Cell Structure and Function
... • Cyanobacteria closely related to chloroplasts in higher plants. ...
... • Cyanobacteria closely related to chloroplasts in higher plants. ...
Joanne Tracy “Innovation at the Cutting Edge of Academic Publishing”
... biological sciences. In this capacity, she is responsible for the overall strategic direction of the business, product development and acquisition, as well as the innovation processes. Cell Press is a recognized leader in innovation of the presentation of scientific literature, introducing new eleme ...
... biological sciences. In this capacity, she is responsible for the overall strategic direction of the business, product development and acquisition, as well as the innovation processes. Cell Press is a recognized leader in innovation of the presentation of scientific literature, introducing new eleme ...
Notes-Organelles - Svetz-wiki
... molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi apparatus from ER proteins are packaged and exported near membrane Jobs of the Golgi Apparat ...
... molecules made in the cell and used elsewhere -- front end (cis) faces the ER, and the back end (trans) faces the cell membrane --the folded stacks are called cisternae --unprocessed proteins enter the Golgi apparatus from ER proteins are packaged and exported near membrane Jobs of the Golgi Apparat ...
Cell Theory
... Cells taken from an organism often survive for a time, but smaller parts of an organism do not. Thus, cells are the smallest units of life that are capable of survival. ...
... Cells taken from an organism often survive for a time, but smaller parts of an organism do not. Thus, cells are the smallest units of life that are capable of survival. ...
Structure and Function of the Mitochondria - Room N
... Cells • In humans all of your mitochondria come from your mother • Have their own DNA ...
... Cells • In humans all of your mitochondria come from your mother • Have their own DNA ...
Name
... Which Cell Parts Can You See With the Microscope? Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what enter/exits a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell ...
... Which Cell Parts Can You See With the Microscope? Introduction: Living things are made of cells. All cells have parts that do certain jobs. Cells have an outer covering called the cell (plasma) membrane. The cell membrane controls what enter/exits a cell. The clear jellylike material inside the cell ...
Hemocyte Density and Differentiation in Apis mellifera Worker Bees
... Newly hatched worker bees were captured from four separate hives and chilled on ice for 15 minutes. Then 31 g sterile insulin syringes were prepared with 10μL of either insect ringer or E. coli in PBS. Bees were then immediately incubated at 34˚C for 2 hours Use of a stock of E.coli cultured in LB b ...
... Newly hatched worker bees were captured from four separate hives and chilled on ice for 15 minutes. Then 31 g sterile insulin syringes were prepared with 10μL of either insect ringer or E. coli in PBS. Bees were then immediately incubated at 34˚C for 2 hours Use of a stock of E.coli cultured in LB b ...
File
... All cells are classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus, while eukaryotic cell do. Only bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, all other organisms are eukaryotes. Prokaryotes also do not have the membrane bound organelles found in eukaryotes. Organelle ...
... All cells are classified as either prokaryotic or eukaryotic. Prokaryotic cells do not contain a nucleus, while eukaryotic cell do. Only bacteria and archaea are prokaryotes, all other organisms are eukaryotes. Prokaryotes also do not have the membrane bound organelles found in eukaryotes. Organelle ...
chas_112009_swaja
... Biofabrication – Plus and Minus Organs generated using patient’s stem cells – no host rejection issues. Organs can be tailored to patient’s specific characteristics. Capable of industrial-type production. It’s a big endeavor and it is going to take some time, but it will be worth the effort. ...
... Biofabrication – Plus and Minus Organs generated using patient’s stem cells – no host rejection issues. Organs can be tailored to patient’s specific characteristics. Capable of industrial-type production. It’s a big endeavor and it is going to take some time, but it will be worth the effort. ...
2 Cells A
... Bone marrow stem cells give rise to new blood cells. Embryonic stem cells give rise to any type of cells, including neurons (adults don’t have neural stem cells) and pancreatic cells (diabetics don’t have pancreatic stem cells). Stem cells are named by type + suffix: BLAST Erythrocyte = RBC. ...
... Bone marrow stem cells give rise to new blood cells. Embryonic stem cells give rise to any type of cells, including neurons (adults don’t have neural stem cells) and pancreatic cells (diabetics don’t have pancreatic stem cells). Stem cells are named by type + suffix: BLAST Erythrocyte = RBC. ...
Question Sheet
... Cells are the basic unit of all living things; all living things are made up of cells. The cell contains many specialised organelles each of which carry out a particular function. You will need to refer to these organelles throughout the 2 years of your course. Task A- Using the associated PDF file, ...
... Cells are the basic unit of all living things; all living things are made up of cells. The cell contains many specialised organelles each of which carry out a particular function. You will need to refer to these organelles throughout the 2 years of your course. Task A- Using the associated PDF file, ...
7.3 Structures and Organelles
... that are used for transport · most nuclei contain a small spherical area called a nucleolus (site where ribosomes are assembled form proteins and RNA) ...
... that are used for transport · most nuclei contain a small spherical area called a nucleolus (site where ribosomes are assembled form proteins and RNA) ...
Synthetic Biology: From Parts to Modules to Therapeutic Systems
... describe the implementation of genetic circuits and modules with finely-tuned digital and analog behavior and the use of artificial cell-cell communication to coordinate the behavior of cell populations. The first system to be presented is a genetic circuit that can detect and destroy specific cance ...
... describe the implementation of genetic circuits and modules with finely-tuned digital and analog behavior and the use of artificial cell-cell communication to coordinate the behavior of cell populations. The first system to be presented is a genetic circuit that can detect and destroy specific cance ...
Tour Of The Cell
... • What is the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus called? • The cytoplasm. This includes the organelles and the cytosol • The cytosol is the fluid medium found in the cytoplasm • The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often much larger than the corresponding volume ...
... • What is the space between the cell membrane and the nucleus called? • The cytoplasm. This includes the organelles and the cytosol • The cytosol is the fluid medium found in the cytoplasm • The volume enclosed by the plasma membrane of plant cells is often much larger than the corresponding volume ...
Unit 1 Lesson 3 - Epiphany Catholic School
... • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire alphabet on each strip • Make the first loop in the chain and tape it together • Now make a chain by threading the loops ...
... • Use scissors to cut out each strip • Use a pen or pencil to write the entire alphabet on each strip • Make the first loop in the chain and tape it together • Now make a chain by threading the loops ...
Other types of transport
... Cells also send material out of the cell in the same way. • When this happens, a vacuole fuses with the cell membrane and the contents are forced outside of the cell. • Both of these processes are types of active transport because they require energy ...
... Cells also send material out of the cell in the same way. • When this happens, a vacuole fuses with the cell membrane and the contents are forced outside of the cell. • Both of these processes are types of active transport because they require energy ...
Clonetics™ Lung Fibroblast Cell Systems
... exclusively, and the recommend protocols are followed. The performance of cells is not guaranteed if any modifications are made to the complete Cell System. Cryopreserved NHLF and DHLF are assured to be viable and functional when thawed and maintained properly. ...
... exclusively, and the recommend protocols are followed. The performance of cells is not guaranteed if any modifications are made to the complete Cell System. Cryopreserved NHLF and DHLF are assured to be viable and functional when thawed and maintained properly. ...
Notes - Endosymbiotic Theory
... The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells by endocytosis. This resulted in the first eukaryotic cells. First ...
... The endosymbiotic theory is the idea that a long time ago, prokaryotic cells engulfed other prokaryotic cells by endocytosis. This resulted in the first eukaryotic cells. First ...
7th Grade Geography Assessment Task 1
... Student will construct a 3-D model of a cell. By labeling each organelle, the student will identify its function. After researching the cell structure, students will make the model with organelles in appropriate size in relationship to each other. Concepts: What is the structure of a cell? Recogni ...
... Student will construct a 3-D model of a cell. By labeling each organelle, the student will identify its function. After researching the cell structure, students will make the model with organelles in appropriate size in relationship to each other. Concepts: What is the structure of a cell? Recogni ...
We investigated the role of GTP as inducer of differentiation in
... (myogenin and p21 dependent, respectively) followed by the expression of myosin heavy chain (MHC) proteins and cell fusion (Andres V. and Walsh K., JCB 132:657, 1996). In this study we investigated the role of extracellular 500M GTP during C2C12 differentiation. Our data indicate that the presence ...
... (myogenin and p21 dependent, respectively) followed by the expression of myosin heavy chain (MHC) proteins and cell fusion (Andres V. and Walsh K., JCB 132:657, 1996). In this study we investigated the role of extracellular 500M GTP during C2C12 differentiation. Our data indicate that the presence ...
Chapter 7_The Cell
... Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes (membrane-bound organelles). The nucleus is a distinct central organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA). Organelles are specialized structures that carry out specific cell functions. They enable cell functions ...
... Contain a nucleus and other organelles that are bound by membranes (membrane-bound organelles). The nucleus is a distinct central organelle that contains the cell’s genetic material (DNA). Organelles are specialized structures that carry out specific cell functions. They enable cell functions ...
White blood cells
... the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. ...
... the process by which a less specialized cell becomes a more specialized cell type. ...
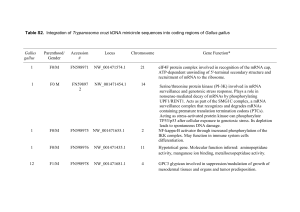
Table S2. Integration of Trypanosoma cruzi kDNA minicircle
... activity, manganese ion binding, metalloexopeptidase activity. ...
... activity, manganese ion binding, metalloexopeptidase activity. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.