Supplementary Materials and Methods
... domain of RSK which then phosphorylates substrates such as S6 (S235/S236). RSK amino acid numbering in this figure is taken from RSK1. Figure S5. Treatment of Calu-6 lung cancer cells with LY2606368 results in rapid accumulation of DNA strand breaks in early S-phase. Calu-6 cells were treated with ...
... domain of RSK which then phosphorylates substrates such as S6 (S235/S236). RSK amino acid numbering in this figure is taken from RSK1. Figure S5. Treatment of Calu-6 lung cancer cells with LY2606368 results in rapid accumulation of DNA strand breaks in early S-phase. Calu-6 cells were treated with ...
Slide 1
... Intermediate filaments work together with Microtubules and actin filaments to give the cell added strength, help define the cell shape, and aid cell and organelle motility. Intermediate filaments are stable, durable. They range in diameter from 8-10 nm (intermediate in size compared with thin filame ...
... Intermediate filaments work together with Microtubules and actin filaments to give the cell added strength, help define the cell shape, and aid cell and organelle motility. Intermediate filaments are stable, durable. They range in diameter from 8-10 nm (intermediate in size compared with thin filame ...
Cell Model lesson
... 1. Ask the students why models are important when discussing cells. Ask why we often depend on models. What were the limitations you encountered of your model? 2. Students will orally present how his/her selected items are a part and function of an animal and plant cell. ...
... 1. Ask the students why models are important when discussing cells. Ask why we often depend on models. What were the limitations you encountered of your model? 2. Students will orally present how his/her selected items are a part and function of an animal and plant cell. ...
Video Guide
... 7. What part of the phospholipid hydrophilic? 8. What does hydrophobic mean? 9. What part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic? 10. Which part of the phospholipid faces the water on the inside and outside of the cell? 11. Which part of the phospholipid faces away from the water inside and outside of t ...
... 7. What part of the phospholipid hydrophilic? 8. What does hydrophobic mean? 9. What part of the phospholipid is hydrophobic? 10. Which part of the phospholipid faces the water on the inside and outside of the cell? 11. Which part of the phospholipid faces away from the water inside and outside of t ...
Lec.1
... The bacterial cytoplasm contains several different types of granules that serve as storage areas for nutrients and stain with certain dyes. When the source of nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus is limited or when the pH is low, excess carbon in the medium is converted to starch and glycogen. These gra ...
... The bacterial cytoplasm contains several different types of granules that serve as storage areas for nutrients and stain with certain dyes. When the source of nitrogen, sulfur or phosphorus is limited or when the pH is low, excess carbon in the medium is converted to starch and glycogen. These gra ...
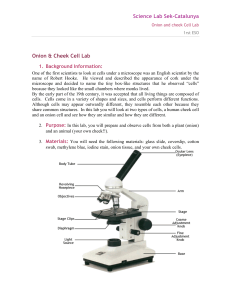
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... One of the first scientists to look at cells under a microscope was an English scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chamb ...
... One of the first scientists to look at cells under a microscope was an English scientist by the name of Robert Hooke. He viewed and described the appearance of cork under the microscope and decided to name the tiny box-like structures that he observed “cells” because they looked like the small chamb ...
Evolution of Eukaryotic Cells
... Many critical genes moved into the host nucleoid/nucleus of Organelle The endosymbiont has become an organelle ...no longer capable of independent respiration The mitochondrion has two bounding membranes The host vesicle membrane (more phospholipid) The endosymbiont cell membrane (mostly glyco- or s ...
... Many critical genes moved into the host nucleoid/nucleus of Organelle The endosymbiont has become an organelle ...no longer capable of independent respiration The mitochondrion has two bounding membranes The host vesicle membrane (more phospholipid) The endosymbiont cell membrane (mostly glyco- or s ...
Document
... • Unlike any other membrane in nature • A lipid bilayer with the outside layer made of lipopolysaccharides instead of ...
... • Unlike any other membrane in nature • A lipid bilayer with the outside layer made of lipopolysaccharides instead of ...
Revision sheet Grade: VI ..... Subject: Biology Date: ______ Roll no
... 4) If living organisms did not Reproduce ...
... 4) If living organisms did not Reproduce ...
Nucleus Nucleolus Cytoplasm The control center of the cell and
... ER, but without the ribosomes. Produces lipids, involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. ...
... ER, but without the ribosomes. Produces lipids, involved in carbohydrate metabolism, and detoxification of drugs and poisons. ...
Organelle Membrane Bound Description/Function Plant/ Animal
... Surrounded by nuclear envelope; Directs the cells activities; stores DNA Located inside the nucleus, it the site of ribosome manufacturing Small organelle consisting of RNA and proteins; They Produces Proteins Double Membranes; It converts food into usable energy for cells Double membranes with thyl ...
... Surrounded by nuclear envelope; Directs the cells activities; stores DNA Located inside the nucleus, it the site of ribosome manufacturing Small organelle consisting of RNA and proteins; They Produces Proteins Double Membranes; It converts food into usable energy for cells Double membranes with thyl ...
Anatomy of a cell
... exhibits the most important characteristics of many distinctive cell types. Examples of cell types: Nerve cells, muscle cells, red blood cells, gland cells, and immune cells ...
... exhibits the most important characteristics of many distinctive cell types. Examples of cell types: Nerve cells, muscle cells, red blood cells, gland cells, and immune cells ...
Outline for Cell structure and membranes
... 1. involves particles moving across the membrane in the natural direction (high to low) 2. particles move through the protein "gates" because they are too large or too polar to diffuse through the lipid layer. 3. examples: sugar, some hormones, ions such as K+ and Na+ D. Active transport (see fig. 5 ...
... 1. involves particles moving across the membrane in the natural direction (high to low) 2. particles move through the protein "gates" because they are too large or too polar to diffuse through the lipid layer. 3. examples: sugar, some hormones, ions such as K+ and Na+ D. Active transport (see fig. 5 ...
Grade IX Science Ch-5 CW Notes
... When a living plant cell looses water through osmosis, it results in contraction of contents of the cell away from cell wall. The cells which are in the condition of plasmolysis are called flaccid cells. 16) Structure of nucleus: i) Nucleus contains double layer covering called as nuclear membrane w ...
... When a living plant cell looses water through osmosis, it results in contraction of contents of the cell away from cell wall. The cells which are in the condition of plasmolysis are called flaccid cells. 16) Structure of nucleus: i) Nucleus contains double layer covering called as nuclear membrane w ...
Student Objectives
... o meiosis: the division of a cell into four haploid gametes (sperm or egg cells). In humans, each new cell receives 23 chromosomes. ...
... o meiosis: the division of a cell into four haploid gametes (sperm or egg cells). In humans, each new cell receives 23 chromosomes. ...
Chapter Outline
... In a hypertonic solution there is a higher percentage of solute outside than inside the cell, which can cause the cells to shrink or shrivel. Transport by Carrier Proteins Carrier proteins are specific; each can combine only with a certain type of molecule or ion, which is then transported through ...
... In a hypertonic solution there is a higher percentage of solute outside than inside the cell, which can cause the cells to shrink or shrivel. Transport by Carrier Proteins Carrier proteins are specific; each can combine only with a certain type of molecule or ion, which is then transported through ...
Pretest
... 14. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, many of the chemical reactions that are necessary for life would either take too long or not occur at all. 15. DNA is the genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring. The ...
... 14. Enzymes speed up chemical reactions in living things. Without enzymes, many of the chemical reactions that are necessary for life would either take too long or not occur at all. 15. DNA is the genetic material that carries information about an organism and is passed from parent to offspring. The ...
Chapter 7: Cell Structure and Function
... comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Be prepared to share with your partner, and then with the class! ...
... comparing and contrasting prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. Be prepared to share with your partner, and then with the class! ...
Answer the following questions, define key terms, and outline
... Answer the following questions, define key terms, and outline processes. This guide is to help remind you of important concepts that were covered during the course. This is not an all inclusive list; some material related to these concepts can be covered on the midterm. Completing this review guide ...
... Answer the following questions, define key terms, and outline processes. This guide is to help remind you of important concepts that were covered during the course. This is not an all inclusive list; some material related to these concepts can be covered on the midterm. Completing this review guide ...
samplequestex1
... A) 100 times more acidic. B) 10 times more acidic. C) 10 times more basic. D) 100 times more basic. ...
... A) 100 times more acidic. B) 10 times more acidic. C) 10 times more basic. D) 100 times more basic. ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.