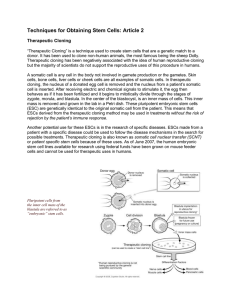
Techniques for Obtaining Stem Cells: Article 2 Therapeutic Cloning
... cloning, the nucleus of a donated egg cell is removed and the nucleus from a patient’s somatic cell is inserted. After receiving electric and chemical signals to stimulate it, the egg then behaves as if it has been fertilized and it begins to mitotically divide through the stages of zygote, morula, ...
... cloning, the nucleus of a donated egg cell is removed and the nucleus from a patient’s somatic cell is inserted. After receiving electric and chemical signals to stimulate it, the egg then behaves as if it has been fertilized and it begins to mitotically divide through the stages of zygote, morula, ...
Cell Structure Part II - Mr. Lesiuk
... consists of about a dozen large flattened sacs. It acts a bit like a shipping and receiving warehouse. Vesicles from the Smooth and Rough E.R. come in on one side to drop off their contents. The proteins that are dropped off are then slightly modified, sorted, and then repackaged and shipped to wher ...
... consists of about a dozen large flattened sacs. It acts a bit like a shipping and receiving warehouse. Vesicles from the Smooth and Rough E.R. come in on one side to drop off their contents. The proteins that are dropped off are then slightly modified, sorted, and then repackaged and shipped to wher ...
Cell Reproduction - wentworth science
... the original cell, called a parent cell. These daughter cells can then divide into two more, and so on, and so on. ...
... the original cell, called a parent cell. These daughter cells can then divide into two more, and so on, and so on. ...
File
... Rudolf Virchow Virchow was a man who worn many hats. He was a doctor, anthropologist, pathologist, biologist and politician. Virchow was from a farming family, he studied medicine and chemistry in Berlin at the Prussian Military Academy. In 1845, while working as an intern alongside Robert Froriep, ...
... Rudolf Virchow Virchow was a man who worn many hats. He was a doctor, anthropologist, pathologist, biologist and politician. Virchow was from a farming family, he studied medicine and chemistry in Berlin at the Prussian Military Academy. In 1845, while working as an intern alongside Robert Froriep, ...
7.1 What are cells?
... others led to an important theory in life science. Theodor Schwann (1810-1882). Hulton • The cell theory explains Archive/Archive Photos/Getty Images the relationship between cells and living things. ...
... others led to an important theory in life science. Theodor Schwann (1810-1882). Hulton • The cell theory explains Archive/Archive Photos/Getty Images the relationship between cells and living things. ...
Cell Membrane & Transport
... • Cells, tissues, organs, and organisms must maintain a balance. • Cells do so by controlling and regulating what gets into and out of the cell. ...
... • Cells, tissues, organs, and organisms must maintain a balance. • Cells do so by controlling and regulating what gets into and out of the cell. ...
Cell Transport Notes Learning Targets 8. Explain the significance of
... 10 Explain the terms: hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic in relationship to the internal environments of cells. ...
... 10 Explain the terms: hypotonic, hypertonic or isotonic in relationship to the internal environments of cells. ...
RIDDLES - Mexico Central School District
... •They have such powerful enzymes they can destroy a whole cell. Example: Tadpole’s tail. ...
... •They have such powerful enzymes they can destroy a whole cell. Example: Tadpole’s tail. ...
THE CELL – Chapter 3
... c. hypotonic-when solution has more water than the cell-water moves into cell and cell swells 2. Osmotic pressure is the difference in concentration of particles, and this pressure creates movement and water moves toward more particles D. Filtration-molecules are forced through membranes by hydrosta ...
... c. hypotonic-when solution has more water than the cell-water moves into cell and cell swells 2. Osmotic pressure is the difference in concentration of particles, and this pressure creates movement and water moves toward more particles D. Filtration-molecules are forced through membranes by hydrosta ...
Chapter 4: Ecosystems - Blair Community Schools
... a. chain of sugars acts like a marker to identify type of cell ...
... a. chain of sugars acts like a marker to identify type of cell ...
Cell Structures
... Finished proteins leave in a vacuole and are taken to their final destination (thanks to motor proteins) ...
... Finished proteins leave in a vacuole and are taken to their final destination (thanks to motor proteins) ...
LIVING CHARACTERISTICS Organization
... electron microscopes: TEM (transmission electron microscope) and SEM (scanning electron microscope) Medical researchers use fiber optics to create microscopes that can be used to see inside the body. ...
... electron microscopes: TEM (transmission electron microscope) and SEM (scanning electron microscope) Medical researchers use fiber optics to create microscopes that can be used to see inside the body. ...
Plasma Membrane Transport
... • There are less solute (salt) molecules outside the cell, since salt sucks, water will move into the cell. • The cell will gain water and grow larger. In plant cells, the central vacuoles will fill and the plant becomes stiff and rigid, the cell wall keeps the plant from bursting • In animal cells, ...
... • There are less solute (salt) molecules outside the cell, since salt sucks, water will move into the cell. • The cell will gain water and grow larger. In plant cells, the central vacuoles will fill and the plant becomes stiff and rigid, the cell wall keeps the plant from bursting • In animal cells, ...
Theory =
... (see left page) Origin of Life Cell Theory 1. all living things are made of ________ 2. cells are basic unit of _______________ & ________________ 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. What is the big question this theory raises? ...
... (see left page) Origin of Life Cell Theory 1. all living things are made of ________ 2. cells are basic unit of _______________ & ________________ 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. What is the big question this theory raises? ...
Cellular Functions
... By slide #: 2- carbohydrates, 3- energy, 4-lipids, 5proteins, 6-nucleic acids, 7- many of the chemical reactions take place in water, 8chains of carbon atoms, 9-chemical energy, 10photosynthesis, 11- glucose, 12-cellular respiration, 13-mitochondria, 14-fermentation, 15-concentration, 16-diffusion, ...
... By slide #: 2- carbohydrates, 3- energy, 4-lipids, 5proteins, 6-nucleic acids, 7- many of the chemical reactions take place in water, 8chains of carbon atoms, 9-chemical energy, 10photosynthesis, 11- glucose, 12-cellular respiration, 13-mitochondria, 14-fermentation, 15-concentration, 16-diffusion, ...
Eukaryotic cell
... 3. cell-shape, mechanical support, provides anchorage for many organelles and cytosolic enzymes ...
... 3. cell-shape, mechanical support, provides anchorage for many organelles and cytosolic enzymes ...
2.4.08 105K lecture
... The function of Aquaporin is to allow the passive diffusion of water across the cell membrane. The structure of Aquaporin is a donut and water goes through the donut hole. Aquaporin increases the rate of osmosis. ...
... The function of Aquaporin is to allow the passive diffusion of water across the cell membrane. The structure of Aquaporin is a donut and water goes through the donut hole. Aquaporin increases the rate of osmosis. ...
File
... from passive? Complete the chart. 2. What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? 3. How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? 4. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? ...
... from passive? Complete the chart. 2. What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? 3. How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? 4. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? ...
Cells Webquest - Warren County Schools
... http://science.jrank.org/kids/pages/30/Cells-At-Work.html (for number 10 only) 7. ______________________ cells protect the body. These cells cover the ____________________ and ______________________ of our body’s organs. 8. Why are nerve cells important to the human body? ...
... http://science.jrank.org/kids/pages/30/Cells-At-Work.html (for number 10 only) 7. ______________________ cells protect the body. These cells cover the ____________________ and ______________________ of our body’s organs. 8. Why are nerve cells important to the human body? ...
REVISION QUESTIONS: CELL BIOLOGY 2 Which one of the
... 5 The drawings below show stages in cell division but in the wrong order. What is the most likely sequence of events? ...
... 5 The drawings below show stages in cell division but in the wrong order. What is the most likely sequence of events? ...
013368718X_CH07_097
... 19. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria lack genetic information in the form of DNA ...
... 19. Both chloroplasts and mitochondria lack genetic information in the form of DNA ...
Cell Structure
... part of a larger organism, such as the cells that make up your body. The cell is the smallest unit of life in our bodies. In the body, there are brain cells, skin cells, liver cells, stomach cells, and the list goes on. All of these cells have unique functions and ...
... part of a larger organism, such as the cells that make up your body. The cell is the smallest unit of life in our bodies. In the body, there are brain cells, skin cells, liver cells, stomach cells, and the list goes on. All of these cells have unique functions and ...
Chapter 7 Exam Review Sheet
... In the diffusion, which way do molecules move in terms of concentration? What is Osmosis? Facilitated Diffusion uses what structure to help molecules get through the membrane? Which process of movement of molecules through a membrane requires energy? In Active Transport, what source of energy is use ...
... In the diffusion, which way do molecules move in terms of concentration? What is Osmosis? Facilitated Diffusion uses what structure to help molecules get through the membrane? Which process of movement of molecules through a membrane requires energy? In Active Transport, what source of energy is use ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.