Chapter 7 section 1,2 and 4- The Cell
... List the features that are common to all cells Know the difference between prokaryote and eukaryote; give examples of each 6. Identify organelles related to both plant and animal cells; be able to describe their functions 7. Understand how the cell functions, be able to identify cell components in a ...
... List the features that are common to all cells Know the difference between prokaryote and eukaryote; give examples of each 6. Identify organelles related to both plant and animal cells; be able to describe their functions 7. Understand how the cell functions, be able to identify cell components in a ...
Slide 1
... are converted into excretable non-toxic soluble compounds Ca2++ sequestering: Examples- muscle cells (ER is called sarcoplamic reticulum), nerve cells. Golgi bodies: Membrane bound flattened sacs stacked over each other. Functionally distinct parts (cis and trans parts) Contains protein modification ...
... are converted into excretable non-toxic soluble compounds Ca2++ sequestering: Examples- muscle cells (ER is called sarcoplamic reticulum), nerve cells. Golgi bodies: Membrane bound flattened sacs stacked over each other. Functionally distinct parts (cis and trans parts) Contains protein modification ...
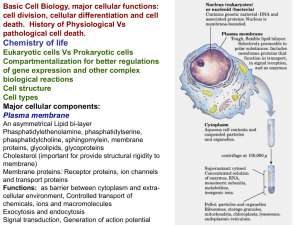
Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize
... Houses most of the cell’s DNA material. contains most of the genes but some are located in the mitochondria and chloroplast ...
... Houses most of the cell’s DNA material. contains most of the genes but some are located in the mitochondria and chloroplast ...
Name - Humble ISD
... II. Cell Identification - Identify which cell (A, B, or C) is a plant cell, which is an animal cell, and which is a bacterial cell. A. ________________________________________ B. ________________________________________ C. ________________________________________ III. Structure Identification - Corr ...
... II. Cell Identification - Identify which cell (A, B, or C) is a plant cell, which is an animal cell, and which is a bacterial cell. A. ________________________________________ B. ________________________________________ C. ________________________________________ III. Structure Identification - Corr ...
STUDY GUIDE FOR CHAPTER THREE
... 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucl ...
... 1. All organisms are made of one or more cells 2. The cell is the basic unit of all living things 3. All cells come from existing cells 8. Explain the difference between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell. -Prokaryotic Cells: an organism that consists of a single cell that does not have a nucl ...
Phagocytosis - mrswalmsley
... using a carrier protein. ATP activates the protein to move glucose into the cell even though the concentration outside the cell is ...
... using a carrier protein. ATP activates the protein to move glucose into the cell even though the concentration outside the cell is ...
cell_variety_lab_
... Background: Cell theory states that cells are the basic unit of life; this means that all living things are made of one or more cells. Cells have some basic similarities in their structures, however cells have evolved to have many different functions; human skin cells have a very different function ...
... Background: Cell theory states that cells are the basic unit of life; this means that all living things are made of one or more cells. Cells have some basic similarities in their structures, however cells have evolved to have many different functions; human skin cells have a very different function ...
The Cell
... 2. Discuss structure and function of cell organelles. 3. Describe the chemical composition of the plasma membrane and relate it to membrane function. 4. Compare the structure and function of tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap ...
... 2. Discuss structure and function of cell organelles. 3. Describe the chemical composition of the plasma membrane and relate it to membrane function. 4. Compare the structure and function of tight junctions, desmosomes, and gap ...
UNIT 2 Part A - Loudoun County Public Schools
... lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus located inside the nucleolus, makes the ribosomes for the cell. c) Nuclear Memb ...
... lysosome, cell membrane, cell wall, nucleolus, cilia/flagella, vacuoles, microtubules, centrioles and nuclear membrane. a) Nucleus controls cell’s activities and contains DNA. Only found in eukaryotic cells. b) Nucleolus located inside the nucleolus, makes the ribosomes for the cell. c) Nuclear Memb ...
Day 8: Organelles and what they do
... in the synthesis of proteins. Some ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm, but most are attached to the ...
... in the synthesis of proteins. Some ribosomes are found in the cytoplasm, but most are attached to the ...
Unit 2: Cell Biology Study Guide
... 25. The cell wall provides ________________ and protection for plant cells like roses, Christmas trees, and carrots. 26. The cell wall is made of ____________________. 27. Photosynthesis occurs in the ____________________ organelle. 28. The pigment involved in ________________ is chlorophyll. 29. Th ...
... 25. The cell wall provides ________________ and protection for plant cells like roses, Christmas trees, and carrots. 26. The cell wall is made of ____________________. 27. Photosynthesis occurs in the ____________________ organelle. 28. The pigment involved in ________________ is chlorophyll. 29. Th ...
ON-Line Assignment - Biology
... Fungi Plantae Monera 16. Which one of the following statements is true? a) DDT does not help prevent disease from passing from agricultural animals to humans ...
... Fungi Plantae Monera 16. Which one of the following statements is true? a) DDT does not help prevent disease from passing from agricultural animals to humans ...
Unit 3 Guided Notes File
... o Small molecules can pass easily (like water, glucose, amino acids, carbon dioxide, and oxygen) o Large molecules cannot pass easily (like _____________________________________) o This is why large nutrients get broken down into the building blocks during digestion! ...
... o Small molecules can pass easily (like water, glucose, amino acids, carbon dioxide, and oxygen) o Large molecules cannot pass easily (like _____________________________________) o This is why large nutrients get broken down into the building blocks during digestion! ...
File
... chromosomes, attached to the spindle fibers, move to the center of the cell chromosomes are now lined up at the equator Equator of Cell ...
... chromosomes, attached to the spindle fibers, move to the center of the cell chromosomes are now lined up at the equator Equator of Cell ...
Cell Review packet
... responsible for allowing the food particles to enter the cell? ___________________________ - Is food energy entering your cells an example of endocytosis or exocytosis? ___________________________________ 6. Your body is made up of proteins. What cell part is always busy making these proteins for gr ...
... responsible for allowing the food particles to enter the cell? ___________________________ - Is food energy entering your cells an example of endocytosis or exocytosis? ___________________________________ 6. Your body is made up of proteins. What cell part is always busy making these proteins for gr ...
Unit Details: Bio 1
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Bio.1.1.2 Compare prokaryotic a ...
... Summarize the structure and function of organelles in eukaryotic cells (including the nucleus, plasma membrane, cell wall, mitochondria, vacuoles, chloroplasts, and ribosomes) and ways that these organelles interact with each other to perform the function of the cell. Bio.1.1.2 Compare prokaryotic a ...
File
... c. All organisms are multicellular. d. All cells have identical parts. ______ 8. The surface area–to-volume ratio of a cell limits a. the number of organelles that the cell has. b. the size of the cell. c. where the cell lives. d. the types of nutrients that a cell needs. ______ 9. Two types of orga ...
... c. All organisms are multicellular. d. All cells have identical parts. ______ 8. The surface area–to-volume ratio of a cell limits a. the number of organelles that the cell has. b. the size of the cell. c. where the cell lives. d. the types of nutrients that a cell needs. ______ 9. Two types of orga ...
Cell Organelles
... the center of the cell. • In most houses, the living room is where the most action happens; families and friends gather, entertainment is produced and much more. • In a cell, some of the more important things happen in the nucleus; transcription, translation and replication. ...
... the center of the cell. • In most houses, the living room is where the most action happens; families and friends gather, entertainment is produced and much more. • In a cell, some of the more important things happen in the nucleus; transcription, translation and replication. ...
Cell Discovery
... • The smallest cell in the human body? male sperm (175,000 sperm cells weigh as much as a single egg cell) ...
... • The smallest cell in the human body? male sperm (175,000 sperm cells weigh as much as a single egg cell) ...
Jello cell rubric
... Edible Cell Rubric 100 points Objective: To synthesize an edible cell that has organelles similar in shape and function to a real plant or animal cell. Materials: You can use materials such as jello, pizza, cake, etc for the main part of the cell (the structure). You can use candies or food to repre ...
... Edible Cell Rubric 100 points Objective: To synthesize an edible cell that has organelles similar in shape and function to a real plant or animal cell. Materials: You can use materials such as jello, pizza, cake, etc for the main part of the cell (the structure). You can use candies or food to repre ...
Can EVERY molecule pass through the cell membrane freely? Why
... Active Transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient. Molecules are moved from lower to higher concentration. It does require energy input from the cell. ...
... Active Transport occurs when a cell uses energy to move molecules against a concentration gradient. Molecules are moved from lower to higher concentration. It does require energy input from the cell. ...
Parts of the Cell
... f. Lysosomes: Small organelles that contain enzymes which digest proteins, carbs, lipids, DNA and RNA. Also digests virus and bacteria that have been ingested by the cell. g. Cytoskeleton: “Skeleton” of the cell; maintains shape and size. i. Microfilaments: made up of actin and contribute to cell mo ...
... f. Lysosomes: Small organelles that contain enzymes which digest proteins, carbs, lipids, DNA and RNA. Also digests virus and bacteria that have been ingested by the cell. g. Cytoskeleton: “Skeleton” of the cell; maintains shape and size. i. Microfilaments: made up of actin and contribute to cell mo ...
Cell cycle
The cell cycle or cell-division cycle is the series of events that take place in a cell leading to its division and duplication (replication) that produces two daughter cells. In prokaryotes which lack a cell nucleus, the cell cycle occurs via a process termed binary fission. In cells with a nucleus, as in eukaryotes, the cell cycle can be divided into three periods: interphase, the mitotic (M) phase, and cytokinesis. During interphase, the cell grows, accumulating nutrients needed for mitosis, preparing it for cell division and duplicating its DNA. During the mitotic phase, the cell splits itself into two distinct daughter cells. During the final stage, cytokinesis, the new cell is completely divided. To ensure the proper division of the cell, there are control mechanisms known as cell cycle checkpoints.The cell-division cycle is a vital process by which a single-celled fertilized egg develops into a mature organism, as well as the process by which hair, skin, blood cells, and some internal organs are renewed. After cell division, each of the daughter cells begin the interphase of a new cycle. Although the various stages of interphase are not usually morphologically distinguishable, each phase of the cell cycle has a distinct set of specialized biochemical processes that prepare the cell for initiation of cell division.