using the compound microscope to study animal and plant cells
... Epithelial cells from the inner cheek Methylene blue (a dye) Procedure 1. Place a drop of methylene blue solution on a clean slide. Run the end of a toothpick carefully over the inside of your cheek and place the material in the dye on the slide, mixing it up a little. Gently add a cover slip and ex ...
... Epithelial cells from the inner cheek Methylene blue (a dye) Procedure 1. Place a drop of methylene blue solution on a clean slide. Run the end of a toothpick carefully over the inside of your cheek and place the material in the dye on the slide, mixing it up a little. Gently add a cover slip and ex ...
普通生物學 - 高雄師範大學生物科技系
... 7. Which type of cell would probably provide the best opportunity to study lysosomes? (a) muscle cell (b) nerve cell (c) phagocytic white blood cell (d) leaf cell of a plant (e) bacterial cell. 8. Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because (a) they are able to maintain a cooler in ...
... 7. Which type of cell would probably provide the best opportunity to study lysosomes? (a) muscle cell (b) nerve cell (c) phagocytic white blood cell (d) leaf cell of a plant (e) bacterial cell. 8. Some bacteria are metabolically active in hot springs because (a) they are able to maintain a cooler in ...
Cell Structure We will be looking at two types of cells in this unit. The
... Cell Structure We will be looking at two types of cells in this unit. The first cell is the cell. The second type of cell is the have little structures inside of them called ...
... Cell Structure We will be looking at two types of cells in this unit. The first cell is the cell. The second type of cell is the have little structures inside of them called ...
Cellular Inheritance
... disease, can be attributed to protein misfolding that aggregates and accumulates in the cell. The underlying genes have nucleotide triplet-repeat mutations, which produce a protein with an expanded run of the same amino acid, commonly glutamine. Proteins with such polyglutamine stretches fold and fu ...
... disease, can be attributed to protein misfolding that aggregates and accumulates in the cell. The underlying genes have nucleotide triplet-repeat mutations, which produce a protein with an expanded run of the same amino acid, commonly glutamine. Proteins with such polyglutamine stretches fold and fu ...
A Robust Approach for In Vitro Generation of Functional Beta Cells
... Salk investigators have now discovered a way to create functional pancreatic beta cells. They expressed a protein called estrogen-related receptor (ERR)gamma in a beta-like cell derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in vitro, which activates a transcriptional network that promotes mito ...
... Salk investigators have now discovered a way to create functional pancreatic beta cells. They expressed a protein called estrogen-related receptor (ERR)gamma in a beta-like cell derived from induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) in vitro, which activates a transcriptional network that promotes mito ...
Parts of the Cell
... 3. Nucleus – “brain” of the cell. Contains the genetic (DNA,RNA) material that instructs the cell what to do. 4. Ribosome – site of protein synthesis. Found along the Endoplasmic Reticulum and floating freely in cytoplasm. ...
... 3. Nucleus – “brain” of the cell. Contains the genetic (DNA,RNA) material that instructs the cell what to do. 4. Ribosome – site of protein synthesis. Found along the Endoplasmic Reticulum and floating freely in cytoplasm. ...
Cell Book Notes Pgs. 1
... makes plant cells rigid. Helps to protect and support the plant cell. Made of a tough non-living substance called cellulose. Some substances like water and oxygen can pass through the cell wall. *Both plant and animal cells have small parts inside of them called organelles that have very specific fu ...
... makes plant cells rigid. Helps to protect and support the plant cell. Made of a tough non-living substance called cellulose. Some substances like water and oxygen can pass through the cell wall. *Both plant and animal cells have small parts inside of them called organelles that have very specific fu ...
Cell Review Study Guide Key
... NAME ____________________________ DATE ____________ PERIOD _____ ...
... NAME ____________________________ DATE ____________ PERIOD _____ ...
3.5.3 - OpenStudy
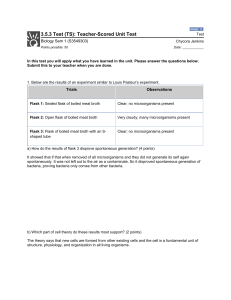
... It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving bacteria only comes from other bacteria. ...
... It showed that if that when removed of all microorganisms and they did not generate its self again spontaneously. It was not left out to the air as a contaminate. So it disproved spontaneous generation of bacteria, proving bacteria only comes from other bacteria. ...
3.1 - Investigating Structure of Cells
... • Although plant cells have a plasma membrane, they also have a supporting structure called a CELL WALL. • The cell wall is made of cellulose which allows the cell wall to be flexible as well as strong. • The function of a cell wall is to support the plant cell and stop it from bursting. ...
... • Although plant cells have a plasma membrane, they also have a supporting structure called a CELL WALL. • The cell wall is made of cellulose which allows the cell wall to be flexible as well as strong. • The function of a cell wall is to support the plant cell and stop it from bursting. ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells All organisms (living things) have
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
... Here's a simple visual comparison between a prokaryotic cell and a eukaryotic cell: ...
What the Cell? - Effingham County Schools
... These fellahs, despite their simplicity, carryout activities like any other living creature; in fact, they grow, reproduce, respond to their environment and can move. They are older and smaller than Eukaryotes. ...
... These fellahs, despite their simplicity, carryout activities like any other living creature; in fact, they grow, reproduce, respond to their environment and can move. They are older and smaller than Eukaryotes. ...
What structures of living things are cells involved?
... living things? 3. What do cells form? 4. What structures of living things are cells involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
... living things? 3. What do cells form? 4. What structures of living things are cells involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
File - Dr. Wall`s Science
... Biology seeks to create models of the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems • Basically reducing the amount of information ...
... Biology seeks to create models of the dynamic behavior of whole biological systems • Basically reducing the amount of information ...
Title: Deconvolution fluorescence microscopy of yeast cells Author
... Abstract: Fluorescence microscopy presents an fast and cheap alternative to more advanced imaging methods like confocal and electron microscopy, even though it is subject to heavy image distortion. It is possible to recover most of the original distortion-free image using deconvolution in computer i ...
... Abstract: Fluorescence microscopy presents an fast and cheap alternative to more advanced imaging methods like confocal and electron microscopy, even though it is subject to heavy image distortion. It is possible to recover most of the original distortion-free image using deconvolution in computer i ...
Tour de Cell
... water, wastes, and other materials. In plants, there is usually one large vacuole. This sac stores water, food, waste products, and other materials. ...
... water, wastes, and other materials. In plants, there is usually one large vacuole. This sac stores water, food, waste products, and other materials. ...
Active and Passive Transport in Cells – Study Guide ____ 1. Using
... 3. The illustration below shows a membrane large enough to let water molecules pass through, but too small for the sugar (glucose) molecules to pass through. What best describes the movement of the water molecules in this illustration? ...
... 3. The illustration below shows a membrane large enough to let water molecules pass through, but too small for the sugar (glucose) molecules to pass through. What best describes the movement of the water molecules in this illustration? ...
Cells and Systems Characteristics of Living Things Some
... How Do Cells Get Fluid and Minerals? diffusion is a process in which material, like fluids, move in and and out of a cell; but only certain materials can move through the selectively permeable cell membrane. nutrients can move from higher concentration outside to the inside to an area of low concen ...
... How Do Cells Get Fluid and Minerals? diffusion is a process in which material, like fluids, move in and and out of a cell; but only certain materials can move through the selectively permeable cell membrane. nutrients can move from higher concentration outside to the inside to an area of low concen ...
Cell Structure and Function (Honors)
... Some molecules cannot cross the membrane without help Some of the proteins in the membrane form protein channels Materials still move from higher to lower concentrations No energy is required ...
... Some molecules cannot cross the membrane without help Some of the proteins in the membrane form protein channels Materials still move from higher to lower concentrations No energy is required ...
Chromosomes
... Stages of Mitosis Interphase • Most of the cell’s life cycle is spent in this phase. • Cell increases in size just before the next phase begins. - ...
... Stages of Mitosis Interphase • Most of the cell’s life cycle is spent in this phase. • Cell increases in size just before the next phase begins. - ...
Nerve activates contraction
... • Microfibrils of cellulose embedded in a matrix of proteins and other polysaccharides. ...
... • Microfibrils of cellulose embedded in a matrix of proteins and other polysaccharides. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.