Abstract
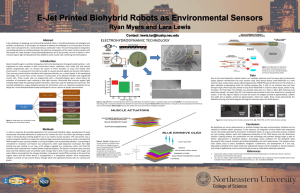
... Recent breakthroughs in synthetic biology have led to the development of programmable bacteria— cells engineered to sense analytes in their environment (toxins, explosives, nitric oxide, pH) and execute specific programmed tasks. To harness the power of these microbes to assay and modify their envir ...
... Recent breakthroughs in synthetic biology have led to the development of programmable bacteria— cells engineered to sense analytes in their environment (toxins, explosives, nitric oxide, pH) and execute specific programmed tasks. To harness the power of these microbes to assay and modify their envir ...
FREE Sample Here
... Uniport refers to the movement of a single molecule. Antiport refers to movement of molecules in the opposite direction. REF: p. 17 25. During which process can lysosomal enzymes be released to degrade engulfed particles? a. Endocytosis b. Pinocytosis c. Phagocytosis d. Exocytosis ANS: C Engulfment ...
... Uniport refers to the movement of a single molecule. Antiport refers to movement of molecules in the opposite direction. REF: p. 17 25. During which process can lysosomal enzymes be released to degrade engulfed particles? a. Endocytosis b. Pinocytosis c. Phagocytosis d. Exocytosis ANS: C Engulfment ...
Chapter 6 Vocabulary - Plain Local Schools
... 11. diffusion: net movement of the particles of a substance from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated (Concept 6.3) 12. equilibrium: point at which the number of diffusing molecules moving in one direction is equal to the number moving in the opposite direction (Conce ...
... 11. diffusion: net movement of the particles of a substance from where they are more concentrated to where they are less concentrated (Concept 6.3) 12. equilibrium: point at which the number of diffusing molecules moving in one direction is equal to the number moving in the opposite direction (Conce ...
Location
... • Function: based on type: Leucoplast (store starch), chromoplast (store pigments), chloroplast ...
... • Function: based on type: Leucoplast (store starch), chromoplast (store pigments), chloroplast ...
cell
... • Function: based on type: Leucoplast (store starch), chromoplast (store pigments), chloroplast ...
... • Function: based on type: Leucoplast (store starch), chromoplast (store pigments), chloroplast ...
File
... that is flexible and interacts with the environment. Only certain cells have a cell wall, which is rigid and provides shape and support to cells. 15. They enable plants to convert solar energy into energy-rich molecules that cells can use. 16. endoplasmic reticulum 17. mitochondrion ...
... that is flexible and interacts with the environment. Only certain cells have a cell wall, which is rigid and provides shape and support to cells. 15. They enable plants to convert solar energy into energy-rich molecules that cells can use. 16. endoplasmic reticulum 17. mitochondrion ...
Lucifer Yellow Uptake in Cells and Protoplasts of Daucas carota
... demonstrate that LY can be taken up by suspensioncultured cells and delivered to the central vacuole. For example, Fig. 1A shows a Normarski image of a typical cell after 18 h in LY. The cytoplasm is closely appressed to the wall, and nuclei (arrowheads) and central vacuoles (asterisks) are easily i ...
... demonstrate that LY can be taken up by suspensioncultured cells and delivered to the central vacuole. For example, Fig. 1A shows a Normarski image of a typical cell after 18 h in LY. The cytoplasm is closely appressed to the wall, and nuclei (arrowheads) and central vacuoles (asterisks) are easily i ...
Mitosis Notes
... Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all parts of a cell? Work with a partner to complete this activity ...
... Materials move through cells by diffusion. Oxygen and food move into cells, while waste products move out of cells. How does the size of a cell affect how efficiently materials get to all parts of a cell? Work with a partner to complete this activity ...
The Cell Cycle Control System
... released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide • Another example of external signals is density-dependent inhibition, in which crowded cells stop dividing • Most animal cells also exhibit anchorage dependence, in which they must be attached to a substratum in order to divide ...
... released by certain cells that stimulate other cells to divide • Another example of external signals is density-dependent inhibition, in which crowded cells stop dividing • Most animal cells also exhibit anchorage dependence, in which they must be attached to a substratum in order to divide ...
BI211StudyObjectivesChapters6
... 3. Describe how membrane proteins associate with the lipid bilayer, and discuss the functions and importance of membrane proteins. 4. Contrast the physical processes of passive and active transport, including diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, & carrier-mediated active transport – which mole ...
... 3. Describe how membrane proteins associate with the lipid bilayer, and discuss the functions and importance of membrane proteins. 4. Contrast the physical processes of passive and active transport, including diffusion, osmosis, facilitated diffusion, & carrier-mediated active transport – which mole ...
Lecture02
... • However, it cannot be created or destroyed. • This is the conservation of energy principle. ...
... • However, it cannot be created or destroyed. • This is the conservation of energy principle. ...
inside cell - Cloudfront.net
... Plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer (two layers of phospholipids or lipids with phosphates) 2 layers = 1 plasma membrane ...
... Plasma membrane is composed of a phospholipid bilayer (two layers of phospholipids or lipids with phosphates) 2 layers = 1 plasma membrane ...
emboj2009123-sup
... prometaphase by treatment with 200 ng/ml nocodazole, followed by mitotic shake-off. Cells were then released into the cell cycle in the presence of cycloheximide (CHX) to avoid de novo protein synthesis. Lysates were prepared at the time points indicated and subjected to WB with the antibodies indic ...
... prometaphase by treatment with 200 ng/ml nocodazole, followed by mitotic shake-off. Cells were then released into the cell cycle in the presence of cycloheximide (CHX) to avoid de novo protein synthesis. Lysates were prepared at the time points indicated and subjected to WB with the antibodies indic ...
Movement of Materials Through the Plasma Membrane
... These proteins let a cell sense its surroundings so that it can change and maintain homeostasis. ...
... These proteins let a cell sense its surroundings so that it can change and maintain homeostasis. ...
Minireview The Stem Cell Concept in Plants: A Matter of Debate
... (see below). In the second approach, cells are purified based, for example, on the presence of cell surface molecules and are then tested for their clonogenic properties in an appropriate host. This is not possible in plants, but has been successfully applied to identify single animal stem cells (Os ...
... (see below). In the second approach, cells are purified based, for example, on the presence of cell surface molecules and are then tested for their clonogenic properties in an appropriate host. This is not possible in plants, but has been successfully applied to identify single animal stem cells (Os ...
Membrane structure, I
... • loosely bound to surface of membrane • ex: cell surface identity marker (antigens) ...
... • loosely bound to surface of membrane • ex: cell surface identity marker (antigens) ...
Homework 2 BSC 1005 Fall 2011
... c. actively pump nutrients into the cell. d. have a very small surface area compared to their volume. 42.The fluid-mosaic model considers the cellular membranes to consist of ________ layer(s) of phospholipid molecules and that the individual phospholipids are able to move about within the structure ...
... c. actively pump nutrients into the cell. d. have a very small surface area compared to their volume. 42.The fluid-mosaic model considers the cellular membranes to consist of ________ layer(s) of phospholipid molecules and that the individual phospholipids are able to move about within the structure ...
Bacteria and Viruses
... Other people think that they are descendents of complex living organisms but they dropped or lost their cell structure Others think they arose from DNA that ...
... Other people think that they are descendents of complex living organisms but they dropped or lost their cell structure Others think they arose from DNA that ...
Self Quiz Match the Function to the Organelle
... 1. Which cell structure contains the cell’s genetic material and controls many of the cell’s activities? - f 2. Which organelle breaks down compounds into small particles? - l 3. Which organelle makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? - e 4. Which organelle converts the c ...
... 1. Which cell structure contains the cell’s genetic material and controls many of the cell’s activities? - f 2. Which organelle breaks down compounds into small particles? - l 3. Which organelle makes proteins using coded instructions that come from the nucleus? - e 4. Which organelle converts the c ...
chapter 7 cellular basis of antibody diversity: clonal selection
... antibody response is generated, we can set out three facts regarding antibody specificity which are based on experimental findings: 1) An animal can produce antibodies to many different epitopes. This has been known since the early days of immunology, based simply on the variety of distinct molecule ...
... antibody response is generated, we can set out three facts regarding antibody specificity which are based on experimental findings: 1) An animal can produce antibodies to many different epitopes. This has been known since the early days of immunology, based simply on the variety of distinct molecule ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.























