Presentation 4 – Application Example – Can breast cancer be cured
... to become specialised according to the tissue that they make up • A healthy cell performs the correct functions according to its type and specialised state • This feature of cells is controlled by our DNA ...
... to become specialised according to the tissue that they make up • A healthy cell performs the correct functions according to its type and specialised state • This feature of cells is controlled by our DNA ...
Describing Matter & Energy
... New organisms result from the combination of genetic material from 2 parent organisms The traits are determined by genetic material from both the male and female parents Genetic material is re-sorted, over and over, each time reproduction occurs this is why you resemble your parents more than your ...
... New organisms result from the combination of genetic material from 2 parent organisms The traits are determined by genetic material from both the male and female parents Genetic material is re-sorted, over and over, each time reproduction occurs this is why you resemble your parents more than your ...
Cell Unit
... protists live in moist surroundings. In general, the protist kingdom includes organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane and who do not fit into the other kingdoms. ...
... protists live in moist surroundings. In general, the protist kingdom includes organisms whose cells have a nucleus enclosed by a membrane and who do not fit into the other kingdoms. ...
Leukocytes (White Blood Cells)
... Monocytes are immature cells while still in the blood and have little ability to fight infectious agents at that time. However, once they enter the tissues, they mature into macrophages, and they are extremely capable of combating disease agents in the tissues. Monocyte ...
... Monocytes are immature cells while still in the blood and have little ability to fight infectious agents at that time. However, once they enter the tissues, they mature into macrophages, and they are extremely capable of combating disease agents in the tissues. Monocyte ...
Ch 3 Cell Size and Scientists
... How about your big toe? How about a drop of blood? Can we just keep dividing things into smaller and smaller parts, or is there a point at which what’s left is no longer alive? As you will see, there is such a limit, the smallest living unit of any organism is- the cell. The average life span for a ...
... How about your big toe? How about a drop of blood? Can we just keep dividing things into smaller and smaller parts, or is there a point at which what’s left is no longer alive? As you will see, there is such a limit, the smallest living unit of any organism is- the cell. The average life span for a ...
organelle notes
... Cell walls are like our classroom walls. They protect what is inside and help give structure to the physical shape of the room. ...
... Cell walls are like our classroom walls. They protect what is inside and help give structure to the physical shape of the room. ...
Chapter 6: A Tour of the Cell The Cell Theory • All living organisms
... o Have membrane-bound organelles o Cytoplasm – region b/w plasma membrane & nucleus Cytosol – liquid outside organelles o Generally much larger than prokaryotic cells (1-5 vs 10-100 micrometer) Cell Parts Plasma Membrane o Selective barrier allowing passage of oxygen, nutrients, & waste o Genera ...
... o Have membrane-bound organelles o Cytoplasm – region b/w plasma membrane & nucleus Cytosol – liquid outside organelles o Generally much larger than prokaryotic cells (1-5 vs 10-100 micrometer) Cell Parts Plasma Membrane o Selective barrier allowing passage of oxygen, nutrients, & waste o Genera ...
Cell Organelle Notes A. Cell Wall
... N. Vacuoles 1. Saclike structure that stores water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates 2. Plant cells—single, large, central, fluid— turgor pressure a. Small Vacuoles are called Vesicles • used for transporting substances in the cell ...
... N. Vacuoles 1. Saclike structure that stores water, salts, proteins, carbohydrates 2. Plant cells—single, large, central, fluid— turgor pressure a. Small Vacuoles are called Vesicles • used for transporting substances in the cell ...
Name - Mrs. Glazebrook
... tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of biology. The cell theory has three major principles: • All organisms are made of cells. • All exist ...
... tiny cells. Most cells are so small that they cannot be seen without a microscope. The discoveries of scientists from the 1600s through the 1800s led to the cell theory, which is a unifying concept of biology. The cell theory has three major principles: • All organisms are made of cells. • All exist ...
cell slide show 2015
... The largest organelle in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is usually the nucleus, a structure that directs all the activities of the cell. ...
... The largest organelle in the cytoplasm of a eukaryotic cell is usually the nucleus, a structure that directs all the activities of the cell. ...
cell structure and function 2010
... where ribosomes are constructed. • It is not membrane bound • It is rich is proteins and nucleic acids, so it appears darker. • There may be more than one nucleolus ...
... where ribosomes are constructed. • It is not membrane bound • It is rich is proteins and nucleic acids, so it appears darker. • There may be more than one nucleolus ...
cell structure packet
... 4. The cell wall is what makes plants __________. 5. List three important things that can pass through the cell wall of a plant. 6. Besides a plant, what other kind of cell has a cell wall? ...
... 4. The cell wall is what makes plants __________. 5. List three important things that can pass through the cell wall of a plant. 6. Besides a plant, what other kind of cell has a cell wall? ...
What is the Concentration of my Solution
... • It’s easier to mass the balloons in the bowl….so mass the bowl by itself first, then subtract the weight of the bowl from the bowl/balloon mass 2. Compare the mass of what the cell used to be and what it is now. Document how much it changed (for instance, -5 grams means it shrunk by 5 grams, lost ...
... • It’s easier to mass the balloons in the bowl….so mass the bowl by itself first, then subtract the weight of the bowl from the bowl/balloon mass 2. Compare the mass of what the cell used to be and what it is now. Document how much it changed (for instance, -5 grams means it shrunk by 5 grams, lost ...
Plant Cells and Tissues, Part 2
... have thick primary cell walls, and are covered on their outer surface by a special cuticle with an outer waxy layer. The cells are tightly interlocked in different patterns. ...
... have thick primary cell walls, and are covered on their outer surface by a special cuticle with an outer waxy layer. The cells are tightly interlocked in different patterns. ...
Looking Inside Cells
... down certain materials in the cell – some chemicals break down large food particles into smaller ones. They also break down old cell parts and release the substances so they can be used again ...
... down certain materials in the cell – some chemicals break down large food particles into smaller ones. They also break down old cell parts and release the substances so they can be used again ...
Cell Structure
... Cell Structure Analysis of the functional interrelationships of cell structures ...
... Cell Structure Analysis of the functional interrelationships of cell structures ...
Cells - World of Teaching
... They get their names from their size. One unit is larger than than the other so they are called large and small subunits. Both these subunits are necessary for protein synthesis in the cell. When the two units are docked together with a special information unit called messenger RNA, they make protei ...
... They get their names from their size. One unit is larger than than the other so they are called large and small subunits. Both these subunits are necessary for protein synthesis in the cell. When the two units are docked together with a special information unit called messenger RNA, they make protei ...
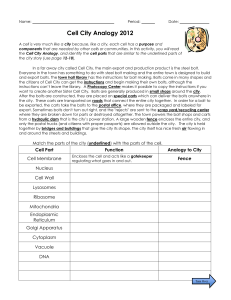
Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
... Cell City Analogy 2012 A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city s ...
Chapter 2 – Chromosomes and Sexual
... – Single, circular chromosome • May have small, accessory plasmids ...
... – Single, circular chromosome • May have small, accessory plasmids ...
Cell Cycle Check
... 1) Identify the stage of the cell cycle for each diagram using the words in the word bank. 2) Place a * next to each stage of mitosis. (0.5 pts each) 3) Sequence the stages. (1 pt each) ...
... 1) Identify the stage of the cell cycle for each diagram using the words in the word bank. 2) Place a * next to each stage of mitosis. (0.5 pts each) 3) Sequence the stages. (1 pt each) ...
Mitosis
... The life of a cell is divided into three stages known as the cell cycle: 1. Interphase: cell carries out normal functions and prepares to divide 2. Mitosis: nucleus divides splits into two 3. Cytokinesis: cell and contents divide into two daughter cells. ...
... The life of a cell is divided into three stages known as the cell cycle: 1. Interphase: cell carries out normal functions and prepares to divide 2. Mitosis: nucleus divides splits into two 3. Cytokinesis: cell and contents divide into two daughter cells. ...
Biology 12 Membrane Notes File
... o Selectively permeable = a living membrane that can use energy to select molecules (even if they are too big or the concentration gradient is going in the opposite direction) ...
... o Selectively permeable = a living membrane that can use energy to select molecules (even if they are too big or the concentration gradient is going in the opposite direction) ...
Presentazione di PowerPoint
... In this model, the skin, the muscles and parts of the thoracic wall have been removed in order to make the internal organs visible. The diaphragm subdivides our model in two cavities. In the upper zone, we find the thoracic cavity, in the lower zone lies the abdominal cavity. Now, have a look at the ...
... In this model, the skin, the muscles and parts of the thoracic wall have been removed in order to make the internal organs visible. The diaphragm subdivides our model in two cavities. In the upper zone, we find the thoracic cavity, in the lower zone lies the abdominal cavity. Now, have a look at the ...
The Cell
... The golgi apparatus also ensures that the completed proteins go to the appropriate area of the cell. (that proteins for the cell membrane get to the membrane, proteins hormones exit the cell etc.) ...
... The golgi apparatus also ensures that the completed proteins go to the appropriate area of the cell. (that proteins for the cell membrane get to the membrane, proteins hormones exit the cell etc.) ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.