer layer of the wall is thicker and gelatinous known as the sheath and mainly constituted of pectic compounds. ...
... the inner of which is thin and firm composed of cellulose. The outer layer of the wall is thicker and gelatinous known as the sheath and mainly constituted of pectic compounds. ...
Your Pre AP biology final exam
... Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: ...
... Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: ...
Your Pre AP biology final exam
... Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: ...
... Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: ...
Document
... Cells are tiny, measuring on average about 0.002 cm (20 um) across. That’s about 1250 cells, “shoulder-to-shoulder” per ...
... Cells are tiny, measuring on average about 0.002 cm (20 um) across. That’s about 1250 cells, “shoulder-to-shoulder” per ...
Your Pre AP biology final exam
... Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: ...
... Where can you find these things? How many chromosomes do you have in your somatic cells? What is a somatic cell How many chromosomes do you have in your gametes? What is a gamete? Why do gametes have a haploid number of chromosomes? Cell cycle: Label the following diagrams with the following terms: ...
Lecture 7: Intro to the cell, cont
... • maintain cell shape by resisting compression • motility via flagella/cilia • anchor nucleus • move organelles and some other organelles • move chromosomes during cell division ...
... • maintain cell shape by resisting compression • motility via flagella/cilia • anchor nucleus • move organelles and some other organelles • move chromosomes during cell division ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.