Cell structure objectives and vocab 2015
... Unit 2- Cell Structure and Function Understandings: • All organisms are composed of cells with structures that perform functions to sustain life. • Tools are used to collect data which can be used to determine characteristics, predict future events, and provide evidence to support theories. • Scient ...
... Unit 2- Cell Structure and Function Understandings: • All organisms are composed of cells with structures that perform functions to sustain life. • Tools are used to collect data which can be used to determine characteristics, predict future events, and provide evidence to support theories. • Scient ...
CHAPTER 43—THE BODY S DEFENSES 1. What s the difference
... 9. Listed below are characteristics of the primary and secondary responses to a specific antigen. Determine if the statement is true of the primary response (1) or the secondary response (2.) ______ Initial response to antigen ______ Does not appear immediately ______ Gradual, sustained rise in conc ...
... 9. Listed below are characteristics of the primary and secondary responses to a specific antigen. Determine if the statement is true of the primary response (1) or the secondary response (2.) ______ Initial response to antigen ______ Does not appear immediately ______ Gradual, sustained rise in conc ...
Bioenergetics Structures and Functions of Cells
... • Individually or in groups, students may be asked to draw a typical plant or animal cell as seen in college textbooks. Drawings should clearly reflect the fine structure of the organelles as seen in the electron microscope. • Each structure in #1 above should be labeled properly. • With a red ball ...
... • Individually or in groups, students may be asked to draw a typical plant or animal cell as seen in college textbooks. Drawings should clearly reflect the fine structure of the organelles as seen in the electron microscope. • Each structure in #1 above should be labeled properly. • With a red ball ...
Immunology Lab
... Below is a list of diseases that result when the immune system attacks the body’s own cells. State what cells the immune system is attacking in each disease. Graves’ disease: _________________________ Type I diabetes: _________________________ Multiple sclerosis: _________________________ Hemolytic ...
... Below is a list of diseases that result when the immune system attacks the body’s own cells. State what cells the immune system is attacking in each disease. Graves’ disease: _________________________ Type I diabetes: _________________________ Multiple sclerosis: _________________________ Hemolytic ...
Worksheet
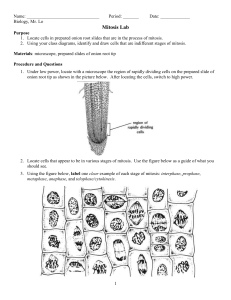
... Procedure and Questions 1. Under low power, locate with a microscope the region of rapidly dividing cells on the prepared slide of onion root tip as shown in the picture below. After locating the cells, switch to high power. ...
... Procedure and Questions 1. Under low power, locate with a microscope the region of rapidly dividing cells on the prepared slide of onion root tip as shown in the picture below. After locating the cells, switch to high power. ...
This is a gelatin-like substance found between the cell membrane
... respiration, in which oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is given off fermentation, in which sugar is broken down and alcohol is given off photosynthesis, in which carbon dioxide is used and sugars are produced ...
... respiration, in which oxygen is used and carbon dioxide is given off fermentation, in which sugar is broken down and alcohol is given off photosynthesis, in which carbon dioxide is used and sugars are produced ...
Name: Date: Period: ______ AP Biology: Unit 5, DBA #1 Review Ms
... ________________________A. Used to regulate the transport of materials into and out of the cell. ________________________B. Used to digest food, old cell parts, etc. using enzymes. ________________________C. Used to capture solar energy and convert it to the chemical energy stored in the molecule gl ...
... ________________________A. Used to regulate the transport of materials into and out of the cell. ________________________B. Used to digest food, old cell parts, etc. using enzymes. ________________________C. Used to capture solar energy and convert it to the chemical energy stored in the molecule gl ...
Unit 1 - Section 2.3 Eukaryotic Evolution
... the masses specialized in function. What would be the evolutionary advantage of cell specialization? Life Cycles and Reproduction Cell division in eukaryotes is diverse. Asexual mitosis still occurs, although many eukaryotes employ MULTIPLE FISSION in which multiple copies of a cell are made at on ...
... the masses specialized in function. What would be the evolutionary advantage of cell specialization? Life Cycles and Reproduction Cell division in eukaryotes is diverse. Asexual mitosis still occurs, although many eukaryotes employ MULTIPLE FISSION in which multiple copies of a cell are made at on ...
Cancer – Cells Out of Control!
... brain, lung, blood cell. The cell even stops being one of those specialized cells – stops differentiating. It is just a tumor cell with one aim, to reproduce. This rogue behavior begins with just one cell. All cells that result from that first cell are also cancerous. One a mass of these cells has a ...
... brain, lung, blood cell. The cell even stops being one of those specialized cells – stops differentiating. It is just a tumor cell with one aim, to reproduce. This rogue behavior begins with just one cell. All cells that result from that first cell are also cancerous. One a mass of these cells has a ...
Biology Chapter 3 Learning Objectives
... 2. Make a chart to contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Include what the name means, what is present or absent, and the types of organisms in each category. 3. Compare the size of a typical prokaryotic cell with that of a eukaryotic cell. 4. List the function and draw a picture of the followin ...
... 2. Make a chart to contrast eukaryotic and prokaryotic cells. Include what the name means, what is present or absent, and the types of organisms in each category. 3. Compare the size of a typical prokaryotic cell with that of a eukaryotic cell. 4. List the function and draw a picture of the followin ...
Title: Surface Area to Volume Ratio Questions: Why can`t cells
... 3. Surface area of one side- A=s2 (A- area, s-side) you will measure your cube in unit. Your smallest cube is one unit long on a side. The largest cube is 4 units long on a side. 4. Total surface Area- A=6 x s2 5. Volume- V= s3 6. The chart also contains the ratio of the total surface area to the vo ...
... 3. Surface area of one side- A=s2 (A- area, s-side) you will measure your cube in unit. Your smallest cube is one unit long on a side. The largest cube is 4 units long on a side. 4. Total surface Area- A=6 x s2 5. Volume- V= s3 6. The chart also contains the ratio of the total surface area to the vo ...
PROKARYOTES vs. Eukaryotes
... are the cells that have helped organisms advance to new levels of specialization beyond imagination. You wouldn't be here if eukaryotic cells did not exist. What makes a eukaryotic cell? Let's watch. (1) Eukaryotic cells have an organized nucleuswith a nuclear envelope. They have a "brain" for the c ...
... are the cells that have helped organisms advance to new levels of specialization beyond imagination. You wouldn't be here if eukaryotic cells did not exist. What makes a eukaryotic cell? Let's watch. (1) Eukaryotic cells have an organized nucleuswith a nuclear envelope. They have a "brain" for the c ...
“Guided Reading and Study” Student Notes Chapter 2.4, “Looking
... b. Replace each incorrect response with the CORRECT response, as seen below. c. Study each question and response by really thinking about the ‘meaning’ of what each statement is ‘messaging’. d. Next, in your own mind, paraphrase what you have just studied! Then, practice studying aloud with some ...
... b. Replace each incorrect response with the CORRECT response, as seen below. c. Study each question and response by really thinking about the ‘meaning’ of what each statement is ‘messaging’. d. Next, in your own mind, paraphrase what you have just studied! Then, practice studying aloud with some ...
Passive vs Active Transport
... Process of Endocytosis • Plasma membrane surrounds material • Edges of membrane meet • Membranes fuse to form vesicle ...
... Process of Endocytosis • Plasma membrane surrounds material • Edges of membrane meet • Membranes fuse to form vesicle ...
Cells - Mission Hills High School
... do that job. • The organelles that make up a certain cell are also determined by the specific functions carried out by the cell ...
... do that job. • The organelles that make up a certain cell are also determined by the specific functions carried out by the cell ...
Year 10 Spring Biology Revision 92.50KB 2017-03
... Recall that immune reactions initially caused by a pathogen can trigger allergies such as skin rashes and asthma. Know that severe physical ill health can lead to depression and other mental illness. Explain the effect of lifestyle on some non-communicable diseases and that they can be caused by and ...
... Recall that immune reactions initially caused by a pathogen can trigger allergies such as skin rashes and asthma. Know that severe physical ill health can lead to depression and other mental illness. Explain the effect of lifestyle on some non-communicable diseases and that they can be caused by and ...
7-4 Lesson Overview (PowerPoint)
... In terms of their numbers, unicellular organisms dominate life on Earth. Unicellular organisms include both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. ...
... In terms of their numbers, unicellular organisms dominate life on Earth. Unicellular organisms include both prokaryotes and eukaryotes. ...
MICROBIOLOGY
... • Used to be known as blue-green algae, but are more closely related to bacteria • They are prokaryotes and have light trapping pigments for photosynthesis • Many are blue, but some are black, green or ...
... • Used to be known as blue-green algae, but are more closely related to bacteria • They are prokaryotes and have light trapping pigments for photosynthesis • Many are blue, but some are black, green or ...
CHAPTER 3: CELLS
... Osmosis Diffusion ______________ Isotonic Cells at ________________________________ Hypertonic Cell in a solution that has a ___________ _________________________Water rushes out of the cell Hypotonic Cell in a solution that has a ___________ ____________________________Water rushes into the c ...
... Osmosis Diffusion ______________ Isotonic Cells at ________________________________ Hypertonic Cell in a solution that has a ___________ _________________________Water rushes out of the cell Hypotonic Cell in a solution that has a ___________ ____________________________Water rushes into the c ...
Cell Structure and Function
... Endoplasmic Reticulum – involved in synthesis and transport Mitochondria – site of intracellular cellular respiration Gogi apparatus – involved in chemical modification and packaging Cytoskeleton – involved in structure and motility ...
... Endoplasmic Reticulum – involved in synthesis and transport Mitochondria – site of intracellular cellular respiration Gogi apparatus – involved in chemical modification and packaging Cytoskeleton – involved in structure and motility ...
Document
... Antigen – a foreign substance Often (but not always) protein. Antibody – a protein (γ-globulin) that specifically combines with an antigen. ...
... Antigen – a foreign substance Often (but not always) protein. Antibody – a protein (γ-globulin) that specifically combines with an antigen. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.