Growth
... Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) since it is not absolutely certain that each colony arose from an individual cell Viable cell counts very sensitive: Any viable cell colony Allow: Identification of organisms Isolation of pure cultures ...
... Results expressed as colony forming units (CFU) since it is not absolutely certain that each colony arose from an individual cell Viable cell counts very sensitive: Any viable cell colony Allow: Identification of organisms Isolation of pure cultures ...
Presentation
... g) How does the nucleus get the instructions from the chromosomes to the organelles in the cytoplasm? ...
... g) How does the nucleus get the instructions from the chromosomes to the organelles in the cytoplasm? ...
The Cell - Harris7Science
... Ribosomes – manufacture of proteins Cytoplasm – substance that holds all other parts in suspension Mitochondria – Release energy for food Lyosomes – gobble up waste materials (very rare in plant cells) ...
... Ribosomes – manufacture of proteins Cytoplasm – substance that holds all other parts in suspension Mitochondria – Release energy for food Lyosomes – gobble up waste materials (very rare in plant cells) ...
Laboratory 4: Cell Structure and Function Part 1: Eukaryotic Cells
... enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate environment and therefore have a plasma membrane that controls which substances are ...
... enormously in size, shape, and function. Some are free living, independent organisms, while others are immovably fixed as part of tissues of multicellular organisms. All cells exchange materials with their immediate environment and therefore have a plasma membrane that controls which substances are ...
PCBC Cell Characterization Core - NHLBI Progenitor Cell Biology
... identifies appropriate candidate pulmonary cells obtained by progenitor differentiation, the Core will also be responsible for characterization of these cells. Applications should also include a bioinformatics component to analyze and organize the data, and disseminate information to the Consortium ...
... identifies appropriate candidate pulmonary cells obtained by progenitor differentiation, the Core will also be responsible for characterization of these cells. Applications should also include a bioinformatics component to analyze and organize the data, and disseminate information to the Consortium ...
Cells and Tissues - Lemon Bay High School
... 3) They are assisted by a membrane carrier. Types of diffusion o Simple diffusion: unassisted movement through the membrane. Solutes are lipidsoluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores What materials will pass through the membrane by SIMPLE DIFFUSION? Lipid-soluble (fats, gas ...
... 3) They are assisted by a membrane carrier. Types of diffusion o Simple diffusion: unassisted movement through the membrane. Solutes are lipidsoluble materials or small enough to pass through membrane pores What materials will pass through the membrane by SIMPLE DIFFUSION? Lipid-soluble (fats, gas ...
Mitosis - Cancer - Hicksville Public Schools
... normal cells lose their ability to limit and direct their growth. They divide too rapidly and grow without any order. ...
... normal cells lose their ability to limit and direct their growth. They divide too rapidly and grow without any order. ...
Chapter 7- Cell structure and Function
... genetic material in the form of DNA. 4. Eukaryotes are cells that contain nuclei ...
... genetic material in the form of DNA. 4. Eukaryotes are cells that contain nuclei ...
PDF File of Transcript for Dawn Tamarkin`s Case Story
... Now if this is not an onion cell but instead it's a cheek cell, there's no cell wall because animal cells don't have it and students can bend this the right way, and put the nucleus in, maybe even show that they've kind of bend the cell a little sticking out on the slide. And even have some bacteria ...
... Now if this is not an onion cell but instead it's a cheek cell, there's no cell wall because animal cells don't have it and students can bend this the right way, and put the nucleus in, maybe even show that they've kind of bend the cell a little sticking out on the slide. And even have some bacteria ...
Lecture 6, Feb 1
... structures such as membrane-bounded organelles,; c. allow movement of components of the cytoskeleton with respect to each other or with respect to other components of the cell. These "movement“ proteins are called "motor" molecules. ...
... structures such as membrane-bounded organelles,; c. allow movement of components of the cytoskeleton with respect to each other or with respect to other components of the cell. These "movement“ proteins are called "motor" molecules. ...
The cytoskeleton The cell surface and junctions
... The cell surface and junctions (Lecture 5) The cytoskeleton: gives the cell shape, anchors some organelles and directs the movement of others, and may enable the entire cell to change shape or move. It may play a regulatory role, by mechanically transmitting signals from the cell's surface to its in ...
... The cell surface and junctions (Lecture 5) The cytoskeleton: gives the cell shape, anchors some organelles and directs the movement of others, and may enable the entire cell to change shape or move. It may play a regulatory role, by mechanically transmitting signals from the cell's surface to its in ...
BIOL 170 Exploring Biology
... 1. List the two functions of carbohydrates in maintaining organisms alive. 2. Why is it that we humans can break down starch into sugar to be used for energy but cannot break down cellulose into sugar? 3. It is reported that fish and all vertebrates are “nutritionally deficient.” What parts of prote ...
... 1. List the two functions of carbohydrates in maintaining organisms alive. 2. Why is it that we humans can break down starch into sugar to be used for energy but cannot break down cellulose into sugar? 3. It is reported that fish and all vertebrates are “nutritionally deficient.” What parts of prote ...
Chapter Three: Cells: The Basic Units of Life Teacher Notes Lesson
... -outermost structure of plant cells made of cellulose -allows plants to stand upright -fungi and yeasts also have cell walls made of chitin -Cell Membrane-a protective barrier that encloses a cell. It separates the cell’s contents from its environment. -all cells have cell membranes -in cells witho ...
... -outermost structure of plant cells made of cellulose -allows plants to stand upright -fungi and yeasts also have cell walls made of chitin -Cell Membrane-a protective barrier that encloses a cell. It separates the cell’s contents from its environment. -all cells have cell membranes -in cells witho ...
Dividing we stand
... kinases) are enzymes that add phosphate groups to proteins to activate them. One of their roles is to activate proteins that initiate DNA replication before mitosis, to ensure this happens at the correct stage. In cancer cells, growth is incorrectly regulated, and this is often due to mutations in g ...
... kinases) are enzymes that add phosphate groups to proteins to activate them. One of their roles is to activate proteins that initiate DNA replication before mitosis, to ensure this happens at the correct stage. In cancer cells, growth is incorrectly regulated, and this is often due to mutations in g ...
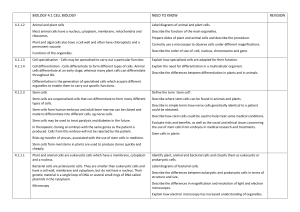
BIOLOGY 4.1 CELL BIOLOGY NEED TO KNOW REVISION
... Differentiation is the generation of specialised cells which acquire different organelles to enable them to carry out specific functions. ...
... Differentiation is the generation of specialised cells which acquire different organelles to enable them to carry out specific functions. ...
Reading Guide for Week 6
... 4. Know which cells kill infected host cells. Know what types of infections, etc. these cell are most effective in eliminating. How do these cells help the antibody producing cells? 5. Know the different types of T-cells and their function. What is the role of T cell receptors? What function do Natu ...
... 4. Know which cells kill infected host cells. Know what types of infections, etc. these cell are most effective in eliminating. How do these cells help the antibody producing cells? 5. Know the different types of T-cells and their function. What is the role of T cell receptors? What function do Natu ...
Intro Unit Notes - Reading Community Schools
... • Cell replicates genetic material to prepare for nuclear division • Cell synthesizes new organelles to prepare for cytoplasmic division ...
... • Cell replicates genetic material to prepare for nuclear division • Cell synthesizes new organelles to prepare for cytoplasmic division ...
Biology Daily Lesson Plan
... Characteristics of Life activity: Students will read a statement and determine the characteristic represented. Deconstruct the standards Students will access the Cell Structure & Function Quizlet from Mrs. Cox’s Quizlet. They will make a list of terms they know, terms they have heard before but cann ...
... Characteristics of Life activity: Students will read a statement and determine the characteristic represented. Deconstruct the standards Students will access the Cell Structure & Function Quizlet from Mrs. Cox’s Quizlet. They will make a list of terms they know, terms they have heard before but cann ...
A1988Q865100002
... drawn through the linear portions of a sample’s dose-response curve. With publication of these results, we termed the entity responsible for this activity “T-cell growth factor” (TCGF) and established methods useful in quantifying other cytokines whose activities would be demonstrated in years to co ...
... drawn through the linear portions of a sample’s dose-response curve. With publication of these results, we termed the entity responsible for this activity “T-cell growth factor” (TCGF) and established methods useful in quantifying other cytokines whose activities would be demonstrated in years to co ...
Biology Unit 3 - Hartland High School
... If the ocular lens or eyepiece was 10X magnification and the total magnification was 300X, then what is the magnification of the objective lens? Show your math!!! 10 x objective lens = 300, so divide 300 by 10 to get 30X. The objective lens is 30X magnification What are some of the differences betwe ...
... If the ocular lens or eyepiece was 10X magnification and the total magnification was 300X, then what is the magnification of the objective lens? Show your math!!! 10 x objective lens = 300, so divide 300 by 10 to get 30X. The objective lens is 30X magnification What are some of the differences betwe ...
Plant Signaling and Plant Hormones
... • Important for pollen development, pollen tube growth • Works with auxin for fruit growth (spray to make seedless grapes) ...
... • Important for pollen development, pollen tube growth • Works with auxin for fruit growth (spray to make seedless grapes) ...
Cell Division
... • Diploid Cells (2n) = 2 sets of chromosomes…one from each parent (Example: human body cell) • Haploid Cells (n)= only have 1 set of chromosomes (Example: Sperm or Egg Cell) ...
... • Diploid Cells (2n) = 2 sets of chromosomes…one from each parent (Example: human body cell) • Haploid Cells (n)= only have 1 set of chromosomes (Example: Sperm or Egg Cell) ...
Pirate viruses caught in their own trap?
... easily and can therefore escape treatment. For these reasons, virologists are seeking to develop antiviral agents that can target these cellular proteins (or factors). But there is one downside, and it is considerable: the factors targeted by this strategy often play a crucial role in the cell, caus ...
... easily and can therefore escape treatment. For these reasons, virologists are seeking to develop antiviral agents that can target these cellular proteins (or factors). But there is one downside, and it is considerable: the factors targeted by this strategy often play a crucial role in the cell, caus ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.