File
... 1839. Cell theory. Theodor Schwann, a German botanist reached the conclusion that not only plants, but animal tissue as well is composed of cells. This ended debates that plants and animals were fundamentally different in structure. He also pulled together and organized previous statement on cells i ...
... 1839. Cell theory. Theodor Schwann, a German botanist reached the conclusion that not only plants, but animal tissue as well is composed of cells. This ended debates that plants and animals were fundamentally different in structure. He also pulled together and organized previous statement on cells i ...
cell_organelles
... energy from food into energy that can be used by the cell. Enclosed by two membranes---an outer one and another that is folded up inside the mitochondrion ...
... energy from food into energy that can be used by the cell. Enclosed by two membranes---an outer one and another that is folded up inside the mitochondrion ...
Cancer stem cells: AMLs show the way
... therapies. In order to learn more about the nature of the events involved in cancer, research should focus more on CSCs and not on the bulk cells that makes up the majority of the tumour. Existing therapies have been developed largely against the bulk population. The lack of durable response in most ...
... therapies. In order to learn more about the nature of the events involved in cancer, research should focus more on CSCs and not on the bulk cells that makes up the majority of the tumour. Existing therapies have been developed largely against the bulk population. The lack of durable response in most ...
2.4 Mitosis Notes
... o Chromatin condenses and DNA forms chromatids (chromosomes) o The nuclear envelope (membrane) disappears o Spindle fibers form and connect to the chromosomes (move them around the cell) ...
... o Chromatin condenses and DNA forms chromatids (chromosomes) o The nuclear envelope (membrane) disappears o Spindle fibers form and connect to the chromosomes (move them around the cell) ...
cells
... Cells: The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Example: white blood cell, muscle cell ...
... Cells: The cell is the basic unit of structure and function of all living things. Example: white blood cell, muscle cell ...
7-3 Cell Transport - MrKanesSciencePage
... Most molecules cannot dissolve in the lipid bilayer of the cell; therefore, they cannot ...
... Most molecules cannot dissolve in the lipid bilayer of the cell; therefore, they cannot ...
Unit 2 _Cells_ Plan
... Every living thing is made of cells and there are certain minimum requirements to qualify as a living cell. Cellular organelles divide the cell’s labor of making proteins. Some items can move directly through the cell membrane, others require the help of proteins and/or energy. The structure ...
... Every living thing is made of cells and there are certain minimum requirements to qualify as a living cell. Cellular organelles divide the cell’s labor of making proteins. Some items can move directly through the cell membrane, others require the help of proteins and/or energy. The structure ...
Cytoskeleton 14
... Usually one/cell. Membrane proteins on cilia transmit molecular signals from the environment of the cell to the interior. Flagella and cilia are similar in ultrastructure. Nine doublets of microtubules make a ring having two single microtubles in the center. Cross linking motor proteins along the ...
... Usually one/cell. Membrane proteins on cilia transmit molecular signals from the environment of the cell to the interior. Flagella and cilia are similar in ultrastructure. Nine doublets of microtubules make a ring having two single microtubles in the center. Cross linking motor proteins along the ...
Cell Biology - Land of Mayo
... they are involved with protein synthesis * made of RNA, and proteins ...
... they are involved with protein synthesis * made of RNA, and proteins ...
Chapter 7 - Angelfire
... Cell Theory • Robert Hooke (1600s, English) used a compound light microscope to study cork, the dead cells of oak bark • He saw small, geometric shapes that reminded him of the small rooms monks lived in called cells • Cells are the basic units of all living things ...
... Cell Theory • Robert Hooke (1600s, English) used a compound light microscope to study cork, the dead cells of oak bark • He saw small, geometric shapes that reminded him of the small rooms monks lived in called cells • Cells are the basic units of all living things ...
Biology 218 – Human Anatomy - RIDDELL
... Metaphase: when condensed chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell Anaphase: when one copy of each chromosome goes to each pole of the cell ...
... Metaphase: when condensed chromosomes line up along the equator of the cell Anaphase: when one copy of each chromosome goes to each pole of the cell ...
10 The Cell Theory
... can go in, some cannot; some things can exit, some never can) *made up of phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded that allow for needed passage of large molecules ...
... can go in, some cannot; some things can exit, some never can) *made up of phospholipid bilayer with proteins embedded that allow for needed passage of large molecules ...
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
... • Plants can have cell walls that are multiple layers – _____________ cell wall develops in young plants – A ______________ cell wall can develop in more mature plants • Wood is an example of a secondary cell wall ...
... • Plants can have cell walls that are multiple layers – _____________ cell wall develops in young plants – A ______________ cell wall can develop in more mature plants • Wood is an example of a secondary cell wall ...
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells • All cells fall into one of the two major classifications of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes were here first and for billions of years were the only form of life. • Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms, found in all environments. Prokaryotes are the larges ...
... Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells • All cells fall into one of the two major classifications of prokaryotes and eukaryotes. Prokaryotes were here first and for billions of years were the only form of life. • Prokaryotes are unicellular organisms, found in all environments. Prokaryotes are the larges ...
Cell Cycle
... a class of proteins active only when proper regulatory signals activate them What happens in oncogene mutations? Activity of mutant oncoprotein becomes uncoupled from normal regulatory pathway Leads to continuous unregulated expression Categorized according to uncoupling of regulatory function Gain ...
... a class of proteins active only when proper regulatory signals activate them What happens in oncogene mutations? Activity of mutant oncoprotein becomes uncoupled from normal regulatory pathway Leads to continuous unregulated expression Categorized according to uncoupling of regulatory function Gain ...
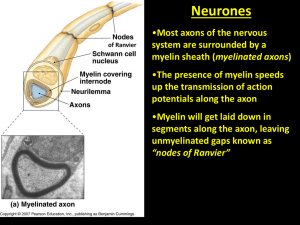
Myelin Sheaths Plant Hormone Intro
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
... • The part of a shoot sensitive to light is the tip. • The part of the shoot which responds to the stimulus is the part just below the tip. • These two parts of the shoot must be communicating with one another by means hormones. • Plant hormones are chemical that affect the activities of particular ...
Cell Review Worksheet - ANSWERS Cell Theory
... c. Lipids and Nucleic Acids nuclear envelope – made of lipids and protects the nucleus d. Carbohydrates and Proteins produce ATP that enzyme proteins need to function, ribosomes need ATP to produce proteins e. Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids carbohydrates make ATP and ATP is needed to duplicate nucl ...
... c. Lipids and Nucleic Acids nuclear envelope – made of lipids and protects the nucleus d. Carbohydrates and Proteins produce ATP that enzyme proteins need to function, ribosomes need ATP to produce proteins e. Carbohydrates and Nucleic Acids carbohydrates make ATP and ATP is needed to duplicate nucl ...
Cell Analogy Worksheet
... In a faraway city called Grant City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all sh ...
... In a faraway city called Grant City, the main export and production product is the steel widget. Everyone in the town has something to do with steel widget making and the entire town is designed to build and export widgets. The town hall has the instructions for widget making, widgets come in all sh ...
File - Flipped Out Science with Mrs. Thomas!
... Move your mouse around on the diagram of the cell diagram and the organelle name will appear in the window. When you are done with an organelle, click on “Return to Cell Diagram” (bottom of pict ...
... Move your mouse around on the diagram of the cell diagram and the organelle name will appear in the window. When you are done with an organelle, click on “Return to Cell Diagram” (bottom of pict ...
DOX(+)
... cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which encodes a single membrane-spanning glycoprotein belong to the family of immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules(IgCAMs) The cytoplasmic tail of TSLC1 contains a juxtamembrane sequence interacting with protein 4.1 and a class II PDZ binding motif In a primar ...
... cell lung cancer (NSCLC), which encodes a single membrane-spanning glycoprotein belong to the family of immunoglobulin superfamily cell adhesion molecules(IgCAMs) The cytoplasmic tail of TSLC1 contains a juxtamembrane sequence interacting with protein 4.1 and a class II PDZ binding motif In a primar ...
Language: English Day: 1
... Problem 2. Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral, and let diagonals AC and BD intersect at X. Let C1 , D1 and M be the midpoints of segments CX, DX and CD, respectively. Lines AD1 and BC1 intersect at Y , and line M Y intersects diagonals AC and BD at different points E and F , respectively. Prove that ...
... Problem 2. Let ABCD be a cyclic quadrilateral, and let diagonals AC and BD intersect at X. Let C1 , D1 and M be the midpoints of segments CX, DX and CD, respectively. Lines AD1 and BC1 intersect at Y , and line M Y intersects diagonals AC and BD at different points E and F , respectively. Prove that ...
Concept Review Question #2 Name: Biology Due Date: ______
... Concept Review Question #2 Biology ...
... Concept Review Question #2 Biology ...
Topic 3 Autoimmunity
... Multiple Myeloma Malignancy of mature plasma cells. Most serious and common of plasma cell dyscrasias. Age of diagnosis 40 to 70 years, found in blacks twice as ...
... Multiple Myeloma Malignancy of mature plasma cells. Most serious and common of plasma cell dyscrasias. Age of diagnosis 40 to 70 years, found in blacks twice as ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.