Cell Reading 2 with lysosomes, golgi and vacuoles.rtf
... After billions of observations over hundreds of years, scientists concluded that all living things are made of cells. They also observed that single cells divided to produce two identical cells. These facts were tied together to form the CELL THEORY. a. All living things are made of cells. b. All ce ...
... After billions of observations over hundreds of years, scientists concluded that all living things are made of cells. They also observed that single cells divided to produce two identical cells. These facts were tied together to form the CELL THEORY. a. All living things are made of cells. b. All ce ...
Previous attempts to "grow" inner-ear hair cells in standard
... have worked poorly in part because necessary cues to develop hair bundles—a hallmark of sensory hair cells and a structure critically important for detecting auditory or vestibular signals—are lacking in the flat cell-culture dish. But, Dr. Hashino said, the team determined that the cells needed to ...
... have worked poorly in part because necessary cues to develop hair bundles—a hallmark of sensory hair cells and a structure critically important for detecting auditory or vestibular signals—are lacking in the flat cell-culture dish. But, Dr. Hashino said, the team determined that the cells needed to ...
013368718X_CH04_047
... The Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celled organisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life. Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, ...
... The Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celled organisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life. Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, ...
Mini-lesson on prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
... Chloroplasts and mitochondria • Evidence suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria were once bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship with cells that have a nucleus • Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own circular DNA that is not a part of the host’s genome. • Yes plants have both ...
... Chloroplasts and mitochondria • Evidence suggests that chloroplasts and mitochondria were once bacteria that developed a symbiotic relationship with cells that have a nucleus • Chloroplasts and mitochondria have their own circular DNA that is not a part of the host’s genome. • Yes plants have both ...
Homeostasis and Cells - science-b
... The Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celled organisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life. Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, ...
... The Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celled organisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life. Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, ...
Characteristics of Life
... • it can take in nutrients, convert these nutrients into energy, carry out specialized functions, and reproduce as necessary AND stores its own set of instructions for carrying out each of these activities. ...
... • it can take in nutrients, convert these nutrients into energy, carry out specialized functions, and reproduce as necessary AND stores its own set of instructions for carrying out each of these activities. ...
7.4 Homeostasis and Cells
... The Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celled organisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life. Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, ...
... The Cell as an Organism Sometimes a single cell is an organism. Single-celled organisms must be able to carry out all the functions necessary for life. Unicellular organisms maintain homeostasis, relatively constant internal conditions, by growing, responding to the environment, transforming energy, ...
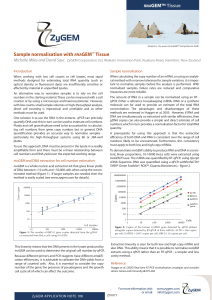
Sample normalisation with RNAGEM™ Tissue
... molecule can be used to provide an estimate of the total RNA concentration. The advantages and disadvantages of these methods are reviewed in Hugget et al. 2005. However, if RNA and DNA are simultaneously co-extracted with similar efficiencies, then gDNA copies can also provide a simple and direct e ...
... molecule can be used to provide an estimate of the total RNA concentration. The advantages and disadvantages of these methods are reviewed in Hugget et al. 2005. However, if RNA and DNA are simultaneously co-extracted with similar efficiencies, then gDNA copies can also provide a simple and direct e ...
Topic 1: Cell Biology
... more materials in and out • Large cell: less SA than smaller one • Large animals do not have large cells, just more cells. ...
... more materials in and out • Large cell: less SA than smaller one • Large animals do not have large cells, just more cells. ...
Cell Biology Lecture
... Eukaryotic Cells and Viruses • Q: Which have an outer membrane? • A: Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic ...
... Eukaryotic Cells and Viruses • Q: Which have an outer membrane? • A: Prokaryotic/Eukaryotic ...
The Cell
... and draw a diagram of the cells under • To prepare a slide from plant magnification tissue: ...
... and draw a diagram of the cells under • To prepare a slide from plant magnification tissue: ...
Cell Walls and Boundaries Cells protect themselves by their cell
... If the substance can cross the cell membrane, its particles will tend to move toward the area of less concentration until it is even or at a state of equilibrium ...
... If the substance can cross the cell membrane, its particles will tend to move toward the area of less concentration until it is even or at a state of equilibrium ...
Plant Tissues and Growth Worksheet Cs`)
... AW in the blank with the appropriate term from above. Terms may be used once, more than once or not at alt ...
... AW in the blank with the appropriate term from above. Terms may be used once, more than once or not at alt ...
Weekly Assignment #1
... Prokaryotic DNA is arranged in a circular “chromosome”. Eukaryotic DNA is arranged in linear, true chromosomes ...
... Prokaryotic DNA is arranged in a circular “chromosome”. Eukaryotic DNA is arranged in linear, true chromosomes ...
Week 2 Lecture Summarys copy
... - First 36 hours-fertilized ovum (now cell called zygote) makes the first cell division - cells continue to divide every 12-15hrs as it takes the 3 day trip down the fallopian tubes - once it is past the uterine cavity-the cell sheds its outer wall and becomes different layers (now called blastocyst ...
... - First 36 hours-fertilized ovum (now cell called zygote) makes the first cell division - cells continue to divide every 12-15hrs as it takes the 3 day trip down the fallopian tubes - once it is past the uterine cavity-the cell sheds its outer wall and becomes different layers (now called blastocyst ...
Site of haemopoiesis
... lymphoid progenitor cell and a common myeloid progenitor cell respectively. This haemopoietic stem cell is rare, perhaps 1 in every 20 million nucleated cells in bone marrow. Although its exact phenotype is unknown, on immunological testing it is CD34+ CD38- and has the appearance of a small or medi ...
... lymphoid progenitor cell and a common myeloid progenitor cell respectively. This haemopoietic stem cell is rare, perhaps 1 in every 20 million nucleated cells in bone marrow. Although its exact phenotype is unknown, on immunological testing it is CD34+ CD38- and has the appearance of a small or medi ...
Cell Study Guide - Miss Gleason`s Science
... Be able to identify the stages of mitosis. Be able to identify a centromere, a chromosome, a chromatid, a centriole, and spindle fibers in the stages of mitosis. Label the cell below: ...
... Be able to identify the stages of mitosis. Be able to identify a centromere, a chromosome, a chromatid, a centriole, and spindle fibers in the stages of mitosis. Label the cell below: ...
Transport Phenomena in Cell Biology - Thermal
... Diffusion dominates at short length scales, while active processes drive flow over larger length scales. ...
... Diffusion dominates at short length scales, while active processes drive flow over larger length scales. ...
Sample pages 2 PDF
... Organelles. Within the cytoplasm are mitochrondria (k), dictyosomes (Golgi bodies), microbodies, and microtubules (m). Microtubules are represented by an array of parallel tubular tracks and facilitate movement of proteins and organelles within the cell. The ER is a system of tubes and sacs, that wo ...
... Organelles. Within the cytoplasm are mitochrondria (k), dictyosomes (Golgi bodies), microbodies, and microtubules (m). Microtubules are represented by an array of parallel tubular tracks and facilitate movement of proteins and organelles within the cell. The ER is a system of tubes and sacs, that wo ...
Download PDF
... electric fields couple through intracellular signaling pathways to alter cell physiology. It is well known that electric fields used for DEP can not only stress cells via temperatures rises due to Joule heating of the culture media, but can also potentially directly interact with cells (e.g., via vo ...
... electric fields couple through intracellular signaling pathways to alter cell physiology. It is well known that electric fields used for DEP can not only stress cells via temperatures rises due to Joule heating of the culture media, but can also potentially directly interact with cells (e.g., via vo ...
Elodea PPT
... thought they looked like little rooms, called cells, that monks lived in at the monastery. In a book that he wrote in 1665, Robert Hooke was the first to describe the tiny units in the plants that he observed as cells. The word caught on and is still used today. ...
... thought they looked like little rooms, called cells, that monks lived in at the monastery. In a book that he wrote in 1665, Robert Hooke was the first to describe the tiny units in the plants that he observed as cells. The word caught on and is still used today. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.