O A RIGINAL RTICLES
... Tumor begins a single cell mutates in such a way that lead to uncontrolled growth. A tumor cell can mutate in two important ways: the growth suppressing signals telling cells not divide are turned off or the signals telling cells to begin dividing are left on continuously. (W.W. Gibbs, 2003)Thus, tu ...
... Tumor begins a single cell mutates in such a way that lead to uncontrolled growth. A tumor cell can mutate in two important ways: the growth suppressing signals telling cells not divide are turned off or the signals telling cells to begin dividing are left on continuously. (W.W. Gibbs, 2003)Thus, tu ...
Receptor-Mediated Endocytosis in Plant Cells
... elicitor was internalized (Figures 2g and 2h). This similar behavior, despite the probable differences in chemical nature between the two elicitors, suggests that plant cells may remove different elicitor molecules from their cell surface receptors by common endocytotic pathways. Because extracellul ...
... elicitor was internalized (Figures 2g and 2h). This similar behavior, despite the probable differences in chemical nature between the two elicitors, suggests that plant cells may remove different elicitor molecules from their cell surface receptors by common endocytotic pathways. Because extracellul ...
Supplementary Material
... Thurber et al (5). (For this paper, the Biot number = 0.0225 for the average diameter of vessels found in our human ovarian tumors (Table 1). This is similar to the value 0.024 calculated in (5)). This number concurs with a reflection coefficient of 0.95-0.98 for antibodies inside of vessels (9), a ...
... Thurber et al (5). (For this paper, the Biot number = 0.0225 for the average diameter of vessels found in our human ovarian tumors (Table 1). This is similar to the value 0.024 calculated in (5)). This number concurs with a reflection coefficient of 0.95-0.98 for antibodies inside of vessels (9), a ...
Cell Membrane - holyoke
... efficient barrier by only allowing a very small number of non-polar molecules to freely enter or exit a cell. While for the most part this selectivity is a valuable function and allows the cell to maintain its integrity, cells do need to move ...
... efficient barrier by only allowing a very small number of non-polar molecules to freely enter or exit a cell. While for the most part this selectivity is a valuable function and allows the cell to maintain its integrity, cells do need to move ...
editor`s corner: what`s inside
... commercialization of cellular immunotherapies. This article was authored by Aby J. Mathew, Ph.D., Chief Technology Officer, and Senior Application Scientists Brian Hawkins, Ph.D., and Alireza Abarazi, Ph.D., two recent additions to the BioLife team. A strategic market segment for BioLife’s products ...
... commercialization of cellular immunotherapies. This article was authored by Aby J. Mathew, Ph.D., Chief Technology Officer, and Senior Application Scientists Brian Hawkins, Ph.D., and Alireza Abarazi, Ph.D., two recent additions to the BioLife team. A strategic market segment for BioLife’s products ...
Development
... There are no oogonia present in the adult female. The primary oocytes are arrested in prophase I and become quiescent until puberty. Cyclical changes in LH and FSH will trigger three or four primary oocytes to finish meiosis each uterine cycle. During the two meiotic divisions, all the cytoplasm wil ...
... There are no oogonia present in the adult female. The primary oocytes are arrested in prophase I and become quiescent until puberty. Cyclical changes in LH and FSH will trigger three or four primary oocytes to finish meiosis each uterine cycle. During the two meiotic divisions, all the cytoplasm wil ...
Chapter 21 - Genetic Development
... Problems Associated with Animal Cloning • In most nuclear transplantation studies, only a small percentage of cloned embryos have developed normally to birth • Many epigenetic changes, such as acetylation of histones or methylation of DNA, must be reversed in the nucleus from a donor animal in orde ...
... Problems Associated with Animal Cloning • In most nuclear transplantation studies, only a small percentage of cloned embryos have developed normally to birth • Many epigenetic changes, such as acetylation of histones or methylation of DNA, must be reversed in the nucleus from a donor animal in orde ...
Measuring the stiffness of bacterial cells from growth
... mechanically stable and may be polymerized with userdefined stiffness spanning the kPa to MPa regime (Figs S1 and S2), (iii) it is relatively transparent to the diffusion of ions, small molecules, secondary metabolites and metabolic waste, and gases, which is an important feature for maintaining nor ...
... mechanically stable and may be polymerized with userdefined stiffness spanning the kPa to MPa regime (Figs S1 and S2), (iii) it is relatively transparent to the diffusion of ions, small molecules, secondary metabolites and metabolic waste, and gases, which is an important feature for maintaining nor ...
The Plastidial 2-C-Methyl-D-Erythritol 4-Phosphate
... snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus) flowers produce both monoterpenoid (C10) and sesquiterpenoid (C15) volatiles that are derived from the MEP pathway (Dudareva et al., 2005). Thus, the extent to which transport of isoprenoid intermediates across the plastid envelope contributes to the biosynthesis of is ...
... snapdragon (Antirrhinum majus) flowers produce both monoterpenoid (C10) and sesquiterpenoid (C15) volatiles that are derived from the MEP pathway (Dudareva et al., 2005). Thus, the extent to which transport of isoprenoid intermediates across the plastid envelope contributes to the biosynthesis of is ...
video slide
... Problems Associated with Animal Cloning • In most nuclear transplantation studies, only a small percentage of cloned embryos have developed normally to birth • Many epigenetic changes, such as acetylation of histones or methylation of DNA, must be reversed in the nucleus from a donor animal in orde ...
... Problems Associated with Animal Cloning • In most nuclear transplantation studies, only a small percentage of cloned embryos have developed normally to birth • Many epigenetic changes, such as acetylation of histones or methylation of DNA, must be reversed in the nucleus from a donor animal in orde ...
Batteries (cells with spontaneous redox reactions)
... small for the deposition of metals, but often large (~1 V) for the evolution of gases. This explains why you can plate out Cr3+ and Ni2+, and produce Cl2(g) in the electrolysis of NaCl(aq), even though they have unfavorable half-cell potentials. ...
... small for the deposition of metals, but often large (~1 V) for the evolution of gases. This explains why you can plate out Cr3+ and Ni2+, and produce Cl2(g) in the electrolysis of NaCl(aq), even though they have unfavorable half-cell potentials. ...
Programmed cell death in plant development
... also be eliminated. In apomictic species, the fruits develop without fertilisation which means that the ovaries with ovules are retained forming fruit, while the other flower parts are eliminated. In parthenocarpic species that bear fruits without seeds, only walls of ovaries continue development. A ...
... also be eliminated. In apomictic species, the fruits develop without fertilisation which means that the ovaries with ovules are retained forming fruit, while the other flower parts are eliminated. In parthenocarpic species that bear fruits without seeds, only walls of ovaries continue development. A ...
ochromonas malhamensis
... fed E. coli showed no increase in acid hydrolase specific activity as compared to controls not fed E. coli. The latency of lysosomal acid hydrolases in cells fixed with glutaraldehyde was reduced, suggesting that this fixative increases lysosomal membrane permeability and may release enzymes or thei ...
... fed E. coli showed no increase in acid hydrolase specific activity as compared to controls not fed E. coli. The latency of lysosomal acid hydrolases in cells fixed with glutaraldehyde was reduced, suggesting that this fixative increases lysosomal membrane permeability and may release enzymes or thei ...
Clostridium sordellii Lethal-Toxin Autoprocessing and
... and gastrointestinal infections in livestock. One of the principle virulence factors is TcsL, a large protein toxin which glucosylates host GTPases to cause cytopathic and cytotoxic effects. TcsL has two enzymatic domains, an N-terminal glucosyltransferase domain (GTD) and an autoprocessing domain r ...
... and gastrointestinal infections in livestock. One of the principle virulence factors is TcsL, a large protein toxin which glucosylates host GTPases to cause cytopathic and cytotoxic effects. TcsL has two enzymatic domains, an N-terminal glucosyltransferase domain (GTD) and an autoprocessing domain r ...
DeadEnd Fluorometric TUNEL System Technical
... bodies that are readily phagocytosed and digested by macrophages or by neighboring cells without generating an inflammatory response. This is in contrast to the type of cell death known as necrosis, characterized by cell swelling, chromatin flocculation, loss of membrane integrity, cell lysis and ge ...
... bodies that are readily phagocytosed and digested by macrophages or by neighboring cells without generating an inflammatory response. This is in contrast to the type of cell death known as necrosis, characterized by cell swelling, chromatin flocculation, loss of membrane integrity, cell lysis and ge ...
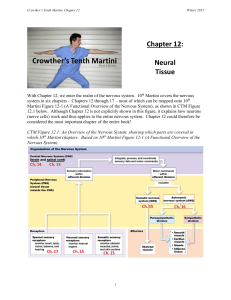
Chapter 12: Neural Tissue
... A “resting” neuron typically has a membrane potential of about -70 mV. When ions move into or out of a neuron, its membrane potential changes. Such changes transmit information through the nervous system. 12.3: Electrochemical gradients: which way will ions go? Each ion’s direction of movement ...
... A “resting” neuron typically has a membrane potential of about -70 mV. When ions move into or out of a neuron, its membrane potential changes. Such changes transmit information through the nervous system. 12.3: Electrochemical gradients: which way will ions go? Each ion’s direction of movement ...
PDF
... taxa with arthropods within Protostomia to the exclusion of vertebrates. Thus, if the urbilaterian was segmented, and assuming uniform average rates of divergence, it might be predicted that segmentation processes in annelids and arthropods would show greater similarity to each other than to those i ...
... taxa with arthropods within Protostomia to the exclusion of vertebrates. Thus, if the urbilaterian was segmented, and assuming uniform average rates of divergence, it might be predicted that segmentation processes in annelids and arthropods would show greater similarity to each other than to those i ...
White Paper: Backhaul Security for Wi-Fi and Small Cells
... for femtocells and public-access small cells. For example, Integration and coordination with the macro- and microcell layers as regards handover and provisioning is going to be very important for public-access small cells. And unlike in the femtocell environment, many operators are likely to want th ...
... for femtocells and public-access small cells. For example, Integration and coordination with the macro- and microcell layers as regards handover and provisioning is going to be very important for public-access small cells. And unlike in the femtocell environment, many operators are likely to want th ...
Identification and localization of a β‐COP‐like protein involved in the
... immunolocalized on the same membraneous structures as b-COP. Moreover, b-COP and other COPI antibodies stained the cell plate in dividing cells. It is further shown that, in maize root cells, and in contrast to observations upon mammalian cells, the drug Brefeldin A (BFA) does not induce the release ...
... immunolocalized on the same membraneous structures as b-COP. Moreover, b-COP and other COPI antibodies stained the cell plate in dividing cells. It is further shown that, in maize root cells, and in contrast to observations upon mammalian cells, the drug Brefeldin A (BFA) does not induce the release ...
Host B7x Promotes Pulmonary Metastasis of Breast Cancer
... mice on a BALB/c background and a syngeneic pulmonary metastasis model, 4T1, to explore the effect of tissue-expressed B7x on cancer metastasis. Like naive B7x2/2 mice on a 129 background (26), naive BALB/c B7x2/2 mice had no apparent phenotype and had normal numbers and distribution of immune cells ...
... mice on a BALB/c background and a syngeneic pulmonary metastasis model, 4T1, to explore the effect of tissue-expressed B7x on cancer metastasis. Like naive B7x2/2 mice on a 129 background (26), naive BALB/c B7x2/2 mice had no apparent phenotype and had normal numbers and distribution of immune cells ...
Small molecule intervention in microtubule
... (14), the depsipetide Phomopsin A (15) and d-24851 (16). As microtubule dynamics are of vital importance for all dividing cells, disruption of this process will affect both cancerous and normal cells alike; the increased rate of proliferation of cancer cells renders antimotic drugs 1 –8 useful and p ...
... (14), the depsipetide Phomopsin A (15) and d-24851 (16). As microtubule dynamics are of vital importance for all dividing cells, disruption of this process will affect both cancerous and normal cells alike; the increased rate of proliferation of cancer cells renders antimotic drugs 1 –8 useful and p ...
The role of c-myc in cellular growth control
... discontinuous, cells grow by continuously increasing synthesis of all their proteins and macromolecules. In general, DNA doubling and cell division are dependent on attainment of a critical growth rate in order to conserve cellular resources until daughter cell survival is assured. This principle wa ...
... discontinuous, cells grow by continuously increasing synthesis of all their proteins and macromolecules. In general, DNA doubling and cell division are dependent on attainment of a critical growth rate in order to conserve cellular resources until daughter cell survival is assured. This principle wa ...
Bio-engineered and native red blood cells from cord blood exhibit
... of RBCs a major medical challenge.1 We have recently developed a method to produce mature RBCs in vitro, starting from bone marrow, peripheral blood, leukapheresis or cord blood-derived CD34+ cells. This method is based on a 3-step protocol using a serum-free medium supplemented with cytokines.2 Her ...
... of RBCs a major medical challenge.1 We have recently developed a method to produce mature RBCs in vitro, starting from bone marrow, peripheral blood, leukapheresis or cord blood-derived CD34+ cells. This method is based on a 3-step protocol using a serum-free medium supplemented with cytokines.2 Her ...
Cell encapsulation

Cell microencapsulation technology involves immobilization of the cells within a polymeric semi-permeable membrane that permits the bidirectional diffusion of molecules such as the influx of oxygen, nutrients, growth factors etc. essential for cell metabolism and the outward diffusion of waste products and therapeutic proteins. At the same time, the semi-permeable nature of the membrane prevents immune cells and antibodies from destroying the encapsulated cells regarding them as foreign invaders.The main motive of cell encapsulation technology is to overcome the existing problem of graft rejection in tissue engineering applications and thus reduce the need for long-term use of immunosuppressive drugs after an organ transplant to control side effects.