The Molecularly Crowded Cytoplasm of Bacterial Cells: Dividing
... Tens of thousands of ribosomes. Ribosome-transcript localization for some membrane protein synthesis Some cell division proteins localized at the mid-cell location. Non-specific molecular interactions over different time scales. Cells in a viable but-nonculturable (VBNC) state may have less molecula ...
... Tens of thousands of ribosomes. Ribosome-transcript localization for some membrane protein synthesis Some cell division proteins localized at the mid-cell location. Non-specific molecular interactions over different time scales. Cells in a viable but-nonculturable (VBNC) state may have less molecula ...
The role of c-myc in cellular growth control
... (cdc63) are speci®c regulators of START (Hanic-Joyce et al., 1987). The cdc63 version of prt-1 cells are mutant in the Z component of the eukaryotic translation initiation complex 3 (eIF3Z). Intriguingly, at dierent temperatures the cdc63 arrest phenotype changes from a non-speci®c arrest at all st ...
... (cdc63) are speci®c regulators of START (Hanic-Joyce et al., 1987). The cdc63 version of prt-1 cells are mutant in the Z component of the eukaryotic translation initiation complex 3 (eIF3Z). Intriguingly, at dierent temperatures the cdc63 arrest phenotype changes from a non-speci®c arrest at all st ...
DAB photo-oxidation as a tool for detecting low amounts of free and
... 2012) and multilamellar bodies (Figure 3d) (lipid storage/secretory organelles related to defective lipid metabolism and/or autophagic activities; Schmitz and Muller, 1991). Calcium ions The ultrastructural localization of non electrondense ions is generally difficult, in particular when they are hi ...
... 2012) and multilamellar bodies (Figure 3d) (lipid storage/secretory organelles related to defective lipid metabolism and/or autophagic activities; Schmitz and Muller, 1991). Calcium ions The ultrastructural localization of non electrondense ions is generally difficult, in particular when they are hi ...
CYCLIC CHANGES IN THE CELL SURFACE I. Change in
... point is low and the radioactive pool is saturated by 15 min . At 4 h (Fig . 4 B) some cells have started to enter S and the rate of incorporation of [3H]thymidine has increased . The total uptake curve no longer reaches equilibrium . Between 4 h and 10 h (Fig . 4 C-E) the rate of incorporation of [ ...
... point is low and the radioactive pool is saturated by 15 min . At 4 h (Fig . 4 B) some cells have started to enter S and the rate of incorporation of [3H]thymidine has increased . The total uptake curve no longer reaches equilibrium . Between 4 h and 10 h (Fig . 4 C-E) the rate of incorporation of [ ...
Connective Tissue
... The starting embryonic tissue is mesenchyme - jellylike, with a few thin fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal cells As the mesenchymal cells become fibroblasts, these can make the tissue, by fiber packing, loose or dense The fibroblasts may align the fibers parallel to make a regular tissue ,or arra ...
... The starting embryonic tissue is mesenchyme - jellylike, with a few thin fibers and unspecialized mesenchymal cells As the mesenchymal cells become fibroblasts, these can make the tissue, by fiber packing, loose or dense The fibroblasts may align the fibers parallel to make a regular tissue ,or arra ...
3.2 Cell Organelles Cells have an internal structure.
... processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
... processing proteins. • The nucleus stores genetic information. • Many processes occur in the endoplasmic reticulum. • There are two types of endoplasmic reticulum. – rough endoplasmic reticulum – smooth endoplasmic reticulum ...
Signaling in Single-Celled Organisms
... Signaling in bacteria enables bacteria to monitor extracellular conditions, ensure that there are su cient amounts of nutrients, and ensure that hazardous situations are avoided. There are circumstances, however, when bacteria communicate with each other. The rst evidence of bacterial communication ...
... Signaling in bacteria enables bacteria to monitor extracellular conditions, ensure that there are su cient amounts of nutrients, and ensure that hazardous situations are avoided. There are circumstances, however, when bacteria communicate with each other. The rst evidence of bacterial communication ...
The complex cell cycle of the dinoflagellate protoctist
... arrow). Successive stages of the mitosis from prophase (in which cytoplasmic channels are clearly visible) to cytokinesis are shown in Fig. 2(C-G), and the second mitosis, from early prophase to telophase with four nuclei within the cyst, is shown in Fig. 2(H-J). Cell cycle in a synchronized populat ...
... arrow). Successive stages of the mitosis from prophase (in which cytoplasmic channels are clearly visible) to cytokinesis are shown in Fig. 2(C-G), and the second mitosis, from early prophase to telophase with four nuclei within the cyst, is shown in Fig. 2(H-J). Cell cycle in a synchronized populat ...
A-P Chapter 3
... two hollow cylinders called centrioles that function in the separation of chromosomes during cell division. i. Cilia and flagella are motile extensions from the cell; shorter cilia are abundant on the free surfaces of certain epithelial cells (respiratory linings, for example), and a lengthy flagell ...
... two hollow cylinders called centrioles that function in the separation of chromosomes during cell division. i. Cilia and flagella are motile extensions from the cell; shorter cilia are abundant on the free surfaces of certain epithelial cells (respiratory linings, for example), and a lengthy flagell ...
Translational control of meiotic cell cycle progression
... eIF4G via the HA epitope tag resulted in co-immunoprecipitation of Myc-eIF4E1, as expected, visualized by western blot of the precipitate with anti-Myc (Fig. 1B, lane 2). Likewise, even though the HA-eIF4G2 was either less abundantly expressed or transferred to the blot less efficiently than HA-eIF4 ...
... eIF4G via the HA epitope tag resulted in co-immunoprecipitation of Myc-eIF4E1, as expected, visualized by western blot of the precipitate with anti-Myc (Fig. 1B, lane 2). Likewise, even though the HA-eIF4G2 was either less abundantly expressed or transferred to the blot less efficiently than HA-eIF4 ...
A phenylalanine-based folding determinant in intestinal sucrase
... al., 2002). For the assessment of temperature-sensitive characteristics the cells were cultured 1 day after transfection at 20°C for almost 18 hours (overnight) and the temperature was then raised to 37°C for 4 hours. ...
... al., 2002). For the assessment of temperature-sensitive characteristics the cells were cultured 1 day after transfection at 20°C for almost 18 hours (overnight) and the temperature was then raised to 37°C for 4 hours. ...
Skin Anatomy
... process called keratinization – a tough, waterproof protein called keratin is produced inside the cell and the cell fills up with keratin. By the time the skin cells (keratinocytes) reach the surface, they are completely filled with keratin and have died because they are so far from a blood supply. ...
... process called keratinization – a tough, waterproof protein called keratin is produced inside the cell and the cell fills up with keratin. By the time the skin cells (keratinocytes) reach the surface, they are completely filled with keratin and have died because they are so far from a blood supply. ...
PPT 2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... a. manufactures new cell organelles b. assists in movement of some cells from one place to another c. releases energy in cells d. modifies, sorts, and packages proteins ...
... a. manufactures new cell organelles b. assists in movement of some cells from one place to another c. releases energy in cells d. modifies, sorts, and packages proteins ...
Nod factor internalization and microtubular
... In legumes such as alfalfa and vetch, the nodule meristem remains active for several weeks, thus leading to the formation of elongated indeterminate nodules comprising central and peripheral tissues. Histologically, central tissues are organized into five well-defined zones: the apical meristematic ...
... In legumes such as alfalfa and vetch, the nodule meristem remains active for several weeks, thus leading to the formation of elongated indeterminate nodules comprising central and peripheral tissues. Histologically, central tissues are organized into five well-defined zones: the apical meristematic ...
Flow Cytometry and Sorting, Part 1
... Example Channel Layout for PMT Laser-based Flow Cytometry ...
... Example Channel Layout for PMT Laser-based Flow Cytometry ...
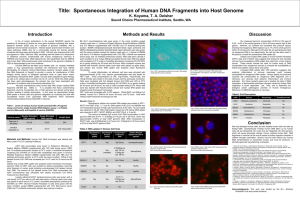
Title: Spontaneous Integration of Human DNA Fragments into Host
... A trio of recent publications in the journal NEURON reports the presence of hundreds of diverse de novo gene mutations indicating that autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be a disease of genomic instability, with a significant environmental component. Altered double strand break formation and repair ...
... A trio of recent publications in the journal NEURON reports the presence of hundreds of diverse de novo gene mutations indicating that autism spectrum disorder (ASD) may be a disease of genomic instability, with a significant environmental component. Altered double strand break formation and repair ...
Combined pharmacophore based small molecule design for direct
... suppressed human GBM in vitro and suppressed OLIG2 target genes ...
... suppressed human GBM in vitro and suppressed OLIG2 target genes ...
Crosstalk between Notch signaling Pathway and Glutamine uptake
... CD4+ T cells along with simultaneous activation of Notch1 signaling pathway prevented IL2 and INFγ production while inhibiting presenilin enhanced the T cell proliferation upon stimulation (Eagar, T. N. 2004[18] ) . On the other hand stimulation of Notch3 by Delta1 ligand during activation of CD4+ c ...
... CD4+ T cells along with simultaneous activation of Notch1 signaling pathway prevented IL2 and INFγ production while inhibiting presenilin enhanced the T cell proliferation upon stimulation (Eagar, T. N. 2004[18] ) . On the other hand stimulation of Notch3 by Delta1 ligand during activation of CD4+ c ...
Career of Carolyn Bertozzi
... Which sugar moieties - glycans or oligosaccharides - are attached to which proteins? How do glycosylation patterns differ from human and bacterial or cancerous cells? Does the pattern change over the course of a person or diseaseʼs lifetime? Is there a sugar code, comparable to the genetic code? ...
... Which sugar moieties - glycans or oligosaccharides - are attached to which proteins? How do glycosylation patterns differ from human and bacterial or cancerous cells? Does the pattern change over the course of a person or diseaseʼs lifetime? Is there a sugar code, comparable to the genetic code? ...
ABSTRACT “SPIN” Protective effects induced by a mixture of
... mobile phones, radio repeaters, etc. ...), resulting in various forms of electromagnetic unbalance in animal bodies. Such side-effects have a detrimental influence on cellular functions in living organisms. In particular, the production levels of so-called free radicals and oxygenation dynamics with ...
... mobile phones, radio repeaters, etc. ...), resulting in various forms of electromagnetic unbalance in animal bodies. Such side-effects have a detrimental influence on cellular functions in living organisms. In particular, the production levels of so-called free radicals and oxygenation dynamics with ...
Review Interaction between the immune system and bone
... Essential role of osteoclasts in bone destruction associated with inflammation The bone destruction observed in the joints of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients presents a challenging clinical problem.5), 6) Osteoclasts are now known to play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of bone destruction in R ...
... Essential role of osteoclasts in bone destruction associated with inflammation The bone destruction observed in the joints of rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients presents a challenging clinical problem.5), 6) Osteoclasts are now known to play a pivotal role in the pathogenesis of bone destruction in R ...
Peroxiredoxin-controlled G-CSF signalling at the endoplasmic
... defence against bacteria. In non-phagocytic cells, H2O2 has long been considered as an unwanted by-product of cell metabolism, potentially hazardous because of the damaging effects on proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids (Rhee, 2006; Rhee et al., 2005b). There is increasing evidence tha ...
... defence against bacteria. In non-phagocytic cells, H2O2 has long been considered as an unwanted by-product of cell metabolism, potentially hazardous because of the damaging effects on proteins, lipids, carbohydrates and nucleic acids (Rhee, 2006; Rhee et al., 2005b). There is increasing evidence tha ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.