Cell Transport Review Sheet
... in which the cell does not need to use any energy. 5. During active transport molecules move from an area of ___________ concentration to an area of ____________ concentration. 6. ________________ is a form of active transport in which the cell sends materials out of the cell using vesicles, small s ...
... in which the cell does not need to use any energy. 5. During active transport molecules move from an area of ___________ concentration to an area of ____________ concentration. 6. ________________ is a form of active transport in which the cell sends materials out of the cell using vesicles, small s ...
Lesson 2: Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (1
... Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions where as prokaryotic cells are usually smaller and microscopic in size. Eukaryotic cells are larger; however, both have cytoplasm. A prokaryotic lacks a nucleus; while a eukaryotic cell has a membrane-bound nucleus and so ...
... Eukaryotic cells have internal membranes that compartmentalize their functions where as prokaryotic cells are usually smaller and microscopic in size. Eukaryotic cells are larger; however, both have cytoplasm. A prokaryotic lacks a nucleus; while a eukaryotic cell has a membrane-bound nucleus and so ...
Chapter 3: Cell
... • Genes: The Blueprint for Protein Structure • gene is defined as a DNA segment that carries the information for building one protein or polypeptide chain. • Proteins are key substances for all aspects of cell life. • enzymes, biological catalysts that regulate chemical reactions in the cells, are f ...
... • Genes: The Blueprint for Protein Structure • gene is defined as a DNA segment that carries the information for building one protein or polypeptide chain. • Proteins are key substances for all aspects of cell life. • enzymes, biological catalysts that regulate chemical reactions in the cells, are f ...
What a Cells Do
... Active Transport is the process in which a cell actively goes after and takes in food molecules. Unlike passive transport (diffusion, osmosis), active transport is purposeful and active, it does require energy on part of the cell. Cell Growth and Division Cells, like every other living thing, grow. ...
... Active Transport is the process in which a cell actively goes after and takes in food molecules. Unlike passive transport (diffusion, osmosis), active transport is purposeful and active, it does require energy on part of the cell. Cell Growth and Division Cells, like every other living thing, grow. ...
Mitosis Notes
... CELL DIVISION • 1 cell ÷ into 2 identical daughter cells (same genetic info) • Eukaryotes (cells w/ nucleus) go through 2 stages of ÷ • Mitosis – ÷ of nucleus – Cytokinesis – ÷ of cytoplasm ...
... CELL DIVISION • 1 cell ÷ into 2 identical daughter cells (same genetic info) • Eukaryotes (cells w/ nucleus) go through 2 stages of ÷ • Mitosis – ÷ of nucleus – Cytokinesis – ÷ of cytoplasm ...
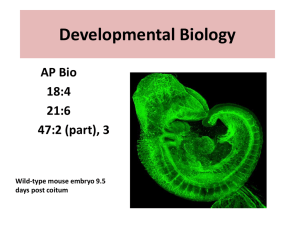
Developmental Biology
... types in a multicellular organism • During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types • Cell types are organized successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism ...
... types in a multicellular organism • During embryonic development, a fertilized egg gives rise to many different cell types • Cell types are organized successively into tissues, organs, organ systems, and the whole organism ...
File
... Sporulation in bacteria is not a means of reproduction. This process does not increase the number of cells. ...
... Sporulation in bacteria is not a means of reproduction. This process does not increase the number of cells. ...
Name: Date: _ Period: ___ Critical Thinking Questions – Honors
... higher salt concentration within the cell, to retain the water within it and not diffuse quickly. Without these adaptations, the cell will become plasmolyzed. Protists in a changing salt concentration will have a semi-permeable membrane in order to keep up with fluctuations in concentration and take ...
... higher salt concentration within the cell, to retain the water within it and not diffuse quickly. Without these adaptations, the cell will become plasmolyzed. Protists in a changing salt concentration will have a semi-permeable membrane in order to keep up with fluctuations in concentration and take ...
BIOFE (Biology OFE)
... Please describe the following two organelles below and answer the questions 1) Name each organelle? Can you name more… 2) Which organelle is only in plants? 3) Which organelle is found more in animal cells? 4) What goes into and out of #1 during photosynthesis? 5) What goes into and out of #2 during ...
... Please describe the following two organelles below and answer the questions 1) Name each organelle? Can you name more… 2) Which organelle is only in plants? 3) Which organelle is found more in animal cells? 4) What goes into and out of #1 during photosynthesis? 5) What goes into and out of #2 during ...
Plants and Animals
... • We interact with plants and animals more often than other types of cells • These two cells are similar to each other but very different from prokaryotes ...
... • We interact with plants and animals more often than other types of cells • These two cells are similar to each other but very different from prokaryotes ...
The Cell Theory - Cardinal Newman
... “All cells are from other pre-existing cells.” Discovered while researching cancer cells. ...
... “All cells are from other pre-existing cells.” Discovered while researching cancer cells. ...
Directed Reading 18.3 - Blair Community Schools
... 5. In the three-domain system, two domains have ______________________ cell structure. 6. The most abundant kind of organism on Earth are the ______________________. 7. Archeans that live in hot springs that exceed 100oC are called ______________________. Complete each statement by underlining the c ...
... 5. In the three-domain system, two domains have ______________________ cell structure. 6. The most abundant kind of organism on Earth are the ______________________. 7. Archeans that live in hot springs that exceed 100oC are called ______________________. Complete each statement by underlining the c ...
Cell Analogy Project - Warren Hills Regional School District
... Name___________________________________Block_______Date________ The Cell as a _____________________________________________________ ...
... Name___________________________________Block_______Date________ The Cell as a _____________________________________________________ ...
cells - Teacherpage
... Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes – CONTAIN A NUCLEUS, cell membrane, cytoplasm – Generally larger and more complex – Contains membrane bound organelles (internal membranes) – Genetic material found in nucleus – Examples: plants, animals, fungi, and protists ...
... Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes • Eukaryotes – CONTAIN A NUCLEUS, cell membrane, cytoplasm – Generally larger and more complex – Contains membrane bound organelles (internal membranes) – Genetic material found in nucleus – Examples: plants, animals, fungi, and protists ...
Tour of Cell Organelles
... Viruses are NOT composed of cells. But they do contain genetic material (DNA and/or RNA). They also can reproduce in the presence of a host cell. Some cell parts (mitochondria and chloroplast) contain their own genetic material (DNA and/or RNA) and can reproduce in a cell. ...
... Viruses are NOT composed of cells. But they do contain genetic material (DNA and/or RNA). They also can reproduce in the presence of a host cell. Some cell parts (mitochondria and chloroplast) contain their own genetic material (DNA and/or RNA) and can reproduce in a cell. ...
Cell City - We Heart Science
... to apply knowledge of central dogma, and osmosis. Shows evidence of understanding of differences between eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and viruses. Report is typed or neatly written. Minimal grammar and spelling errors. For extra credit a design is drawn neatly with all structures labeled, ...
... to apply knowledge of central dogma, and osmosis. Shows evidence of understanding of differences between eukaryotic cells, prokaryotic cells, and viruses. Report is typed or neatly written. Minimal grammar and spelling errors. For extra credit a design is drawn neatly with all structures labeled, ...
me239 mechanics of the cell 1.2 introduction to the cell 1.2
... the cytoskeleton actin filaments are 7nm in diameter and consist of two intertwined actin chains. they are tension bearing members of the cell. being located close to the cell membrane, they are responsible for inter- and intracellular transduction. together with myosin, they from the contraction ap ...
... the cytoskeleton actin filaments are 7nm in diameter and consist of two intertwined actin chains. they are tension bearing members of the cell. being located close to the cell membrane, they are responsible for inter- and intracellular transduction. together with myosin, they from the contraction ap ...
NC-3000™ Cell Cycle Assays
... – For rapid measurement of G1/G0, S and G2/M cell cycle phases The cell cycle represents the most fundamental and important process in eukaryotic cells and is an ordered set of events, culminating in cell growth and division into two daughter cells. In a given population, cells will be distributed a ...
... – For rapid measurement of G1/G0, S and G2/M cell cycle phases The cell cycle represents the most fundamental and important process in eukaryotic cells and is an ordered set of events, culminating in cell growth and division into two daughter cells. In a given population, cells will be distributed a ...
- Smart Science
... Inform the students that, as they are animals, their cheek cells are a type of animal cell. Ask them to refer back to the drawing of their cheek cells that they made last lesson. They work in pairs and use page 14 of the Student’s Book to discuss what parts of the cell they can see on their drawings ...
... Inform the students that, as they are animals, their cheek cells are a type of animal cell. Ask them to refer back to the drawing of their cheek cells that they made last lesson. They work in pairs and use page 14 of the Student’s Book to discuss what parts of the cell they can see on their drawings ...
Virtual Cell Worksheet
... 4. Mitochondrion is thepowerhouse of the cell. It is the site of respiration. It has a double membrane. The inner membrane is where most aerobic respiration occurs. The inner membrane is ruffled with a very large surface area. These ruffles are calledcristae. Mitochondria have their own DNA and manu ...
... 4. Mitochondrion is thepowerhouse of the cell. It is the site of respiration. It has a double membrane. The inner membrane is where most aerobic respiration occurs. The inner membrane is ruffled with a very large surface area. These ruffles are calledcristae. Mitochondria have their own DNA and manu ...
Cell and Organelle
... Students will form a small group according to their learning styles. Visual and verbal learners: Students will draw the cell and organelles. They will use different colors to distinguish one from another. From the presentation given, the students will identify the functions of the cell parts. Active ...
... Students will form a small group according to their learning styles. Visual and verbal learners: Students will draw the cell and organelles. They will use different colors to distinguish one from another. From the presentation given, the students will identify the functions of the cell parts. Active ...
Exporter la page en pdf
... Anthracyclines such as doxorubicin are used extensively in the treatment of cancers. Anthraquinone-related angucyclines also exhibit antiproliferative properties and have been proposed to operate via similar mechanisms, including direct genome targeting. Here, we report the chemical synthesis of mar ...
... Anthracyclines such as doxorubicin are used extensively in the treatment of cancers. Anthraquinone-related angucyclines also exhibit antiproliferative properties and have been proposed to operate via similar mechanisms, including direct genome targeting. Here, we report the chemical synthesis of mar ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.