Specialized Cells
... The cells of fungi are similar to plant cells. They have a nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes and mitochondria. While fungi do have a cell wall, it is made of chitin, a different type of carbohydrate from cellulose. They are however not green – they don’t photosynthesize and so don’t contain chloroplast ...
... The cells of fungi are similar to plant cells. They have a nucleus, cytoplasm, ribosomes and mitochondria. While fungi do have a cell wall, it is made of chitin, a different type of carbohydrate from cellulose. They are however not green – they don’t photosynthesize and so don’t contain chloroplast ...
Cell-tastic Drama
... create pores which will allow the oxygen and nutrients into the cell. The mitochondria will use these nutrients and oxygen to create energy in the cell and some of them will be sent back out of the cell as carbon dioxide. The lysosomes will be busy breaking up parts of the cell which are worn out fo ...
... create pores which will allow the oxygen and nutrients into the cell. The mitochondria will use these nutrients and oxygen to create energy in the cell and some of them will be sent back out of the cell as carbon dioxide. The lysosomes will be busy breaking up parts of the cell which are worn out fo ...
Group 3
... to low concentration) 1 Factor that controls osmosis: concentration gradient-unequal distribution of particles #3: water diffusing across a selectively permeable membrane the number of sugar molecules did not change on each side of the membrane but the number of water molecules on either side did ch ...
... to low concentration) 1 Factor that controls osmosis: concentration gradient-unequal distribution of particles #3: water diffusing across a selectively permeable membrane the number of sugar molecules did not change on each side of the membrane but the number of water molecules on either side did ch ...
CELLS: THE BASIC UNIT OF LIFE
... Scientists believe that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as a prokaryotic cell that was “eaten” by larger cells. They ended up surviving inside. ...
... Scientists believe that mitochondria and chloroplasts originated as a prokaryotic cell that was “eaten” by larger cells. They ended up surviving inside. ...
iPSC - Coriell Cell Repositories
... 2. Transfer cell suspension into sterile 15ml conical containing warm culture medium and gently mix cells. 3. Centrifuge conical tube containing cells at 228 ± 24 g for 2 min at room temperature. 4. Aspirate supernatant and g e n t l y r e s u s p e n d cells into 2 ml of warm culture medium ...
... 2. Transfer cell suspension into sterile 15ml conical containing warm culture medium and gently mix cells. 3. Centrifuge conical tube containing cells at 228 ± 24 g for 2 min at room temperature. 4. Aspirate supernatant and g e n t l y r e s u s p e n d cells into 2 ml of warm culture medium ...
The Cell In Its Environment Slide Show Notes
... • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that ente ...
... • Cells have structures that protect their contents from the world outside. • All cells are surrounded by a cell membrane that separates the cell from the outside environment. • The cell membrane is selectively permeable, which lets some things enter and leave the cell. • Name 3 substances that ente ...
SAMPLE – 90 Minute Block Agenda
... functions in living cells. (a) Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. ...
... functions in living cells. (a) Explain the role of cell organelles for both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, including the cell membrane, in maintaining homeostasis and cell reproduction. ...
Stem Cells and Meristems - Smithycroft Secondary School
... Meristems in plants • Plants continue to grow throughout life • New cells are produced at meristems • This allows growth to take place • Tips of shoots and roots • Some unspecialised cells continue to divide • Others develop into specialised cells ...
... Meristems in plants • Plants continue to grow throughout life • New cells are produced at meristems • This allows growth to take place • Tips of shoots and roots • Some unspecialised cells continue to divide • Others develop into specialised cells ...
Section: 2.3 Name: Question of the Day
... contains the __________________, which is a gelatin-like aqueous fluid. The cytoplasm contains multiple cell parts known as ____________________________. Organelle means “little organ”, and similar to the organs in your body, they work together to aid in the survival of the cell. Each organelle has ...
... contains the __________________, which is a gelatin-like aqueous fluid. The cytoplasm contains multiple cell parts known as ____________________________. Organelle means “little organ”, and similar to the organs in your body, they work together to aid in the survival of the cell. Each organelle has ...
Plant cell Lab Instructions
... Obtain ONE leaf from the aquatic Elodea plant. Prepare a wet mount using water only (no stain is needed since it is already green). Focus with scanning objective (4x red). Switch to Low Power (10x yellow), resolve focus. Switch to High Power (40x blue), resolve focus. Note the small green circular o ...
... Obtain ONE leaf from the aquatic Elodea plant. Prepare a wet mount using water only (no stain is needed since it is already green). Focus with scanning objective (4x red). Switch to Low Power (10x yellow), resolve focus. Switch to High Power (40x blue), resolve focus. Note the small green circular o ...
Cell Theory Reading
... biological thought: what could be the minimal unit carrying the potential for life? The cell theory Hints at the idea that the cell is the basic component of living organisms emerged well before 1838–39, which was when the cell theory was officially formulated. Cells were not seen as undifferentiate ...
... biological thought: what could be the minimal unit carrying the potential for life? The cell theory Hints at the idea that the cell is the basic component of living organisms emerged well before 1838–39, which was when the cell theory was officially formulated. Cells were not seen as undifferentiate ...
In the space at the left, write true if the statement is true
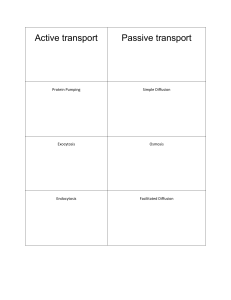
... 4. _____________________ Pinocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which liquid droplets are taken into a cell. 5. _____________________ Diffusion does occur when a system is at equilibrium. 6. _____________________ Facilitated diffusion is the process of passive transport in which proteins aid the pa ...
... 4. _____________________ Pinocytosis is a form of endocytosis in which liquid droplets are taken into a cell. 5. _____________________ Diffusion does occur when a system is at equilibrium. 6. _____________________ Facilitated diffusion is the process of passive transport in which proteins aid the pa ...
Cell Theory Reading
... biological thought: what could be the minimal unit carrying the potential for life? The cell theory Hints at the idea that the cell is the basic component of living organisms emerged well before 1838–39, which was when the cell theory was officially formulated. Cells were not seen as undifferentiate ...
... biological thought: what could be the minimal unit carrying the potential for life? The cell theory Hints at the idea that the cell is the basic component of living organisms emerged well before 1838–39, which was when the cell theory was officially formulated. Cells were not seen as undifferentiate ...
Science Grade 7 Date: March 21, 2014 ET Cells obtain energy t
... MOLECULAR BASIS OF LIFE - Compare life processes (e.g. growth, digestion) at the organism level with life processes at the cellular level. ...
... MOLECULAR BASIS OF LIFE - Compare life processes (e.g. growth, digestion) at the organism level with life processes at the cellular level. ...
Handout 37 - Plant Cell Diagram
... vacuole. A vacuole is the ____________ ___________ of the cell. Vacuoles store __________ and other materials by the cell. They can also store __________ products. Most of the plant’s ______________ is stored in vacuoles to keep the plant firm. Without it, the plant would wilt. Find the vacuole (I) ...
... vacuole. A vacuole is the ____________ ___________ of the cell. Vacuoles store __________ and other materials by the cell. They can also store __________ products. Most of the plant’s ______________ is stored in vacuoles to keep the plant firm. Without it, the plant would wilt. Find the vacuole (I) ...
Cell Analogy Project - Bismarck Public Schools
... Cell Analogy Project: Name:_________________________________________________Period:_____Date:__________________ Purpose: To relate the structures and functions of an animal or plant cell to another model to create an association of the functions. Procedure: 1. First brainstorm what topic your group ...
... Cell Analogy Project: Name:_________________________________________________Period:_____Date:__________________ Purpose: To relate the structures and functions of an animal or plant cell to another model to create an association of the functions. Procedure: 1. First brainstorm what topic your group ...
Cell
... any type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can g ...
... any type of cell, it is not specialised • All animal cells originate from embryo stem cells. During the development of an embryo, most of these cells become specialised. They cannot later change to become a different type of cell. This process is called cell differentiation. • Adult stem cells can g ...
Chapter 7 1. ______ is a selectively permeable
... ______________ fatty acid tails will make them more viscous. ____________ will also help with stability. 5. Short carbohydrates bound to lipids are called ____________ while short carbohydrates bound to proteins are called _____________. These carbohydrates cover the surface of cells and help mediat ...
... ______________ fatty acid tails will make them more viscous. ____________ will also help with stability. 5. Short carbohydrates bound to lipids are called ____________ while short carbohydrates bound to proteins are called _____________. These carbohydrates cover the surface of cells and help mediat ...
Chapter Review
... alveoli, as tiny sacs surrounded by tiny blood vessels, includes the cells that make up the tissue of the alveoli and the tissue that joins the alveoli to the bronchioles, which are part of the lung.The lungs are made of several kinds of tissue, such as the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. Sample ...
... alveoli, as tiny sacs surrounded by tiny blood vessels, includes the cells that make up the tissue of the alveoli and the tissue that joins the alveoli to the bronchioles, which are part of the lung.The lungs are made of several kinds of tissue, such as the bronchi, bronchioles, and alveoli. Sample ...
Cells: Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
... pushes or pulls cell through water Made up of protein “tubulin” can be single, or a pair Moves back and forth like a whip ...
... pushes or pulls cell through water Made up of protein “tubulin” can be single, or a pair Moves back and forth like a whip ...
L to J PowerPoint
... cells divide to form sperm cells in a male and egg cells in a female – only occurs in reproductive cells MEIOSIS ...
... cells divide to form sperm cells in a male and egg cells in a female – only occurs in reproductive cells MEIOSIS ...
ZOOMING DOWN THE TREE OF LIFE TO LIFE`S BUILDING BLOCKS
... You have found carbohydrates in maple syrup, in the tree trunk, and in green leaves. What do they all have in common? What makes them similar and what makes them different from the other groups of macromolecules in a living cell? ...
... You have found carbohydrates in maple syrup, in the tree trunk, and in green leaves. What do they all have in common? What makes them similar and what makes them different from the other groups of macromolecules in a living cell? ...
Chapter 4 Section 1 Worksheet
... 13. During ___________________ (phase 4) the cell begins to divide into two cells. Close to the equator of the cell, the cell begins to “pinch inward. This area is called the cleavage furrow. This is the location where new cell membranes will be forming for each cell. Now mitosis has completed and w ...
... 13. During ___________________ (phase 4) the cell begins to divide into two cells. Close to the equator of the cell, the cell begins to “pinch inward. This area is called the cleavage furrow. This is the location where new cell membranes will be forming for each cell. Now mitosis has completed and w ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.