1-2 Looking Inside Cells
... sunlight and uses it to produce food ONLY IN PLANTS These give plants their green color Green due to Chlorophyll ...
... sunlight and uses it to produce food ONLY IN PLANTS These give plants their green color Green due to Chlorophyll ...
Document
... Antigen – a foreign substance Often (but not always) protein. Antibody – a protein (γ-globulin) that specifically combines with an antigen. ...
... Antigen – a foreign substance Often (but not always) protein. Antibody – a protein (γ-globulin) that specifically combines with an antigen. ...
Mast cells
... extracellular matrix. They may be immature cells with name ending in blast. These cells can reproduce and form the matrix. May be mature cells names end in - cyte. These cells have a reduced ability to divide and maintain matrix. May be for remodeling of matrix , names end in clasts. The cells of co ...
... extracellular matrix. They may be immature cells with name ending in blast. These cells can reproduce and form the matrix. May be mature cells names end in - cyte. These cells have a reduced ability to divide and maintain matrix. May be for remodeling of matrix , names end in clasts. The cells of co ...
Tissue Engineering
... • Deliver and retain cells and biochemical factors • Enable diffusion of vital cell nutrients and expressed products • Exert certain mechanical and biological influences to modify the behavior of the cell phase • Need a certain porosity, biodegradability, ...
... • Deliver and retain cells and biochemical factors • Enable diffusion of vital cell nutrients and expressed products • Exert certain mechanical and biological influences to modify the behavior of the cell phase • Need a certain porosity, biodegradability, ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods (doc 73K)
... insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1; 10 ng/mL, all from Peprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA)3. Cells were then grown for 7 days in differentiation culture medium (IMDM medium) supplemented with VEGF (60 ng/mL) and SCGF (100 ng/mL)4. ...
... insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF1; 10 ng/mL, all from Peprotech, Rocky Hill, NJ, USA)3. Cells were then grown for 7 days in differentiation culture medium (IMDM medium) supplemented with VEGF (60 ng/mL) and SCGF (100 ng/mL)4. ...
A prokaryotic cell
... cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells . prokaryotic are unable to take any material unless it is first made soluble .Bacteria have no nucleus but all the chemical elements of nucleic acid and protein synthesis are present . Although their nutritional requirements vary greatly ,most bacteria are free living ...
... cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells . prokaryotic are unable to take any material unless it is first made soluble .Bacteria have no nucleus but all the chemical elements of nucleic acid and protein synthesis are present . Although their nutritional requirements vary greatly ,most bacteria are free living ...
the discovery of cells
... - Organisms that have cells containing internal, membrane bound structures - Organelles = a structure that has a membrane surrounding it. - Organelles isolate the structure from the rest of the cell. - Evolution of organelles allows for cell to be divided into compartments - Activity in each organel ...
... - Organisms that have cells containing internal, membrane bound structures - Organelles = a structure that has a membrane surrounding it. - Organelles isolate the structure from the rest of the cell. - Evolution of organelles allows for cell to be divided into compartments - Activity in each organel ...
Plants - HRSBSTAFF Home Page
... growth of the stem and also cells that will develop into leaves and flowers. ...
... growth of the stem and also cells that will develop into leaves and flowers. ...
Moving Molecules and Cellular Energy Crossword
... 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reactions that convert light energy, water, and ...
... 10. movement from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 11. process during which a cell takes in a substance by surrounding it with the cell membrane 12. diffusion of water molecules only through a membrane Down 1. series of reactions that convert light energy, water, and ...
Worksheet 2.1 - contentextra
... 11 The cell cycle describes the behaviour of cells as they grow and divide. Cell division is one part of the cell cycle. The parts of the cycle include G1, S, G2, M, and cytokinesis. Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which G1, S, and G2 occur. 12 Mitosis (M phase) involves four phases, pr ...
... 11 The cell cycle describes the behaviour of cells as they grow and divide. Cell division is one part of the cell cycle. The parts of the cycle include G1, S, G2, M, and cytokinesis. Interphase is the phase of the cell cycle in which G1, S, and G2 occur. 12 Mitosis (M phase) involves four phases, pr ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function I. 7.1 Life is Cellular A. Early
... proteins from food into particles that can be used by the rest of the cell (also break down organelles) • Vacuoles- __________________ structures that store materials like water, salts, proteins & carbohydrates • ___________________-found in plants -use energy from sunlight to make _________________ ...
... proteins from food into particles that can be used by the rest of the cell (also break down organelles) • Vacuoles- __________________ structures that store materials like water, salts, proteins & carbohydrates • ___________________-found in plants -use energy from sunlight to make _________________ ...
Cell Structure Transport Review
... 6. What is the difference between rough and smooth ER? 7. If a cell, fill with water, what organelle would store it? 8. Protein is made from what organelle? 9. Define organelle. 10. Where is the genetic material located in a prokaryote? 11. What organelles provide energy for the plant cell? 12. A ba ...
... 6. What is the difference between rough and smooth ER? 7. If a cell, fill with water, what organelle would store it? 8. Protein is made from what organelle? 9. Define organelle. 10. Where is the genetic material located in a prokaryote? 11. What organelles provide energy for the plant cell? 12. A ba ...
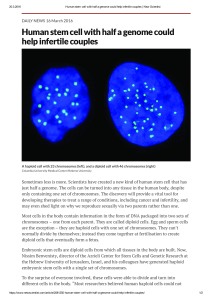
Human stem cell with half a genome could help infertile couples
... the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel, and his colleagues have generated haploid embryonic stem cells with a single set of chromosomes. To the surprise of everyone involved, these cells were able to divide and turn into different cells in the body. “Most researchers believed human haploid cells ...
... the Hebrew University of Jerusalem, Israel, and his colleagues have generated haploid embryonic stem cells with a single set of chromosomes. To the surprise of everyone involved, these cells were able to divide and turn into different cells in the body. “Most researchers believed human haploid cells ...
File
... organelle called the cell wall. Function: Cell walls offer structural support. They let each cell fill up with more water without bursting. This keeps the cells “full” and upright. Since plants have no skeleton, they use turgor pressure (pressure of water against the inside of the cell) to stand up. ...
... organelle called the cell wall. Function: Cell walls offer structural support. They let each cell fill up with more water without bursting. This keeps the cells “full” and upright. Since plants have no skeleton, they use turgor pressure (pressure of water against the inside of the cell) to stand up. ...
THE CELL - TeacherWeb
... which he originally referred to as animalcules, and which we now refer to as microorganisms. He was also the first to record microscopic observations of muscle fibers, bacteria, spermatozoa and blood flow in capillaries (small blood vessels). ...
... which he originally referred to as animalcules, and which we now refer to as microorganisms. He was also the first to record microscopic observations of muscle fibers, bacteria, spermatozoa and blood flow in capillaries (small blood vessels). ...
Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic Cells ppt. File
... 1. They do not have a nucleus, and their genetic material is scattered randomly throughout the cell. 2. They only type of organelle it contains are ribosomes. Prokaryotes are contain cytoplasm, cell membranes (only around the outside of the cell), and flagellum. 3. They are less complicated and smal ...
... 1. They do not have a nucleus, and their genetic material is scattered randomly throughout the cell. 2. They only type of organelle it contains are ribosomes. Prokaryotes are contain cytoplasm, cell membranes (only around the outside of the cell), and flagellum. 3. They are less complicated and smal ...
Unit Three
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells Cells are the smallest living things, the basic unit of organization of all organisms Cells arise only by the division of a previously existing cell ...
... All organisms are composed of one or more cells, and the life processes of metabolism and heredity occur within these cells Cells are the smallest living things, the basic unit of organization of all organisms Cells arise only by the division of a previously existing cell ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.