Student Response Sheets
... 31. Why do some cells in the human pancreas have up to 100 times the amount of endoplasmic reticulum as other parts of the body? ...
... 31. Why do some cells in the human pancreas have up to 100 times the amount of endoplasmic reticulum as other parts of the body? ...
Cell
... ribosome. Ribosome is the site to carry out protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is based on the information of mRNA. The information of mRNA is copied from the DNA of the nucleus. ...
... ribosome. Ribosome is the site to carry out protein synthesis. Protein synthesis is based on the information of mRNA. The information of mRNA is copied from the DNA of the nucleus. ...
What is the name of substances that can not be broken down into
... What type of transport involve materials moving from areas in which they are highly concentrated to areas in which there is a lower concentration ...
... What type of transport involve materials moving from areas in which they are highly concentrated to areas in which there is a lower concentration ...
BioCell **Flight Certified** Research Applications
... Mammalian cells / tissues Other cells / tissues Small organisms Yeast, bacteria, algae ...
... Mammalian cells / tissues Other cells / tissues Small organisms Yeast, bacteria, algae ...
1st Nine Weeks Bundle
... Cells have semi-permeable membranes that regulate the movement of dissolved molecules through it in order to maintain homeostasis. Transport across membranes may or may not require energy. ...
... Cells have semi-permeable membranes that regulate the movement of dissolved molecules through it in order to maintain homeostasis. Transport across membranes may or may not require energy. ...
Cells and Cell Organelles
... Measurements (SI) • Based on powers of 10 • Micrometers are onemillionth of a meter ( the size of a bacterial cell) ...
... Measurements (SI) • Based on powers of 10 • Micrometers are onemillionth of a meter ( the size of a bacterial cell) ...
Question Report - Blue Valley Schools
... These structures play no role in determining cell shape. Sugars and nucleic acids are common components of these structures. Information can be transferred from these structures to the cytoplasm. These structures provide for cytoplasmic connections between adjacent cells. both C and D are CORRECT ...
... These structures play no role in determining cell shape. Sugars and nucleic acids are common components of these structures. Information can be transferred from these structures to the cytoplasm. These structures provide for cytoplasmic connections between adjacent cells. both C and D are CORRECT ...
Slide 1
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
... How do Molecules form Living, Moving, Reproducing Cells? 1683, Leeuwenhoek: “An unbelievably great company of living animalcules, a-swimming more nimbly than any I had ever seen up to this time. The biggest sort bent their body into curves in going forwards." ...
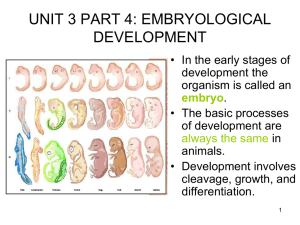
Unit 3 part 4 PPT
... • This means that all the embryo’s cells are alike - they all have all the same genes. • As development progresses groups of cells will become different and make tissues which form the different organs. • These tissues and organs are different because one type of cell uses different genes than anoth ...
... • This means that all the embryo’s cells are alike - they all have all the same genes. • As development progresses groups of cells will become different and make tissues which form the different organs. • These tissues and organs are different because one type of cell uses different genes than anoth ...
A View of the Cell
... Eukaryotic cells – these cells do have a nucleus, they do have organelles attached to the membrane. These cells can be much larger than prokaryotic cells. An organelle is a specialized structure in a cell that carries out a specific function. A “little organ.” ...
... Eukaryotic cells – these cells do have a nucleus, they do have organelles attached to the membrane. These cells can be much larger than prokaryotic cells. An organelle is a specialized structure in a cell that carries out a specific function. A “little organ.” ...
Extracellular components
... Fibronectins • Group of adhesive glycoproteins • 2 long linked proteins • Several binding domains ...
... Fibronectins • Group of adhesive glycoproteins • 2 long linked proteins • Several binding domains ...
SC430 Molecular & Cell Biology
... Under conditions believed to be similar to those found on the early Earth ...
... Under conditions believed to be similar to those found on the early Earth ...
5.3 Regulation of the Cell Cycle
... • External factors include physical and chemical signals. • Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell division. – Most mammal cells form a single layer in a culture dish and stop dividing once they touch other cells. ...
... • External factors include physical and chemical signals. • Growth factors are proteins that stimulate cell division. – Most mammal cells form a single layer in a culture dish and stop dividing once they touch other cells. ...
01 stem cell
... Found in specific mature body tissues as well as the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. They also can be isolated of developing embryos’ different tissues ...
... Found in specific mature body tissues as well as the umbilical cord and placenta after birth. They also can be isolated of developing embryos’ different tissues ...
Exercise 8.2-1 Quick Questions to 8.2 Making Bulk Si Solar Cells
... Quick Questions to 8.2 Making Bulk Si Solar Cells Here are some quick questions Discuss the basic requirements for mass production of solar cells including technical constraints resulting from economical boundary conditions Describe the essential production steps of a mc-Si solar cell. Start with su ...
... Quick Questions to 8.2 Making Bulk Si Solar Cells Here are some quick questions Discuss the basic requirements for mass production of solar cells including technical constraints resulting from economical boundary conditions Describe the essential production steps of a mc-Si solar cell. Start with su ...
Ashley Ajayi
... oxygen. It has at least two membranes that separate the innermost space from the cytosol. Ti has the ability to grow and reproduce with cell. Peroxisome is an organelle with various specialized metabolic functions. It produces hydrogen peroxide. Microvilli are projections that increase the cell’s su ...
... oxygen. It has at least two membranes that separate the innermost space from the cytosol. Ti has the ability to grow and reproduce with cell. Peroxisome is an organelle with various specialized metabolic functions. It produces hydrogen peroxide. Microvilli are projections that increase the cell’s su ...
Cellular basis of yogic exercises
... Recently scientists have discovered that cells in human body change depending on how they are stretched [1]. They have shown that if you pull a stem cell in one way it starts developing into a brain cell; stretch it in other ways and a muscle or a bone cell results ! And the most far reaching conseq ...
... Recently scientists have discovered that cells in human body change depending on how they are stretched [1]. They have shown that if you pull a stem cell in one way it starts developing into a brain cell; stretch it in other ways and a muscle or a bone cell results ! And the most far reaching conseq ...
Cells Ch1 Sec 2 Column Notes Discovery of cells filled
... have too few openings to allow enough materials in and out of the cell membrane. ! ...
... have too few openings to allow enough materials in and out of the cell membrane. ! ...
Cells Pretest - Warren County Schools
... Learning Target 2: I can describe the functions of the cell's organelles. 6. What structure allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosomes c. Cell membrane d. Golgi body 7. What is made of folded membranes that move materials around inside the cell a. Nucleus b ...
... Learning Target 2: I can describe the functions of the cell's organelles. 6. What structure allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosomes c. Cell membrane d. Golgi body 7. What is made of folded membranes that move materials around inside the cell a. Nucleus b ...
Eukaryotic Cell Organelles
... Membrane system of folded sacs and interconnected channels Provides a big workspace within the cell Looks like an accordion or fan folded into the cell Rough ER has ribosomes attached and serves as the site for protein and lipid synthesis The site where ribosomes attach to the ER is where protein sy ...
... Membrane system of folded sacs and interconnected channels Provides a big workspace within the cell Looks like an accordion or fan folded into the cell Rough ER has ribosomes attached and serves as the site for protein and lipid synthesis The site where ribosomes attach to the ER is where protein sy ...
MCF- 7/GFP Cell Line
... estrogen receptors. MCF-7 cells are also sensitive to cytokeratin. When grown in vitro, the cell line is capable of forming domes and the epithelial like cells grow in monolayers. Growth can also be inhibited using tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha). Our MCF-7/GFP cell line stably expresses GFP ...
... estrogen receptors. MCF-7 cells are also sensitive to cytokeratin. When grown in vitro, the cell line is capable of forming domes and the epithelial like cells grow in monolayers. Growth can also be inhibited using tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNF alpha). Our MCF-7/GFP cell line stably expresses GFP ...
Fact sheet B2.1 Cells and tissues
... To treat conditions such as paralysis As they can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells, eg nerve cells At an early stage They retain the ability to differentiate throughout life Repair of tissues Replacement of lost/ dead cells Bacteria and yeast A bacterial cell ...
... To treat conditions such as paralysis As they can be made to differentiate into many different types of cells, eg nerve cells At an early stage They retain the ability to differentiate throughout life Repair of tissues Replacement of lost/ dead cells Bacteria and yeast A bacterial cell ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.