Mitosis and Meiosis Webquest
... 8. A cell with a large volume will have a more difficult time doing what? __________________________ Click on the tab, “The Functions of Mitosis” 9. What are the 2 major functions of mitosis? ________________________________________________ Click on the tab, “Built-in Controls in Mitosis” 10. What a ...
... 8. A cell with a large volume will have a more difficult time doing what? __________________________ Click on the tab, “The Functions of Mitosis” 9. What are the 2 major functions of mitosis? ________________________________________________ Click on the tab, “Built-in Controls in Mitosis” 10. What a ...
Cell Organelle Quiz
... 1. This organelle is considered the “control center” of the cell. 2. This organelle provides energy for the cell through a process known as cellular respiration. 3. If water content in this organelle is low the plant will wilt. 4. Chlorophyll, the green pigment necessary for photosynthesis is found ...
... 1. This organelle is considered the “control center” of the cell. 2. This organelle provides energy for the cell through a process known as cellular respiration. 3. If water content in this organelle is low the plant will wilt. 4. Chlorophyll, the green pigment necessary for photosynthesis is found ...
Section 10–2 Cell Division (pages 244–249)
... 10. What happens during the S phase? Chromosomes are replicated and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. Also, key proteins associated with the chromosomes are synthesized. ...
... 10. What happens during the S phase? Chromosomes are replicated and the synthesis of DNA molecules takes place. Also, key proteins associated with the chromosomes are synthesized. ...
Mitotic Division in Cancer Cells
... in cancer cells is altered. You may have heard of cancer cells being “runaway” which have no controls on their rate of reproduction. It is this characteristic that allows some cancer cells to grow and spread quite rapidly. OBJECTIVE: Analyze data to determine the differences in timing of mitosis bet ...
... in cancer cells is altered. You may have heard of cancer cells being “runaway” which have no controls on their rate of reproduction. It is this characteristic that allows some cancer cells to grow and spread quite rapidly. OBJECTIVE: Analyze data to determine the differences in timing of mitosis bet ...
Chapter 3- Cellular Level of Organization
... Regulation of Cell cycle Proteins & enzymes are responsible 1. Cyclins- family of proteins that increase and decrease in number during cell cycle, bind to kinases to activate them M cyclins- during mitosis S cyclins- during interphase ...
... Regulation of Cell cycle Proteins & enzymes are responsible 1. Cyclins- family of proteins that increase and decrease in number during cell cycle, bind to kinases to activate them M cyclins- during mitosis S cyclins- during interphase ...
Main differences between plant and animal cells: Plant cells have
... - synthesis of the endomembrane system (lipid synthesis) - protein synthesis (on RER): both membrane proteins and soluble proteins - oil body synthesis, protein body synthesis - ER is continuous with the nuclear envelope - ER is continuous through plasmodesmata - RER has associated Ribosomes that ...
... - synthesis of the endomembrane system (lipid synthesis) - protein synthesis (on RER): both membrane proteins and soluble proteins - oil body synthesis, protein body synthesis - ER is continuous with the nuclear envelope - ER is continuous through plasmodesmata - RER has associated Ribosomes that ...
PPT File
... Made of proteins and RNA No membrane Made in nucleolus Location of protein synthesis Free ribosomes make proteins used by the cell Ribosomes on rER make proteins for export to other cells ...
... Made of proteins and RNA No membrane Made in nucleolus Location of protein synthesis Free ribosomes make proteins used by the cell Ribosomes on rER make proteins for export to other cells ...
Unit 2: Cells & Microscope
... A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. ...
... A cell is a membrane-covered structure that contains all of the materials necessary for life. ...
Problems water potential
... 10. Cell A is immersed in a solution with an osmotic pressure of 0.3 MPa. Cell B is immersed in a solution with an osmotic pressure of 0.5 MPa. The cells are allowed to come to equilibrium in their respective solutions. Then the cells are removed and brought into intimate contact. In which direction ...
... 10. Cell A is immersed in a solution with an osmotic pressure of 0.3 MPa. Cell B is immersed in a solution with an osmotic pressure of 0.5 MPa. The cells are allowed to come to equilibrium in their respective solutions. Then the cells are removed and brought into intimate contact. In which direction ...
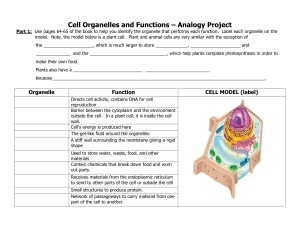
Cell Organelles and Functions – Analogy Project
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
... Part 1: Use pages 64-65 of the book to help you identify the organelle that performs each function. Label each organelle on the model. Note, the model below is a plant cell. Plant and animal cells are very similar with the exception of the ____________________, which is much larger to store ________ ...
Chapter 5 Organelles
... Yes. Although brain cells look quite different from your other cells, they have the same internal structures as other cells. They need the same structures because they need to perform the same tasks, such as making proteins and obtaining energy. ...
... Yes. Although brain cells look quite different from your other cells, they have the same internal structures as other cells. They need the same structures because they need to perform the same tasks, such as making proteins and obtaining energy. ...
Cell Structures - Central Magnet School
... hereditary information (DNA) • Parts of the nucleus –Chromatin and chromosomes –Nucleolus –Nuclear envelope ...
... hereditary information (DNA) • Parts of the nucleus –Chromatin and chromosomes –Nucleolus –Nuclear envelope ...
C, O, N - Madeira City Schools
... because they have no nucleus B. Binary Fission: asexual reproduction (there is no exchange of genetic information) 1. Chromosome is replicated 2. Copies of chromosome attach to the cell membrane 3. Cell grows and the copies separate 4. Cell divides in two as a partition forms down the middle ...
... because they have no nucleus B. Binary Fission: asexual reproduction (there is no exchange of genetic information) 1. Chromosome is replicated 2. Copies of chromosome attach to the cell membrane 3. Cell grows and the copies separate 4. Cell divides in two as a partition forms down the middle ...
plantcells - Iowa State University
... A team of Iowa State University plant scientists and materials chemists have successfully used nanotechnology to penetrate plant cell walls and simultaneously deliver a gene and a chemical that triggers its expression with controlled precision. Their breakthrough brings nanotechnology to plant biolo ...
... A team of Iowa State University plant scientists and materials chemists have successfully used nanotechnology to penetrate plant cell walls and simultaneously deliver a gene and a chemical that triggers its expression with controlled precision. Their breakthrough brings nanotechnology to plant biolo ...
Genes and Chromosomes Justified True or False Worksheet
... brown. So both traits are given to the child so that’s why there’s 2 and they might be different. They get passed from the process of heredity and genes contain the traits that are passed to you that tell whether you get your dad or mom’s eyes. They are found in genes. ...
... brown. So both traits are given to the child so that’s why there’s 2 and they might be different. They get passed from the process of heredity and genes contain the traits that are passed to you that tell whether you get your dad or mom’s eyes. They are found in genes. ...
BCPS Biology Reteaching Guide Cells Vocab Chart
... other protozoans, used for locomotion and to take up food ...
... other protozoans, used for locomotion and to take up food ...
View as Printable PDF
... plaque (which he scraped from his teeth) The organisms he found – that were single cells – he called ...
... plaque (which he scraped from his teeth) The organisms he found – that were single cells – he called ...
Neurodegenerative disease: neurons don`t take all of the blame for
... A recent report from Cai et al. has identified pluripotent cardiac cells in mice that develop into myocytes in the heart wall in addition to cardiac fibroblasts and coronary smooth muscle cells. These stem cells originate in the proepicardium and express the T-box transcription factor Tbx18, which i ...
... A recent report from Cai et al. has identified pluripotent cardiac cells in mice that develop into myocytes in the heart wall in addition to cardiac fibroblasts and coronary smooth muscle cells. These stem cells originate in the proepicardium and express the T-box transcription factor Tbx18, which i ...
Plant Cells
... Mitochondria are in nearly all eukaryotic cells They have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded into cristae The inner membrane creates two compartments: intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix Some metabolic steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix ...
... Mitochondria are in nearly all eukaryotic cells They have a smooth outer membrane and an inner membrane folded into cristae The inner membrane creates two compartments: intermembrane space and mitochondrial matrix Some metabolic steps of cellular respiration are catalyzed in the mitochondrial matrix ...
Irish potato farmers did not allow their plants to undergo sexual
... Their plants were genetically identical. Since the blight fungus could kill one plant, it could kill them all, and that’s what caused a lack of food (famine). ...
... Their plants were genetically identical. Since the blight fungus could kill one plant, it could kill them all, and that’s what caused a lack of food (famine). ...
microbial growth curve
... When growing exponentially by binary fission, the increase in a bacterial population is by geometric progression. If we start with one cell, when it divides, there are 2 cells in the first generation, 4 cells in the second generation, 8 cells in the third generation, and so on. The generation time ...
... When growing exponentially by binary fission, the increase in a bacterial population is by geometric progression. If we start with one cell, when it divides, there are 2 cells in the first generation, 4 cells in the second generation, 8 cells in the third generation, and so on. The generation time ...
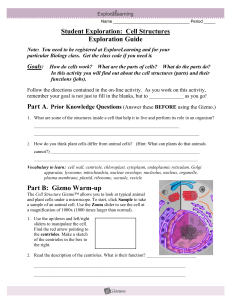
HW Cell Structures Gizmo Gizmo Cell Structures final
... In this activity you will find out about the cell structures (parts) and their functions (jobs). Follow the directions contained in the on-line activity. As you work on this activity, remember your goal is not just to fill in the blanks, but to _____________ as you go! ...
... In this activity you will find out about the cell structures (parts) and their functions (jobs). Follow the directions contained in the on-line activity. As you work on this activity, remember your goal is not just to fill in the blanks, but to _____________ as you go! ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.