Cell Structure
... A) have a smaller demand for cell proteins than the muscle cells of nonathletes B) reproduce less frequently than the muscle cells of nonathletes C) have nuclei containing more DNA than nuclei in the muscle cells of nonathletes D) have a greater demand for energy than the muscle cells of nonathletes ...
... A) have a smaller demand for cell proteins than the muscle cells of nonathletes B) reproduce less frequently than the muscle cells of nonathletes C) have nuclei containing more DNA than nuclei in the muscle cells of nonathletes D) have a greater demand for energy than the muscle cells of nonathletes ...
Cell Organelles Review Package
... Evolution; DNA; Nuclei; Prokaryotes; Mitochondria; Organelles; Symbiotic Theory The first organisms to evolve were (25) ____________________. These simple cells had no (26) ____________________. Today’s bacteria also lack (27) __________________, such as the ER, Golgi Bodies and most other cell part ...
... Evolution; DNA; Nuclei; Prokaryotes; Mitochondria; Organelles; Symbiotic Theory The first organisms to evolve were (25) ____________________. These simple cells had no (26) ____________________. Today’s bacteria also lack (27) __________________, such as the ER, Golgi Bodies and most other cell part ...
Sydney ISCT Australia New Zealand Regional Meeting a great
... Conference themes included ex vivo production of haematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stromal cells, the manipulation of alloreactivity in leukaemia, targeted cellular immunotherapy, induced pluripotency and solid-organ tissue engineering. An open forum with clinicians and Australian regulators ...
... Conference themes included ex vivo production of haematopoietic stem cells and mesenchymal stromal cells, the manipulation of alloreactivity in leukaemia, targeted cellular immunotherapy, induced pluripotency and solid-organ tissue engineering. An open forum with clinicians and Australian regulators ...
PPoint Lec 1
... Some themes repeated throughout the course… CompartmentalizationThere is an inside and an outside to thingsand cells make energy, use energy, and defend themselves by taking advantage of this Statistical ProbabilityThings happen in the cell when particles bump into each othercells cheat by making i ...
... Some themes repeated throughout the course… CompartmentalizationThere is an inside and an outside to thingsand cells make energy, use energy, and defend themselves by taking advantage of this Statistical ProbabilityThings happen in the cell when particles bump into each othercells cheat by making i ...
biology i: cell structure lab
... the thin transparent covering from the inside of the curved section. Mount this thin layer of tissue, being careful to keep it just one layer on the slide, add a drop or two of iodine and a cover slip. Examine it under low power first and then move to medium and high power. Draw 2-3 cells as t ...
... the thin transparent covering from the inside of the curved section. Mount this thin layer of tissue, being careful to keep it just one layer on the slide, add a drop or two of iodine and a cover slip. Examine it under low power first and then move to medium and high power. Draw 2-3 cells as t ...
cells - Piscataway High School
... Phosphate “heads” are attracted to water (hydrophilic). They are oriented to the OUTSIDE of the cell membrane bilayer. ...
... Phosphate “heads” are attracted to water (hydrophilic). They are oriented to the OUTSIDE of the cell membrane bilayer. ...
Development
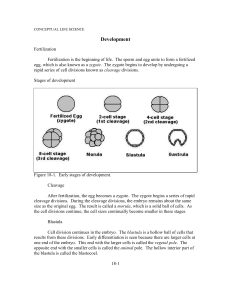
... Figure 18-1. Early stages of development. Cleavage After fertilization, the egg becomes a zygote. The zygote begins a series of rapid cleavage divisions. During the cleavage divisions, the embryo remains about the same size as the original egg. The result is called a morula, which is a solid ball of ...
... Figure 18-1. Early stages of development. Cleavage After fertilization, the egg becomes a zygote. The zygote begins a series of rapid cleavage divisions. During the cleavage divisions, the embryo remains about the same size as the original egg. The result is called a morula, which is a solid ball of ...
THINK ABOUT IT
... Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they contain a nucleus. The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. The nucleus controls the cell’s activities. ...
... Cells fall into two broad categories, depending on whether they contain a nucleus. The nucleus is a large membrane-enclosed structure that contains the cell’s genetic material in the form of DNA. The nucleus controls the cell’s activities. ...
Grade 6 Spelling
... 2. Autotroph- an organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food 3. Heterotroph- organism that cannot make its own food and gets food by consuming other living things 4. Chlorophyll- green photosynthetic pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant ...
... 2. Autotroph- an organism that is able to capture energy from sunlight or chemicals and use it to produce its own food 3. Heterotroph- organism that cannot make its own food and gets food by consuming other living things 4. Chlorophyll- green photosynthetic pigment found in the chloroplasts of plant ...
Cell Unit Review Robert Hooke They turn genes (directions in the
... 5. Which organelle is found on the ER and is a tool for putting proteins together? ...
... 5. Which organelle is found on the ER and is a tool for putting proteins together? ...
Cell Organelle Web Quest
... them in ___________________________, then ____________________ them outside or within the cell. 4. Chloroplasts help plant cells use ______________ through a process called ______________. 5. What do mitochondria produce? What do they use to produce it? 6. What does every cell hold in its nucleus? 7 ...
... them in ___________________________, then ____________________ them outside or within the cell. 4. Chloroplasts help plant cells use ______________ through a process called ______________. 5. What do mitochondria produce? What do they use to produce it? 6. What does every cell hold in its nucleus? 7 ...
Organelle Function Matching
... Directions: Match the organelles with their functions. 1. A cell structure that controls which substances can enter and leave the cell. 2. A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. An organelle that helps to protect and support the cell. (not in ...
... Directions: Match the organelles with their functions. 1. A cell structure that controls which substances can enter and leave the cell. 2. A rigid layer of nonliving material that surrounds the cells of plants and some other organisms. An organelle that helps to protect and support the cell. (not in ...
Cells - Faculty Sites
... • read coded genetic messages • assemble amino acids into proteins – protein synthesis ...
... • read coded genetic messages • assemble amino acids into proteins – protein synthesis ...
Cells Answers - Science Skool!
... 5. How are plant cells different from bacterial cells? Plant cells have a nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, are larger, have a cell wall made from cellulose, have fewer ribosomes 6. Why don't bacterial cells contain mitochondria? The cells are too small 7. How do mitochondria help a sperm cell carry o ...
... 5. How are plant cells different from bacterial cells? Plant cells have a nucleus, vacuole, chloroplasts, are larger, have a cell wall made from cellulose, have fewer ribosomes 6. Why don't bacterial cells contain mitochondria? The cells are too small 7. How do mitochondria help a sperm cell carry o ...
Cell Test Study Guide Answers
... 2) What are the three parts to the cell theory? 1) all living things have cells 2) cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things 3) all cells come from preexisting cells 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? They both make energy for the cells (mitochondr ...
... 2) What are the three parts to the cell theory? 1) all living things have cells 2) cells are the basic unit of structure and function of all living things 3) all cells come from preexisting cells 3) What do chloroplasts and mitochondria have in common? They both make energy for the cells (mitochondr ...
Science - Cells, Muscular and Skeletal Systems
... I can state that cells are the fundamental unit "building block" of organisms I can name some equipment that may be used to observe cells I can list the main parts of cells (cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, vacuole, mitochondria and chloroplasts) I can list some tissues and organs ...
... I can state that cells are the fundamental unit "building block" of organisms I can name some equipment that may be used to observe cells I can list the main parts of cells (cell wall, cell membrane, nucleus, vacuole, mitochondria and chloroplasts) I can list some tissues and organs ...
What is a cell - St Michael School
... Cytoplasm: produces energy, makes things and stores food. Chemical reactions occur in it and these reactions make up metabolism. Ribosomes: play an important part in the production of Proteins. Chloroplast: they contain the green pigment chlorophyll which is used for photosynthesis. Vacuole: filled ...
... Cytoplasm: produces energy, makes things and stores food. Chemical reactions occur in it and these reactions make up metabolism. Ribosomes: play an important part in the production of Proteins. Chloroplast: they contain the green pigment chlorophyll which is used for photosynthesis. Vacuole: filled ...
AP Biology Basic Cell Structure Outline
... B. Cells can only be so large. ( Larger means more traffic going in both directions across the cell membrane) C. A cell must be large enough to contain DNA and Ribosomes for making proteins, and some cytoplasm to act as working “space”. They can only be so big because we have to be able to move enou ...
... B. Cells can only be so large. ( Larger means more traffic going in both directions across the cell membrane) C. A cell must be large enough to contain DNA and Ribosomes for making proteins, and some cytoplasm to act as working “space”. They can only be so big because we have to be able to move enou ...
Microtubules and the shape of plant cells
... John Innes Centre, NORWICH NR4 7UH, UK Microtubules provide the tracks that membrane-bound cellulose synthases follow as they are propelled along the membrane by the extrusion of microfibrils. Ultimately, it is the direction in which these microfibrils are aligned that determines the direction in wh ...
... John Innes Centre, NORWICH NR4 7UH, UK Microtubules provide the tracks that membrane-bound cellulose synthases follow as they are propelled along the membrane by the extrusion of microfibrils. Ultimately, it is the direction in which these microfibrils are aligned that determines the direction in wh ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.