* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Mitosis Root Lab
Biochemical switches in the cell cycle wikipedia , lookup
Cell nucleus wikipedia , lookup
Endomembrane system wikipedia , lookup
Extracellular matrix wikipedia , lookup
Programmed cell death wikipedia , lookup
Cell encapsulation wikipedia , lookup
Tissue engineering wikipedia , lookup
Cellular differentiation wikipedia , lookup
Cytokinesis wikipedia , lookup
Cell culture wikipedia , lookup
Cell growth wikipedia , lookup
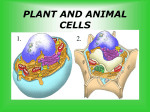
Mitosis Root Lab Name: __________________________________ period: _____ Define mitosis: ________________________________________________________________ Procedure: 1. Write in the cell cycle stages of the cells below and label the organelle X. 2. Examine the drawings of the onion root tips under high power. 3. Below, draw a cell from the drawings for each stage of mitosis. a. Interphase b. Prophase c. Metaphase d. Anaphase e. Telophase Analysis: 1. Is the 1st diagram of cells showing plant or animal cells? _________ How do you know? ____________________________________________________________ 2. Why is the root tip a good place to look for mitosis? ________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 3. How is mitosis in plant and animal cells similar? ____________________________ __________________________________________________________________ 4. What are 2 differences between plant and animal cell mitosis? _______________ __________________________________________________________________ 5. When body cells divide by ______________, the same number of chromosomes would be found in the _____________ cell and the daughter cells. 6. If a fertilized egg of an onion has 16 chromosomes, how many chromosomes would be found in an onion leaf cell? ________ Onion root cell? ______ 7. If a fertilized egg of a human has 46 chromosomes, how many would be found in the liver cell? __________ Skin cell? ________ 8. Similar to the first drawing of cells on the front page, draw and label the cells of a plant as it goes through the cell cycle below. REVIEW 1. Which is NOT an example of asexual reproduction? a. budding b. mitosis c. meiosis d. binary fission 2. The smallest nonliving piece of matter is called ____. a. cell b. atom c. compound 3. Fermentation is most similar to which other process, but without oxygen present. a. photosynthesis b. osmosis c. respiration 4. Which organism is an example of regeneration? a. hydra b. star fish c. spider plant d. blood cells 5. How many times does a compound light microscope with an eyepiece lens of 10X and an objective lens of 4X magnify objects? a. 400X b. 40X c. 4X d. 10X 6. How is a plant cell different from an animal cell? a. Plant cells have mitochondria and vacuoles b. Animal cells have cytoplasm and ribosomes c. Plant cells have cell walls and chloroplasts d. Animal cells have cell walls and chloroplasts 7. What is the organization of your own cells, starting with the smallest unit and going to the level of organism? a. cell, tissue, organ, organ system, organism b. organism, organ system, cell, organ, tissue c. cell, organ, organ system, tissue, organism d. tissue, organ system, organism, organ, cell 8. Why is the nucleus important to the cell? a. The nucleus makes all the energy for the cell b. The nucleus directs all cell activities c. The nucleus makes tRNA and proteins d. The nucleus is not important 9. What is a compound light microscope? a. A microscope with only one lens b. A microscope the uses a magnetic field to bend beams of electrons c. A microscope that has two or more lenses 10. What are the parts of the cell theory? a. All organisms have cells, come from cells and have cells to control all activities b. All nonliving and living things have cells and cells control all activities c. All living things have cells and cells can appear when proper conditions exist in the air 11. Animal cells do NOT have ______. a. centrioles b. chloroplasts c. RNA d. cytoplasm 12. The chromosomes in the nucleus of a cell contain nucleic acids known as ______. a. tRNA b. mitosis c. meiosis d. DNA Part II Matching: Each answer can only be used once in the group it is written next to. 1. Lysosome 2. Vacuoles 3. Mitochondria 4. Nucleus 5. Ribosomes A. B. C. D. E. Storage areas in cells Contains hereditary information Energy is created from food Digests waste Make proteins 6. 7. 8. 9. A. B. C. D. Semi-permeable outer layer Gel-like material inside a cell All structures inside a cell Rigid structure that supports plant cells Organelles Cell membrane Cell wall Cytoplasm