Introduction to the Cell
... ● the # in cells varies and is related to the cell’s metabolic activity (i.e. if a cell uses more energy, it will have more mitochondria!) ...
... ● the # in cells varies and is related to the cell’s metabolic activity (i.e. if a cell uses more energy, it will have more mitochondria!) ...
7-2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... Your body contains numerous types of cells including skin, muscle, and blood. Which of the following reasons is why you have so many types of cells? a. Cells are located in different parts of the body. ...
... Your body contains numerous types of cells including skin, muscle, and blood. Which of the following reasons is why you have so many types of cells? a. Cells are located in different parts of the body. ...
Monte Carlo Modelling of Exciton Diffusion in Polyfluorenes
... An excellent textbook on all types of solar cells is P Würfel Physics of Solar Cells Wiley-VCH 2nd Edition 2009 Can be obtained in paperback For animations of organic device applications see http://www.bath.ac.uk/news/multimedia/?20070417 Linked from the Modecom website ...
... An excellent textbook on all types of solar cells is P Würfel Physics of Solar Cells Wiley-VCH 2nd Edition 2009 Can be obtained in paperback For animations of organic device applications see http://www.bath.ac.uk/news/multimedia/?20070417 Linked from the Modecom website ...
Slide 1
... Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Big Idea: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei and two cells with identical DNA. ...
... Mitosis and the Cell Cycle Big Idea: Mitosis is the process in which the nucleus divides to form two new nuclei and two cells with identical DNA. ...
topic-4.doc
... o Magnetosomes – iron oxide (magnetic – hence name) deposits (in some G-) in vitro can decompose hydrogen peroxide – may in vivo protect organisms against hydrogen peroxide. INTERESTING NOTE: industrial microbiologist developing culture techniques to grow/harvest magnetite from bacteria for making m ...
... o Magnetosomes – iron oxide (magnetic – hence name) deposits (in some G-) in vitro can decompose hydrogen peroxide – may in vivo protect organisms against hydrogen peroxide. INTERESTING NOTE: industrial microbiologist developing culture techniques to grow/harvest magnetite from bacteria for making m ...
Name - Net Start Class
... Store water, food, some waste Breakdown molecules, waste Rigid, give support and shape Produces energy for the cell Synthesizes proteins Assembles molecules and transport them across the cell Transform radiant energy into chemical energy (glucose) Jellylike substance keeps cell organelles in place S ...
... Store water, food, some waste Breakdown molecules, waste Rigid, give support and shape Produces energy for the cell Synthesizes proteins Assembles molecules and transport them across the cell Transform radiant energy into chemical energy (glucose) Jellylike substance keeps cell organelles in place S ...
Cell Review Questions
... These organisms carry out the activities needed to maintain homeostasis by using specialized internal A) tissues C) organs ...
... These organisms carry out the activities needed to maintain homeostasis by using specialized internal A) tissues C) organs ...
Embryonic stem cell Embryonic stem cells Pluripotent: Embryonic
... blood and immune-system related genetic diseases, cancers, and disorders; juvenile diabetes; Parkinson's; blindness and spinal cord injuries. Other potential uses of embryonic stem cells include investigation of early human development, study of genetic disease and as in vitro systems for ...
... blood and immune-system related genetic diseases, cancers, and disorders; juvenile diabetes; Parkinson's; blindness and spinal cord injuries. Other potential uses of embryonic stem cells include investigation of early human development, study of genetic disease and as in vitro systems for ...
Supplementary Information (doc 31K)
... spermatocytes were most abundant in the upper cell fractions (data not shown). Consistent with these observations, semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed that the expression of Oct4, a marker for spermatogonia, was prominent in the lower cell fractions, whereas that of Spo11, Sycp1, and Dmc1, wh ...
... spermatocytes were most abundant in the upper cell fractions (data not shown). Consistent with these observations, semi-quantitative RT-PCR analysis revealed that the expression of Oct4, a marker for spermatogonia, was prominent in the lower cell fractions, whereas that of Spo11, Sycp1, and Dmc1, wh ...
Lesson 1
... Mitochondrion: transform energy for the cell Nucleus: organelle bounded by a double-layered porous membrane Nuclear membrane: encloses the cell’s genetic material or DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) Cytoplasm: supports the nucleus and other organelles, enclosed by the cell membrane. Lysosome: break down ...
... Mitochondrion: transform energy for the cell Nucleus: organelle bounded by a double-layered porous membrane Nuclear membrane: encloses the cell’s genetic material or DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) Cytoplasm: supports the nucleus and other organelles, enclosed by the cell membrane. Lysosome: break down ...
Cell Organelles
... blueprints) and amino acids to assemble proteins. The proteins created are essential to cell and organismal function. Think of proteins as machinery for cell functions much like electricity and plumbing are essential in a real city. For example, enzymes are a type of protein without which life could ...
... blueprints) and amino acids to assemble proteins. The proteins created are essential to cell and organismal function. Think of proteins as machinery for cell functions much like electricity and plumbing are essential in a real city. For example, enzymes are a type of protein without which life could ...
Meiosis Guided Notes
... • DNA coils into ___________ chromosomes, spindle fibers appear, nucleus disappears. • Every chromosome is paired up next to its ______________ (the chromosome that is the same size and shape). • This is called _____________ and does not occur in mitosis. ...
... • DNA coils into ___________ chromosomes, spindle fibers appear, nucleus disappears. • Every chromosome is paired up next to its ______________ (the chromosome that is the same size and shape). • This is called _____________ and does not occur in mitosis. ...
Diapositiva 1
... themselves because they do not have chloroplasts. • These cells obtain their nutrients from the phloem sap that is made in the plant’s autotrophic cells. • Heterotrophic cells are found in the non-green parts of plants, like roots and woody stems. ...
... themselves because they do not have chloroplasts. • These cells obtain their nutrients from the phloem sap that is made in the plant’s autotrophic cells. • Heterotrophic cells are found in the non-green parts of plants, like roots and woody stems. ...
Methods by which pathogens cause disease
... disruption of host cell Draft VFO-Toxins membranes or the stimulation of endocytosis (cells absorbing material) into host cells • Immune response inhibitors: bacterial produce proteins that inhibit the host's immune system defenses, such as binding host antibodies • Toxins: bacteria produce proteins ...
... disruption of host cell Draft VFO-Toxins membranes or the stimulation of endocytosis (cells absorbing material) into host cells • Immune response inhibitors: bacterial produce proteins that inhibit the host's immune system defenses, such as binding host antibodies • Toxins: bacteria produce proteins ...
Nutrition
... Nutrition: is a process by which organisms acquire chemical substances (Nutrients) used in cellular activities such as metabolism and growth. Organisms differ in the use of particular elements, their source and chemical form. Microbial growth Microbial growth refers to both the increase in cell size ...
... Nutrition: is a process by which organisms acquire chemical substances (Nutrients) used in cellular activities such as metabolism and growth. Organisms differ in the use of particular elements, their source and chemical form. Microbial growth Microbial growth refers to both the increase in cell size ...
cell organelles PP
... The organelle that releases energy in the cell. (The powerhouse of the cell) Found in both animal and plant cells. Mitochondria produce ATP using energy stored in food molecules. Location: All cells except prokaryotes Description ...
... The organelle that releases energy in the cell. (The powerhouse of the cell) Found in both animal and plant cells. Mitochondria produce ATP using energy stored in food molecules. Location: All cells except prokaryotes Description ...
Supplementary Information
... U87-MG cells were incubated at normoxia or hypoxia for 6 h and approximately 50 µg of protein from lysates was precipitated in ice-cold acetone for 90 min at -20oC. The protein precipitate obtained by centrifugation at 14.000 rpm for 15 min at 4oC was dissolved in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer c ...
... U87-MG cells were incubated at normoxia or hypoxia for 6 h and approximately 50 µg of protein from lysates was precipitated in ice-cold acetone for 90 min at -20oC. The protein precipitate obtained by centrifugation at 14.000 rpm for 15 min at 4oC was dissolved in 50 mM ammonium bicarbonate buffer c ...
Lecture 7: the cytoskeleton and cell movement
... the cell towards the periphery, where myosins take over moving organelles near the plasma membrane. ...
... the cell towards the periphery, where myosins take over moving organelles near the plasma membrane. ...
Content Lesson Plan (45 minutes total)
... assessment on plant and animal cells taken from regents tests, teachers own questions, and borrowed exams. Students are instructed to work together and to show their reasoning through the problems ( i.e process of elimination, identifiying key words in the question, and a sentence explaining why the ...
... assessment on plant and animal cells taken from regents tests, teachers own questions, and borrowed exams. Students are instructed to work together and to show their reasoning through the problems ( i.e process of elimination, identifiying key words in the question, and a sentence explaining why the ...
Immunity - Seattle Central College
... – Lymphocytes: Smallest WBC; immune response; B & T • produce antibodies & proteins to destroy foreign cells • allergic reactions • reject tissue grafts ...
... – Lymphocytes: Smallest WBC; immune response; B & T • produce antibodies & proteins to destroy foreign cells • allergic reactions • reject tissue grafts ...
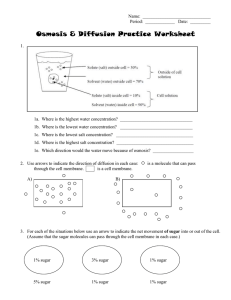
Diffusion, Osmosis, and Active Transport
... 1a. Where is the highest water concentration? ________________________________ 1b. Where is the lowest water concentration? ________________________________ 1c. Where is the lowest salt concentration? __________________________________ 1d. Where is the highest salt concentration? ___________________ ...
... 1a. Where is the highest water concentration? ________________________________ 1b. Where is the lowest water concentration? ________________________________ 1c. Where is the lowest salt concentration? __________________________________ 1d. Where is the highest salt concentration? ___________________ ...
Transport/Diffusion
... Cells must live in a proper water balance. Meaning, if they do not have enough water or if they have too much water they will die. They must have the correct water concentration to live. To study how cells live, we must consider the following 2 processes: 1) Solution concentration: ...
... Cells must live in a proper water balance. Meaning, if they do not have enough water or if they have too much water they will die. They must have the correct water concentration to live. To study how cells live, we must consider the following 2 processes: 1) Solution concentration: ...
Ms. E.Russell`s 7th Grade Life Science Classes START DATE
... Entirely edible ( can be eaten)—NOTE: Your project does not have to be digestible ( will not make you sick0, or even palatable ( tastes good), just edible. No larger than 25cm x 43cm x 10cm ( 10inches by 17 inches by 4 inches), or No smaller than 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm ( 4 in.x 4 in. x 4 in.) ACT ...
... Entirely edible ( can be eaten)—NOTE: Your project does not have to be digestible ( will not make you sick0, or even palatable ( tastes good), just edible. No larger than 25cm x 43cm x 10cm ( 10inches by 17 inches by 4 inches), or No smaller than 10 cm x 10 cm x 10 cm ( 4 in.x 4 in. x 4 in.) ACT ...
Transport in Plants Lesson 10 Biology 10
... 2. When one water molecule is lost another is pulled along by the processes of cohesion and tension. Cohesion: the attraction (sticking together) of different ...
... 2. When one water molecule is lost another is pulled along by the processes of cohesion and tension. Cohesion: the attraction (sticking together) of different ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.