homeostasis and cell transport
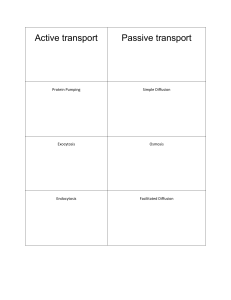
... *passive transport: substances that pass across the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell 1. Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration a. Concentration gradient: the difference in the concentration of molecules across ...
... *passive transport: substances that pass across the cell membrane without any input of energy by the cell 1. Diffusion: the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration a. Concentration gradient: the difference in the concentration of molecules across ...
Protective Antigens
... Protective Antigen 1. This term has several meanings. 2. One example is the anthrax toxin. It is composed of three parts that each play a role in destroying the cell (PA or protective is the first). The antigen is called protective because it is protected from immune destruction once inside the cell ...
... Protective Antigen 1. This term has several meanings. 2. One example is the anthrax toxin. It is composed of three parts that each play a role in destroying the cell (PA or protective is the first). The antigen is called protective because it is protected from immune destruction once inside the cell ...
Cell Structure and Function (Chapter 7)
... food into particles that can be used by the cell Also break down “dead” organelles ...
... food into particles that can be used by the cell Also break down “dead” organelles ...
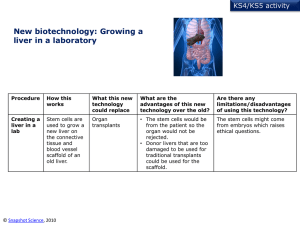
new biotechnology PowerPoint
... Are there any limitations/disadvantages of using this technology? ...
... Are there any limitations/disadvantages of using this technology? ...
Prokaryotic Cells – Single-celled organisms that do not
... cytoplasm. It is a clear gel-like fluid (liquid) which takes up most space inside the cell, where many cell reactions and where organelles are located ...
... cytoplasm. It is a clear gel-like fluid (liquid) which takes up most space inside the cell, where many cell reactions and where organelles are located ...
Living Cells Part A Cell Structure and Function
... is limited. Alcohol becomes toxic to yeast cells and kills them, once the concentration has risen to approximately 14% alcohol. Alcoholic fermentation is now being used to produce an alcohol based alternative to petrol called gasohol. Bacteria are responsible for causing many different diseases. Mod ...
... is limited. Alcohol becomes toxic to yeast cells and kills them, once the concentration has risen to approximately 14% alcohol. Alcoholic fermentation is now being used to produce an alcohol based alternative to petrol called gasohol. Bacteria are responsible for causing many different diseases. Mod ...
The Cell Theory and Membrane Transport
... causing it to SWELL •Cells could rupture if the cell takes in too much water •This increases pressure inside of cell (TURGOR PRESSURE) ...
... causing it to SWELL •Cells could rupture if the cell takes in too much water •This increases pressure inside of cell (TURGOR PRESSURE) ...
organization - Catawba County Schools
... 1. Name 4 characteristics of living things. 2. How did the microscope change human understanding of life? 3. Explain the 3 concepts that make up the cell theory. 4. Relate the characteristics of a scientific theory to the cell theory. 5. Draw a Venn diagram to compare and contrast multicellular and ...
... 1. Name 4 characteristics of living things. 2. How did the microscope change human understanding of life? 3. Explain the 3 concepts that make up the cell theory. 4. Relate the characteristics of a scientific theory to the cell theory. 5. Draw a Venn diagram to compare and contrast multicellular and ...
2.3: Eukaryotic Evolution and Diversity pg. 67 For about 1.5 billion
... Endosymbiosis Endosymbiosis: theory that explains how eukaryotic cells evolved from the symbiotic relationship between two or more prokaryotic cells. One cell engulfs a different type of cell. The engulf cell survives and becomes an internal part of the engulfing cell. Prokaryotes do not have membra ...
... Endosymbiosis Endosymbiosis: theory that explains how eukaryotic cells evolved from the symbiotic relationship between two or more prokaryotic cells. One cell engulfs a different type of cell. The engulf cell survives and becomes an internal part of the engulfing cell. Prokaryotes do not have membra ...
Mitosis Root Lab
... 5. How many times does a compound light microscope with an eyepiece lens of 10X and an objective lens of 4X magnify objects? a. 400X b. 40X c. 4X d. 10X 6. How is a plant cell different from an animal cell? a. Plant cells have mitochondria and vacuoles b. Animal cells have cytoplasm and ribosomes c. ...
... 5. How many times does a compound light microscope with an eyepiece lens of 10X and an objective lens of 4X magnify objects? a. 400X b. 40X c. 4X d. 10X 6. How is a plant cell different from an animal cell? a. Plant cells have mitochondria and vacuoles b. Animal cells have cytoplasm and ribosomes c. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
Cell Structure and Function - Coach Hernandez Biology
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
... Write down any interesting details you would use to describe the slide. Be prepared to share your findings with the group. ...
Cells
... to know more about them. Using microscopes, they learned that all living things are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells are microscopic, meaning that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. ...
... to know more about them. Using microscopes, they learned that all living things are made of cells. A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in living things. Cells are microscopic, meaning that they cannot be seen with the naked eye. ...
Created by Tiarra Moore Crawford Long Middle School Atlanta, GA
... How can substances move into and out of a cell? Diffusion The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Concentration = the amount of a substance in a given volume. ...
... How can substances move into and out of a cell? Diffusion The process by which molecules move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Concentration = the amount of a substance in a given volume. ...
Plant Tissues and Growth Worksheet Cs`)
... consists of loosely packed cells with thin cell walls and carries out both storage and photosynthesis. 4. The tissue type that makes up most of the plant’s interior of roots, stems and leaves is ki’ cs 5. Plant are similar to tumours, because they are produced by the abnormal growth of cells. 6. The ...
... consists of loosely packed cells with thin cell walls and carries out both storage and photosynthesis. 4. The tissue type that makes up most of the plant’s interior of roots, stems and leaves is ki’ cs 5. Plant are similar to tumours, because they are produced by the abnormal growth of cells. 6. The ...
File
... b) Name two structures present in an epithelial cell from the small intestine that are not present in a cholera bacterium. Cholera bacteria can be viewed using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) or a scanning ...
... b) Name two structures present in an epithelial cell from the small intestine that are not present in a cholera bacterium. Cholera bacteria can be viewed using a transmission electron microscope (TEM) or a scanning ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.