Review Guide Ch. 7 CP
... Cell theory – early contributors o Hooke, von Leeuwenhoek, Brown o Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow Cell Theory – 3 parts Cell size – why are all cells small? o Exchange with environment and supply all parts of cell o Large surface area-to-volume ratio Two kinds of cells – prokaryote and eukaryot ...
... Cell theory – early contributors o Hooke, von Leeuwenhoek, Brown o Schleiden, Schwann, Virchow Cell Theory – 3 parts Cell size – why are all cells small? o Exchange with environment and supply all parts of cell o Large surface area-to-volume ratio Two kinds of cells – prokaryote and eukaryot ...
Biology and you - properties of life and the scientific method
... cytoplasm and plasma membrane. They are both much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Pro means no. Bacteria is the only Prokaryote 2. Eukaryote-Has a nucleus surrounded by a membrane and has other internal organelles surrounded by membranes. Protist, fungi, animal, and plant Are just like you, Starts w ...
... cytoplasm and plasma membrane. They are both much smaller than eukaryotic cells. Pro means no. Bacteria is the only Prokaryote 2. Eukaryote-Has a nucleus surrounded by a membrane and has other internal organelles surrounded by membranes. Protist, fungi, animal, and plant Are just like you, Starts w ...
ERYTHROPOIESIS Erythropoiesis: is the formation of red blood
... descendants of the proerythroblast stem cell by the processes of proliferation and differentiation each hemocytoblast stem cell can give rise to as many as 211 mature cells. Proerythroblast is: also called a pronormoblast the earliest stem cell (derived from the hemocytoblast = pluripotent h ...
... descendants of the proerythroblast stem cell by the processes of proliferation and differentiation each hemocytoblast stem cell can give rise to as many as 211 mature cells. Proerythroblast is: also called a pronormoblast the earliest stem cell (derived from the hemocytoblast = pluripotent h ...
Tight Junctions, Desmosomes, and Gap Junctions in Animal Cells
... • fasten cells together into strong Sheets • Intermediate filaments made of sturdy keratin proteins anchor desmosomes in the cytoplasm. • Desmosomes attach muscle cells to each other in a muscle. • Some “muscle tears” involve the rupture of desmosomes. ...
... • fasten cells together into strong Sheets • Intermediate filaments made of sturdy keratin proteins anchor desmosomes in the cytoplasm. • Desmosomes attach muscle cells to each other in a muscle. • Some “muscle tears” involve the rupture of desmosomes. ...
3 - Coastalzone
... Week Three Chapter 5 Cell structure and function Cell Theory (the study of cells is cytology) All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary informatio ...
... Week Three Chapter 5 Cell structure and function Cell Theory (the study of cells is cytology) All organisms are composed of one or more cells. The cell is the basic living unit of organization for all living things All cells arise from preexisting cells Cells contain all of the hereditary informatio ...
Cell Biology Study Guide
... 29. Which type of adaptation is used for movement of each of the following organisms? a. Paramecium b. Euglena c. Amoeba 30. What is the difference between positive and negative chemotaxis? 31. What is the difference between positive and negative phototaxis? 32. Be able to recognize a paramecium, a ...
... 29. Which type of adaptation is used for movement of each of the following organisms? a. Paramecium b. Euglena c. Amoeba 30. What is the difference between positive and negative chemotaxis? 31. What is the difference between positive and negative phototaxis? 32. Be able to recognize a paramecium, a ...
How are white blood cells classified?
... of lymphocytes: T-cell, NK-cell, and B-cell. In healthy adults, 10-15% of the lymphocytes are large granular lymphocytes (LGLs). To learn more about LGL cells, see “A first step in diagnosing LGL leukemia: The blood smear.” A person is diagnosed with LGL leukemia if there is a clonal (copied) popula ...
... of lymphocytes: T-cell, NK-cell, and B-cell. In healthy adults, 10-15% of the lymphocytes are large granular lymphocytes (LGLs). To learn more about LGL cells, see “A first step in diagnosing LGL leukemia: The blood smear.” A person is diagnosed with LGL leukemia if there is a clonal (copied) popula ...
Chapter 2, Lesson 1 Vocabulary
... new cells come from existing cells and cells are the smallest unit of life Cell theory ...
... new cells come from existing cells and cells are the smallest unit of life Cell theory ...
Lymphatic System
... do not elicit a response from the body. An immediate allergic reaction is when the body creates an inflammatory response to the foreign antigen on the allergen (pollen). Tissue rejection occurs because the body does not recognize the antigens on the transplant tissue and the Tcells target the tissue ...
... do not elicit a response from the body. An immediate allergic reaction is when the body creates an inflammatory response to the foreign antigen on the allergen (pollen). Tissue rejection occurs because the body does not recognize the antigens on the transplant tissue and the Tcells target the tissue ...
Ch. 7 Cell Structure and Function
... Transmits electrons through specimen Used to examine the internal structures of a cell ...
... Transmits electrons through specimen Used to examine the internal structures of a cell ...
Chapter 1
... Antibiotics damage bacteria in different ways: - damage cell membrane - damage or affect chromosomes - stop synthesis of cell wall - stop chemical reactions in cytoplasm However, many bacteria develop resistance to the antibiotics Some can develop multiple resistance – e.g. MRSA ...
... Antibiotics damage bacteria in different ways: - damage cell membrane - damage or affect chromosomes - stop synthesis of cell wall - stop chemical reactions in cytoplasm However, many bacteria develop resistance to the antibiotics Some can develop multiple resistance – e.g. MRSA ...
on-level-biology-midterm-review-key
... 34. What are cancer cells and why do they reproduce so rapidly? (254) Cells that have uncontrolled growth, the growth regulating portion of the cell doesn’t work right 35. Why are stem cells important medically? (256-257) They have not specialized yet and can be trained to become any type of cell 36 ...
... 34. What are cancer cells and why do they reproduce so rapidly? (254) Cells that have uncontrolled growth, the growth regulating portion of the cell doesn’t work right 35. Why are stem cells important medically? (256-257) They have not specialized yet and can be trained to become any type of cell 36 ...
THE CELL
... Do all cells look the same? If not, why do they look different? How do materials travel through your cell? Why are we made up of so many cells instead of just a few? Why are cells surrounded by membranes? Why are some organelles and proteins within cells surrounded by membranes? Why is the ...
... Do all cells look the same? If not, why do they look different? How do materials travel through your cell? Why are we made up of so many cells instead of just a few? Why are cells surrounded by membranes? Why are some organelles and proteins within cells surrounded by membranes? Why is the ...
Active Transport Notes
... Occurs when the cell membranes forms a vesicle (like an envelope) around an item that needs to ENTER the cell. ...
... Occurs when the cell membranes forms a vesicle (like an envelope) around an item that needs to ENTER the cell. ...
Cells overviewbio_revised - Appoquinimink High School
... • They pass through one end and continue to pass over the sac until it forms glycoprotein which is a protein that has become chemically processed • When the altered glycoprotein reaches outermost layer, then bubble-like structures (vesicles) form and move through the cell membrane to the outside of ...
... • They pass through one end and continue to pass over the sac until it forms glycoprotein which is a protein that has become chemically processed • When the altered glycoprotein reaches outermost layer, then bubble-like structures (vesicles) form and move through the cell membrane to the outside of ...
Chapter 5 Questions_1
... Multiple Choice 1. Specialized cells are specialized for particular tasks. These types of cells are specialized to provide structure and support. They are called ... a) b) c) d) ...
... Multiple Choice 1. Specialized cells are specialized for particular tasks. These types of cells are specialized to provide structure and support. They are called ... a) b) c) d) ...
Genetic lab 1
... a type of cell division that results in two daughters cells, each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth. ...
... a type of cell division that results in two daughters cells, each having the same number and kind of chromosomes as the parent nucleus, typical of ordinary tissue growth. ...
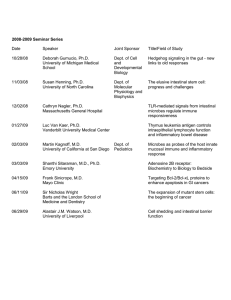
Date Speaker Joint Sponsor
... Thymus leukemia antigen controls intraepithelial lymphocyte function and inflammatory bowel disease ...
... Thymus leukemia antigen controls intraepithelial lymphocyte function and inflammatory bowel disease ...
PowerPoint #1
... I really liked the idea of my project. Though progress was often slow, I was motivated by the fact that when successful, the results would put us one step closer to producing stem cell-derived pancreatic ß cells. A*STAR is a unique place to engage in scientific research, as it is truly comprised of ...
... I really liked the idea of my project. Though progress was often slow, I was motivated by the fact that when successful, the results would put us one step closer to producing stem cell-derived pancreatic ß cells. A*STAR is a unique place to engage in scientific research, as it is truly comprised of ...
target cell. - mleonessciencepage
... body cells to increase in size – major targets bones Antidiuretic hormone – influence water balance in the body – targets kidneys Pancreatic hormones – regulate blood sugar ...
... body cells to increase in size – major targets bones Antidiuretic hormone – influence water balance in the body – targets kidneys Pancreatic hormones – regulate blood sugar ...
2—6 Why do cells have different shapes? Cell Size and Shape
... Cell Size and Shape Some organisms are made of only one cell. They are called unicellular. In unicellular organisms, all of the life processes are carried out by the same cell. Most organisms you are familiar with have more than one cell. These organisms are called multicellular. The cells of these ...
... Cell Size and Shape Some organisms are made of only one cell. They are called unicellular. In unicellular organisms, all of the life processes are carried out by the same cell. Most organisms you are familiar with have more than one cell. These organisms are called multicellular. The cells of these ...
FACS flourescens activeted cell sortering
... becomes more similar to that of the extracellular medium - this manifests itself as a reduction in forward scatter signal. At the same time, intracellular changes and invagination of the cytoplasmic membrane lead to an increase in side (or orthogonal or 90°) scatter. If we add a dead cell discrimina ...
... becomes more similar to that of the extracellular medium - this manifests itself as a reduction in forward scatter signal. At the same time, intracellular changes and invagination of the cytoplasmic membrane lead to an increase in side (or orthogonal or 90°) scatter. If we add a dead cell discrimina ...
Cells!
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
... Objective: Upon completion of this activity, you should be able to describe the cell and identify its parts (organelles). You should be able to distinguish between plant and animal cells. PART I Go to: www.wisc-online.com/objects/index_tj.asp?objid=AP11604 Click “Next” to begin the activity. Answer ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.