The Cell Theory - Cardinal Newman
... “All cells are from other pre-existing cells.” Discovered while researching cancer cells. ...
... “All cells are from other pre-existing cells.” Discovered while researching cancer cells. ...
Cell Organelles
... Takes up most of the cell’s volume Unique to plants Stores water May contain ions, nutrients, and waste When full – causes cell to be rigid because it presses against the cell wall. This makes a plant stand upright REMEMBER… BOTH PLANT AND ANIMAL cells have vacuoles, but only plant cells hav ...
... Takes up most of the cell’s volume Unique to plants Stores water May contain ions, nutrients, and waste When full – causes cell to be rigid because it presses against the cell wall. This makes a plant stand upright REMEMBER… BOTH PLANT AND ANIMAL cells have vacuoles, but only plant cells hav ...
Pre-Bio LP 1.23-2.2
... I can differentiate between prokaryotes & eukaryotes as well as plant & animal cells. Review notes Cell Test What was the hardest part of the test ...
... I can differentiate between prokaryotes & eukaryotes as well as plant & animal cells. Review notes Cell Test What was the hardest part of the test ...
The Eukaryotic Cell (plant and animal cells) Eukaryotes: Organisms
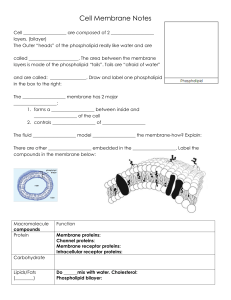
... * involved with enzymatic activity * involved with cell identification -‐ is considered the “gatekeeper” of cell because it controls what goes in and out -‐ cytosol = the _________ of the ce ...
... * involved with enzymatic activity * involved with cell identification -‐ is considered the “gatekeeper” of cell because it controls what goes in and out -‐ cytosol = the _________ of the ce ...
1. To enter or leave a cell, substances must pass through a. a
... 1. To enter or leave a cell, substances must pass through a. a microtubule. b. the Golgi apparatus. c. a ribosome. d. the nucleus. e. the plasma membrane. 2. Bacterial cell are prokaryotic; in comparison to a typical eukaryotic cell they would a. be smaller. b. have a smaller nucleus. c. lack a plas ...
... 1. To enter or leave a cell, substances must pass through a. a microtubule. b. the Golgi apparatus. c. a ribosome. d. the nucleus. e. the plasma membrane. 2. Bacterial cell are prokaryotic; in comparison to a typical eukaryotic cell they would a. be smaller. b. have a smaller nucleus. c. lack a plas ...
Sci8Un6#17ACell+structures
... In your NB, create a T chart to list the major structures found in each cell. ...
... In your NB, create a T chart to list the major structures found in each cell. ...
Cell Function – Cells and their Environment
... Water moves into and out of cells because of the different concentrations of the solutes. Different kinds of cells react differently to osmosis, depending on the solution they are in: ...
... Water moves into and out of cells because of the different concentrations of the solutes. Different kinds of cells react differently to osmosis, depending on the solution they are in: ...
Date - Pearland ISD
... ____________________. The thick ropy strands are the _____________________________. The large solid spot is the _____________________. The nucleolus is a ____________ of chromatin. It manufactures __________________________. The chromatin is _______________ in its active form. It is a ______________ ...
... ____________________. The thick ropy strands are the _____________________________. The large solid spot is the _____________________. The nucleolus is a ____________ of chromatin. It manufactures __________________________. The chromatin is _______________ in its active form. It is a ______________ ...
CELL PROJECT: Due
... transport/passive transport, moves materials in/out of the cell, communication ...
... transport/passive transport, moves materials in/out of the cell, communication ...
Extra cellular components 15
... neighbouring cells are very tightly pressed against each other, bound together by specific proteins. Form continuous seal around the cell. They prevents the extracellular leakage across the epithelial cells. ...
... neighbouring cells are very tightly pressed against each other, bound together by specific proteins. Form continuous seal around the cell. They prevents the extracellular leakage across the epithelial cells. ...
BASICS OF STEM CELLS
... Dr. Niranjan Bhattacharya, D.Sc., M.D., M.S., FACS (USA) Advisor and Consultant, B.P. Poddar Hospital & AMRI (Gol Park) ...
... Dr. Niranjan Bhattacharya, D.Sc., M.D., M.S., FACS (USA) Advisor and Consultant, B.P. Poddar Hospital & AMRI (Gol Park) ...
Controlled Protein Expression Using Iron Oxide Nanoparticles
... The application of nanotechnology to medicine has primarily focused on the delivery of therapeutic agents to specific targets and biosensors to detect the presence of pathogens and environmental hazards. Our investigators have combined approaches in bioengineering with nanotechnology to develop a sy ...
... The application of nanotechnology to medicine has primarily focused on the delivery of therapeutic agents to specific targets and biosensors to detect the presence of pathogens and environmental hazards. Our investigators have combined approaches in bioengineering with nanotechnology to develop a sy ...
Biology Practice Test 1
... Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells, contain many more mitochondria than do other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others? A. ...
... Some cells, such as human nerve and muscle cells, contain many more mitochondria than do other cells, such as skin cells. Why do some cells have more mitochondria than others? A. ...
NC-250™ Cell Cycle Assays
... In a given population, cells will be distributed among three major phases of the cell cycle: G1 /G0 phase (one set of paired chromosomes per cell), S phase (DNA synthesis with variable amount of DNA), and G2/M phase (two sets of paired chromosomes per cell, prior to cell division). The NucleoCounter ...
... In a given population, cells will be distributed among three major phases of the cell cycle: G1 /G0 phase (one set of paired chromosomes per cell), S phase (DNA synthesis with variable amount of DNA), and G2/M phase (two sets of paired chromosomes per cell, prior to cell division). The NucleoCounter ...
Role of Cytokines in Stem Cell Self
... Maintenance of self renewal property in ES via Nanog is independent of LIF/STAT3, and also Oct-3/4 Understanding the molecular mechanism of stem cell renewal and commitment - unparalleled progress for tissue replacement, transplantation and other stem cell ...
... Maintenance of self renewal property in ES via Nanog is independent of LIF/STAT3, and also Oct-3/4 Understanding the molecular mechanism of stem cell renewal and commitment - unparalleled progress for tissue replacement, transplantation and other stem cell ...
quiz quiz trade biology 1 chapter 7 and chapter 8
... The concentration of dissolved substances in the solution is the same as the concentration of dissolved substances inside the cell ...
... The concentration of dissolved substances in the solution is the same as the concentration of dissolved substances inside the cell ...
Bacteria
... Bacteria Chapter 7-2 I. The Bacterial Cell 1. Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes. The genetic material in their cells is not contained in a nucleus. 2. List three characteristics of living things that bacteria possess. a. reproduce b. use energy c. cellular organization 3. What cell structure he ...
... Bacteria Chapter 7-2 I. The Bacterial Cell 1. Bacteria are classified as prokaryotes. The genetic material in their cells is not contained in a nucleus. 2. List three characteristics of living things that bacteria possess. a. reproduce b. use energy c. cellular organization 3. What cell structure he ...
Chapter 7 - Angelfire
... • Cells must maintain proper conditions within itself to function • The plasma membrane is a flexible boundary between the cell and its environment – It allows a steady supply of nutrients into and out of the cell at the appropriate levels ...
... • Cells must maintain proper conditions within itself to function • The plasma membrane is a flexible boundary between the cell and its environment – It allows a steady supply of nutrients into and out of the cell at the appropriate levels ...
Plant Cell Differences Plant Cell and Animal Cell Similarities Animal
... 7. Nucleolus – dark spot INSIDE the nucleus which stores the materials that are used to make ribosomes. 8. Nucleus – large spot in the middle of eukaryotic cells that contains all the cell’s DNA. It is the control center of the cell because it directs ALL of the cell’ 9. Ribosome – smallest and most ...
... 7. Nucleolus – dark spot INSIDE the nucleus which stores the materials that are used to make ribosomes. 8. Nucleus – large spot in the middle of eukaryotic cells that contains all the cell’s DNA. It is the control center of the cell because it directs ALL of the cell’ 9. Ribosome – smallest and most ...
WBA_153-155
... 9. Which is not a new, potential benefit of stem cell research? A. growing new skin cells to repair a cut B. replacing heart cells damaged by heart attacks C. repairing breaks between nerve cells in spinal injuries D. preventing suffering and death caused by cellular damage 10. What is the main reas ...
... 9. Which is not a new, potential benefit of stem cell research? A. growing new skin cells to repair a cut B. replacing heart cells damaged by heart attacks C. repairing breaks between nerve cells in spinal injuries D. preventing suffering and death caused by cellular damage 10. What is the main reas ...
10_4 Cell Differentiation
... 9. Which is not a new, potential benefit of stem cell research? A. growing new skin cells to repair a cut B. replacing heart cells damaged by heart attacks C. repairing breaks between nerve cells in spinal injuries D. preventing suffering and death caused by cellular damage 10. What is the main reas ...
... 9. Which is not a new, potential benefit of stem cell research? A. growing new skin cells to repair a cut B. replacing heart cells damaged by heart attacks C. repairing breaks between nerve cells in spinal injuries D. preventing suffering and death caused by cellular damage 10. What is the main reas ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.