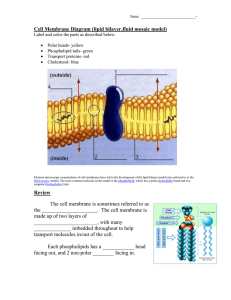
Cell Membrane Diagram (lipid bilayer,fluid mosaic model)
... Polar heads- yellow Phospholipid tails- green Transport proteins- red Cholesterol- blue ...
... Polar heads- yellow Phospholipid tails- green Transport proteins- red Cholesterol- blue ...
Producing New Cells
... Genes are the basic unit of inheritance, and are responsible for the characteristics of an organism. Genes are located on chromosomes. ...
... Genes are the basic unit of inheritance, and are responsible for the characteristics of an organism. Genes are located on chromosomes. ...
year-8-cells-task-2
... 8) How does this disease affect the cells/tissues/organs? That is, does it kill the cells; does it damage part of the cell, etc.? 9) What treatments are available to help treat this disease? How do they work? 10) Are there any treatments that are undergoing trials or being researched? ...
... 8) How does this disease affect the cells/tissues/organs? That is, does it kill the cells; does it damage part of the cell, etc.? 9) What treatments are available to help treat this disease? How do they work? 10) Are there any treatments that are undergoing trials or being researched? ...
Cell Organelle Crossword Puzzle
... One of two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope 10. Thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell 11. In cells, structure that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities 12. Organism wh ...
... One of two tiny structures located in the cytoplasm of animal cells near the nuclear envelope 10. Thin, flexible barrier around a cell; regulates what enters and leaves the cell 11. In cells, structure that contains the cell's genetic material (DNA) and controls the cell's activities 12. Organism wh ...
1. Prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells differ in size and complexity
... • Rates of chemical exchange may be inadequate to maintain a cell with a very large cytoplasm. • The need for a surface sufficiently large to accommodate the volume explains the microscopic size of most cells. • Larger organisms do not generally have larger cells than smaller organisms - simply more ...
... • Rates of chemical exchange may be inadequate to maintain a cell with a very large cytoplasm. • The need for a surface sufficiently large to accommodate the volume explains the microscopic size of most cells. • Larger organisms do not generally have larger cells than smaller organisms - simply more ...
Chapter 7_The Cell
... 1839 – Scientist discovers that animal tissue also consists of individual cells. 1855 – Scientist proposes that all cells are produced from the division of existing cells. The Cell Theory – includes three principles: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic u ...
... 1839 – Scientist discovers that animal tissue also consists of individual cells. 1855 – Scientist proposes that all cells are produced from the division of existing cells. The Cell Theory – includes three principles: 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells. 2. Cells are the basic u ...
Cell Membrane, Photosynthesis and Respiration Name Date Word
... large particle, such as a large protein molecule, water, and carbon dioxide to make food. through a cell membrane into the cytoplasm. b. Green plants use energy from sunlight to unite water and carbon dioxide, thus forming sugar. _________________ _________________ 9. "to exit," "out" ______________ ...
... large particle, such as a large protein molecule, water, and carbon dioxide to make food. through a cell membrane into the cytoplasm. b. Green plants use energy from sunlight to unite water and carbon dioxide, thus forming sugar. _________________ _________________ 9. "to exit," "out" ______________ ...
Cell Transport/Cell Cycle/Meiosis Study Guide
... 9. Cancer is a disorder in which cells have lost their ability to control their _____________ 10. What are tumors? 11. What organisms does cancer affect? Meiosis 1. What is a germ cell? 2. What is meiosis? 3. How many cells are produced during meiosis? 4. In humans, germ cells have _____ chromosomes ...
... 9. Cancer is a disorder in which cells have lost their ability to control their _____________ 10. What are tumors? 11. What organisms does cancer affect? Meiosis 1. What is a germ cell? 2. What is meiosis? 3. How many cells are produced during meiosis? 4. In humans, germ cells have _____ chromosomes ...
Anatomy Chapter 3 section 3 Active Transport Diffusion or facilitated
... Surround LDL particle. Vesicle transports LDL particle to the lysosome , where enzymes digest it and release the cholesterol molecule for cellular use. Receptor mediated endocytosis- allows cells w/ appropriate receptors to remove and process specific types of substances from their surroundings. Pro ...
... Surround LDL particle. Vesicle transports LDL particle to the lysosome , where enzymes digest it and release the cholesterol molecule for cellular use. Receptor mediated endocytosis- allows cells w/ appropriate receptors to remove and process specific types of substances from their surroundings. Pro ...
Directed Reading A
... ______19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ______20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ______21. Chl ...
... ______19. Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ______20. Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ______21. Chl ...
1b. Induced pluripotent stem cells
... reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell–like state by being forced to express genes and factors important for maintaining the defining properties of embryonic stem cells. Although these cells meet the defining criteria for pluripotent stem cells, it is not known if iPSCs and embryonic stem cells diff ...
... reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell–like state by being forced to express genes and factors important for maintaining the defining properties of embryonic stem cells. Although these cells meet the defining criteria for pluripotent stem cells, it is not known if iPSCs and embryonic stem cells diff ...
Slide 1
... Mitochondria – The site of cellular respiration or energy production. Membrane bound. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – forms a link between the nuclear membrane and the cell. Ribosomes are attached to the surface. Proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes and enclosed in vessicles and sent to the Golgi ...
... Mitochondria – The site of cellular respiration or energy production. Membrane bound. Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum – forms a link between the nuclear membrane and the cell. Ribosomes are attached to the surface. Proteins are synthesized in the ribosomes and enclosed in vessicles and sent to the Golgi ...
Studies on BI-010
... this study by collaborating with other researchers at other sites to increase the size of our cohort to hundreds of patients. We have already spoken to several potential sources. Identifying where collections are located and bringing them together will provide a great resource for future studies. If ...
... this study by collaborating with other researchers at other sites to increase the size of our cohort to hundreds of patients. We have already spoken to several potential sources. Identifying where collections are located and bringing them together will provide a great resource for future studies. If ...
I. Introduction to the Cell
... I. Introduction to the Cell “With the cell, biology discovered its atom.” –Jacob A. The cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all processes of life. 1. make energy 2. produce waste 3. reproduce 4. respond to stimulus 5. evolve B. Unicellular: one celled organisms…Protists and Bacteria C. Multi ...
... I. Introduction to the Cell “With the cell, biology discovered its atom.” –Jacob A. The cell is the smallest unit that can carry on all processes of life. 1. make energy 2. produce waste 3. reproduce 4. respond to stimulus 5. evolve B. Unicellular: one celled organisms…Protists and Bacteria C. Multi ...
Ch. 6 - Ltcconline.net
... 3. sticky polysaccharides glue cells together B. Extra cellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells 1. glycoproteins secreted by cells VIII. Cell Surfaces and Junctions A. plasmodesmata B. Cell junctions connect one cell to another in animal tissue 1. tight junctions 2. desmosome 3. gap junctions Homework ...
... 3. sticky polysaccharides glue cells together B. Extra cellular matrix (ECM) of animal cells 1. glycoproteins secreted by cells VIII. Cell Surfaces and Junctions A. plasmodesmata B. Cell junctions connect one cell to another in animal tissue 1. tight junctions 2. desmosome 3. gap junctions Homework ...
product data sheet
... required for activation of androgen receptor (AR)-regulated genes in prostate cancer cells . In addition to prostate cancer, leukemia is ...
... required for activation of androgen receptor (AR)-regulated genes in prostate cancer cells . In addition to prostate cancer, leukemia is ...
Unit 1 and 7 Study Cards You enter the classroom and you see a
... When observing cells, which Microscope of the following pieces of equipment is most appropriate? 1. Hand lens 2. Microscope 3. Telescope Which science tool would be Hand lens appropriate for the close observation of the inside of a bird bone? 1. Hand lens 2. Microscope 3. Telescope Would constructi ...
... When observing cells, which Microscope of the following pieces of equipment is most appropriate? 1. Hand lens 2. Microscope 3. Telescope Which science tool would be Hand lens appropriate for the close observation of the inside of a bird bone? 1. Hand lens 2. Microscope 3. Telescope Would constructi ...
PBOXs: A new treatment for neuroblastoma?
... What’s the advantage? •Unlike other chemotherapeutics, the cells don’t become resistant to the PBOXs •They are not a substrate for these drug pumps •So the PBOXs stay in the cell and induce apoptosis •The can work with other chemotherapeutics to kill even more cells •Can use lower doses….less toxic ...
... What’s the advantage? •Unlike other chemotherapeutics, the cells don’t become resistant to the PBOXs •They are not a substrate for these drug pumps •So the PBOXs stay in the cell and induce apoptosis •The can work with other chemotherapeutics to kill even more cells •Can use lower doses….less toxic ...
Mary Pilson
... arrangement of phospholipids, the purpose of cholesterol, the purpose of two types of cell surface carbohydrates, and the location and function of transport proteins. ...
... arrangement of phospholipids, the purpose of cholesterol, the purpose of two types of cell surface carbohydrates, and the location and function of transport proteins. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.























