Lab 5
... At this point in your pursuit of biological understanding, it should be clear that the most fundamental unit of life is the cell (see image of white and red blood cells to the right). While you may also be at a point where you are beginning to appreciate the sheer diversity of living things, it may ...
... At this point in your pursuit of biological understanding, it should be clear that the most fundamental unit of life is the cell (see image of white and red blood cells to the right). While you may also be at a point where you are beginning to appreciate the sheer diversity of living things, it may ...
• Outline the Cell Theory. • Discuss possible exceptions to the cell
... • 2.1.4 Compare the relative sizes of molecules, cell membrane thickness, viruses, bacteria, organelles, and cells using the appropriate SI unit • 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification. • 2.1.6 Explain the importance of ...
... • 2.1.4 Compare the relative sizes of molecules, cell membrane thickness, viruses, bacteria, organelles, and cells using the appropriate SI unit • 2.1.5 Calculate the linear magnification of drawings and the actual size of specimens in images of known magnification. • 2.1.6 Explain the importance of ...
Mitosis – PowerPoint
... organism in one way or another. Each diploid (2n) daughter cell is genetically identical to the diploid (2n) parent cell. Meiosis is cell division in the ovaries of the female and testes of the male and involves the formation of egg and sperm cells, respectively. Each diploid (2n) parent cell prod ...
... organism in one way or another. Each diploid (2n) daughter cell is genetically identical to the diploid (2n) parent cell. Meiosis is cell division in the ovaries of the female and testes of the male and involves the formation of egg and sperm cells, respectively. Each diploid (2n) parent cell prod ...
Cell cycle and Mitosis
... kinases move the cell onto the next stage of the cell cycle Kinases bind to proteins called cyclins forming a CDK complex. (cyclin dependent kinase complex) They phosphorylate a checkpoint protein which activates it and allows the cell cycle to move on. ...
... kinases move the cell onto the next stage of the cell cycle Kinases bind to proteins called cyclins forming a CDK complex. (cyclin dependent kinase complex) They phosphorylate a checkpoint protein which activates it and allows the cell cycle to move on. ...
Plant and Animal Cells!
... A cell is the basic building block of life. Your school is built from bricks but your body is built from cells. Every living thing, or organism, is mode of cells. ...
... A cell is the basic building block of life. Your school is built from bricks but your body is built from cells. Every living thing, or organism, is mode of cells. ...
Chapt 7 Cell Structure
... 7. Cell Theory – The theory that explains the relationship between cells and living things is called the cell theory. The cell theory states: (1) All living things are made from one or more cells. (2) Cells come only from other cells that already exist. (3) All of an organism’s life functions occur ...
... 7. Cell Theory – The theory that explains the relationship between cells and living things is called the cell theory. The cell theory states: (1) All living things are made from one or more cells. (2) Cells come only from other cells that already exist. (3) All of an organism’s life functions occur ...
H - Midland ISD
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
Microscopes
... 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
... 2. Cells are the basic units of structure and function in living things. 3. New cells are produced from existing cells. ...
Document
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
... To be closely related means the amino acid composition should be almost the same, since that is what the DNA is coding. Between Q and T, only 4 levels are the same – Between R and S only 4 levels are the same – Between Q and S 5 of the levels are the same, but – Between Q and R 5 of the lev ...
Biotechnology and Genetic Engineering-PBIO 450
... With B. subtilis and some others, it is possible to induce secretion of a gene product into the surrounding medium. This method is in use in the pharmaceutical industry in the production of hormones such as insulin and human growth hormone. Disadvantages of bacterial cells The expressed proteins oft ...
... With B. subtilis and some others, it is possible to induce secretion of a gene product into the surrounding medium. This method is in use in the pharmaceutical industry in the production of hormones such as insulin and human growth hormone. Disadvantages of bacterial cells The expressed proteins oft ...
Name________________________________ Common Core: HeLa
... taken off—a healthy part and a cancerous part—without her permission. The cells from her cervix were given to Dr. George Otto Gey. Dr. Gey discovered that Henrietta's cells did something he'd never seen before: They could be kept alive and multiply. Before Henrietta, human cells would only survive f ...
... taken off—a healthy part and a cancerous part—without her permission. The cells from her cervix were given to Dr. George Otto Gey. Dr. Gey discovered that Henrietta's cells did something he'd never seen before: They could be kept alive and multiply. Before Henrietta, human cells would only survive f ...
Cell Theory, Organelles and Cell Cycle Test
... 11. In the animal cell shown, structure A is the ____________________. 12. In the animal cell shown, structure C is the ____________________. 13. In the animal cell shown, structure E is the ____________________. 14. The energy used in photosynthesis comes from ____________________. 15. During the _ ...
... 11. In the animal cell shown, structure A is the ____________________. 12. In the animal cell shown, structure C is the ____________________. 13. In the animal cell shown, structure E is the ____________________. 14. The energy used in photosynthesis comes from ____________________. 15. During the _ ...
Biology Fall Semester Exam Review Unit 1
... Describe Darwin’s observations regarding different species of finches on the Galapagos Islands? Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection (what must occur? Pg 280) How do the following evidences of evolution explain how they support change over time: Fossils – how could you tell which spe ...
... Describe Darwin’s observations regarding different species of finches on the Galapagos Islands? Explain the theory of evolution by natural selection (what must occur? Pg 280) How do the following evidences of evolution explain how they support change over time: Fossils – how could you tell which spe ...
3d cell model directions1
... You may use any materials you want to make the cell and organelles in the cell. Each organel!e should be a different material. Ideas for materials include- yarn, beads, toothpicks, pipe cleaners, shoe boxes, Styrofoam, string, straws, food, play-doh ... Materials can be things you have at home alrea ...
... You may use any materials you want to make the cell and organelles in the cell. Each organel!e should be a different material. Ideas for materials include- yarn, beads, toothpicks, pipe cleaners, shoe boxes, Styrofoam, string, straws, food, play-doh ... Materials can be things you have at home alrea ...
Cell Structure and Function
... transmit signals to inner cell Structural-proteins on inner surface that serve to anchor the plasma membrane to the inner cell Transport- proteins that span the entire membrane, moving needed substances or waste in and out ...
... transmit signals to inner cell Structural-proteins on inner surface that serve to anchor the plasma membrane to the inner cell Transport- proteins that span the entire membrane, moving needed substances or waste in and out ...
Meiosis Skillsheet
... 11. During fertilization, the nuclei of the egg and sperm fuse / separate. 12. Germ / Somatic cells are haploid. 13. The haploid / diploid chromosome number in humans is 23. 14. Each human gamete has one autosome / sex chromosome. Read the descriptions in the table below and then decide which column ...
... 11. During fertilization, the nuclei of the egg and sperm fuse / separate. 12. Germ / Somatic cells are haploid. 13. The haploid / diploid chromosome number in humans is 23. 14. Each human gamete has one autosome / sex chromosome. Read the descriptions in the table below and then decide which column ...
Stem Cell Differentiation
... Another use of stem cells is to make specific cell types for studying human disease in the laboratory. For example, in Parkinson’s disease, neurons of the brain die resulting in motor and brain defects. But the reason why these neurons die is unknown. Scientists cannot easily access neurons from Par ...
... Another use of stem cells is to make specific cell types for studying human disease in the laboratory. For example, in Parkinson’s disease, neurons of the brain die resulting in motor and brain defects. But the reason why these neurons die is unknown. Scientists cannot easily access neurons from Par ...
SG 3.3 Key
... the extracellular fluid and inside the cell because of the cytoplasm 6. The polar heads interact with the watery environments both inside and outside the cell. The nonpolar tails interact with each other inside the membrane. Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company ...
... the extracellular fluid and inside the cell because of the cytoplasm 6. The polar heads interact with the watery environments both inside and outside the cell. The nonpolar tails interact with each other inside the membrane. Copyright by McDougal Littell, a division of Houghton Mifflin Company ...
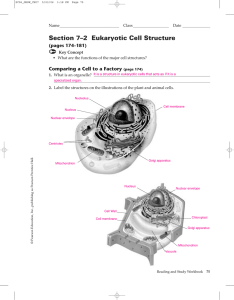
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... d. An internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed e. Saclike structure that stores materials f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces protein following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down food into particle ...
... d. An internal membrane system in which components of cell membrane and some proteins are constructed e. Saclike structure that stores materials f. Small particle of RNA and protein that produces protein following instructions from nucleus g. Filled with enzymes used to break down food into particle ...
1.2 Cells: The Basic Units of Life
... each carrying out specialized tasks that help keep the cell alive. Whether they are nerve cells in the brain of an animal, or epidermal cells in the leaf of a plant, cells are bathed in an aqueous (water-based) solution called extracellular fluid. On the inside, a cell contains an aqueous solution c ...
... each carrying out specialized tasks that help keep the cell alive. Whether they are nerve cells in the brain of an animal, or epidermal cells in the leaf of a plant, cells are bathed in an aqueous (water-based) solution called extracellular fluid. On the inside, a cell contains an aqueous solution c ...
Oscillatoriales ( Harmogonales) Family 3 :Nostocaceae Genus :Nostoc
... are also known as glow caps, a term derived from the yellowish given off by the cap. It is responsible for the black/dark green stains that form on roofs. These black stains are the algae themselves in mass amounts ...
... are also known as glow caps, a term derived from the yellowish given off by the cap. It is responsible for the black/dark green stains that form on roofs. These black stains are the algae themselves in mass amounts ...
Development2 - Napa Valley College
... - demonstrated that a single cell contains all the genetic information of the organism totipotent cells of very early embryos can form any cell type pluripotent cells can form multiple cell types (e.g., embryonic stem cells, bone marrow cells) As development proceeds, cells become increasingly deter ...
... - demonstrated that a single cell contains all the genetic information of the organism totipotent cells of very early embryos can form any cell type pluripotent cells can form multiple cell types (e.g., embryonic stem cells, bone marrow cells) As development proceeds, cells become increasingly deter ...
Cells
... The human body consists of basic units of life known as cells. Groups of cells similar in appearance, function and origin join together to form tissues. Different tissues then interact with each other to form organs. Finally groups of organs interact to form body systems. Thus there are four levels ...
... The human body consists of basic units of life known as cells. Groups of cells similar in appearance, function and origin join together to form tissues. Different tissues then interact with each other to form organs. Finally groups of organs interact to form body systems. Thus there are four levels ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.