Population-Expression Dynamics - q
... of cells in this way yields the distribution of expression levels. These distributions are then measured at multiple time points. In comparison, while gene-arrays yield data for tens of thousands of genes from each patient, their typical use returns only the average cellular expression, giving no ot ...
... of cells in this way yields the distribution of expression levels. These distributions are then measured at multiple time points. In comparison, while gene-arrays yield data for tens of thousands of genes from each patient, their typical use returns only the average cellular expression, giving no ot ...
Cell Structure and Function
... • Surface area represents the “access” available to and from a cell for supplies. • Volume represents how much has to be supplied. • The more “access” you have to supply each unit of volume, the more efficient the cell is. ...
... • Surface area represents the “access” available to and from a cell for supplies. • Volume represents how much has to be supplied. • The more “access” you have to supply each unit of volume, the more efficient the cell is. ...
What Is a Cell?
... • Living things are constructed of cells and can be unicellular (one cell) or multicellular (many cells). • Limits on Cell Size • Cells size is limited because cells must be able to exchange materials with their surroundings. In other words, surface area relative to the volume decreases as size of c ...
... • Living things are constructed of cells and can be unicellular (one cell) or multicellular (many cells). • Limits on Cell Size • Cells size is limited because cells must be able to exchange materials with their surroundings. In other words, surface area relative to the volume decreases as size of c ...
Chapter 4 and 5 Tests
... What is an acid and how do cells control the pH of their internal environment? Which surface proteins and extracellular matrix components are not associated with animal cells? Cholesterol interferes with the fatty acid tail interactions so it serves to stiffen the membrane and control fluidity (know ...
... What is an acid and how do cells control the pH of their internal environment? Which surface proteins and extracellular matrix components are not associated with animal cells? Cholesterol interferes with the fatty acid tail interactions so it serves to stiffen the membrane and control fluidity (know ...
Cell Structure and Function Chapter 7
... Where do green plants get their energy? _____________________________________________ Where do plant-eating animals (herbivores) get their energy? _____________________________________________ ...
... Where do green plants get their energy? _____________________________________________ Where do plant-eating animals (herbivores) get their energy? _____________________________________________ ...
S.T.I.P.E and Misc. Cell Other Organelles notes & Misc
... Organelles Characteristics: The organelles work together to create a properly functioning system (the cell)… just like all the parts of a factory work together to make a properly functioning factory! If one organelle is removed or missing, the cell will not function properly! ...
... Organelles Characteristics: The organelles work together to create a properly functioning system (the cell)… just like all the parts of a factory work together to make a properly functioning factory! If one organelle is removed or missing, the cell will not function properly! ...
Multi-celled and Single-Celled Notes
... Nonvascular Plants-plants absorb water much like a sponge soaks up a liquid. These plants do not have specialized tube-like tissues. Instead, water slowly passes directly form cell to cell. They must live close to a water source The lack of a transport system also prevents them from growing very tal ...
... Nonvascular Plants-plants absorb water much like a sponge soaks up a liquid. These plants do not have specialized tube-like tissues. Instead, water slowly passes directly form cell to cell. They must live close to a water source The lack of a transport system also prevents them from growing very tal ...
Honors Biology Midterm Chapters and Topics 2014
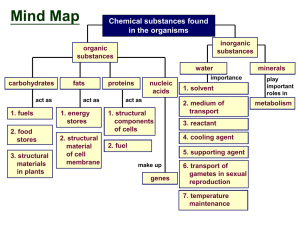
... Properties of water Hydrogen bonds Identifying reactants and products in a chemical equation pH Chapter 3 The Molecules of Cells Organic verses inorganic Polymers and monomers Dehydration and hydrolysis reactions Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids o Monomers of each molecule o Structures ...
... Properties of water Hydrogen bonds Identifying reactants and products in a chemical equation pH Chapter 3 The Molecules of Cells Organic verses inorganic Polymers and monomers Dehydration and hydrolysis reactions Carbohydrates, lipids, proteins, nucleic acids o Monomers of each molecule o Structures ...
Title Hypoxia-inducible factor-1α dependent cytoplasmic B7
... B7-H4 is a co-signaling molecule which has an inhibitory effect on T cell functions. Its expression on cancer tissues has been suggested to correlated with poor survival of cancer patients, indicating that B7-H4 is a critical immune checkpoint in anti-cancer immunity. However, there are few reports ...
... B7-H4 is a co-signaling molecule which has an inhibitory effect on T cell functions. Its expression on cancer tissues has been suggested to correlated with poor survival of cancer patients, indicating that B7-H4 is a critical immune checkpoint in anti-cancer immunity. However, there are few reports ...
Flow of Matter_04_Sample Quiz Questions
... 1) Make sure you include the following words in your explanation: plant cell example of a cellular structure in a plant cell where you would find protein ...
... 1) Make sure you include the following words in your explanation: plant cell example of a cellular structure in a plant cell where you would find protein ...
Direct Nuclear Transport of Aptamer-RNA Chimeras to
... cancerous cells. By delivering an aptamer that inhibits ß-arrestin with the nucleolin-targeting aptamer, we have been able to inhibit ß-arrestin from activating downstream pathways by delivering an aptamer with the nucleolintargeting aptamer. Discussion and Conclusions- Based on this evidence, we be ...
... cancerous cells. By delivering an aptamer that inhibits ß-arrestin with the nucleolin-targeting aptamer, we have been able to inhibit ß-arrestin from activating downstream pathways by delivering an aptamer with the nucleolintargeting aptamer. Discussion and Conclusions- Based on this evidence, we be ...
Science Fast Facts Cells Animal and plant cells are very similar, ex
... have a nucleus which contains their DNA. These cells are complex and contain many organelles. ...
... have a nucleus which contains their DNA. These cells are complex and contain many organelles. ...
Chapter 3
... Nervous - carries messages to/from the brain Epithelial - protective outer layer of skin, lining of organs ...
... Nervous - carries messages to/from the brain Epithelial - protective outer layer of skin, lining of organs ...
Cell and Molecular Biology
... Figure 17-35. Sculpting the digits in the developing mouse paw by apoptosis. (A) The paw in this mouse embryo has been stained with a dye that specifically labels cells that have undergone apoptosis. The apoptotic cells appear as bright green dots between the developing digits. (B) This interdigital ...
... Figure 17-35. Sculpting the digits in the developing mouse paw by apoptosis. (A) The paw in this mouse embryo has been stained with a dye that specifically labels cells that have undergone apoptosis. The apoptotic cells appear as bright green dots between the developing digits. (B) This interdigital ...
Abstract
... Abstract: The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) originates from neural stem cells composed of highly organized neuroepithelial and, subsequently, radial glial cells, which give rise to virtually all neurons in the brain. During development, these neural stem cells and their progeny go through ...
... Abstract: The vertebrate central nervous system (CNS) originates from neural stem cells composed of highly organized neuroepithelial and, subsequently, radial glial cells, which give rise to virtually all neurons in the brain. During development, these neural stem cells and their progeny go through ...
The Cell - SNC2PSylvia2011
... The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
... The Cell Theory 1. All living things are made of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of life. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells. ...
BIOLOGY
... 15. What is the function of Mitochondria? 16. What is the function of Chloroplasts? 17. What characteristic do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts share that make them different than other organelles? ...
... 15. What is the function of Mitochondria? 16. What is the function of Chloroplasts? 17. What characteristic do Mitochondria and Chloroplasts share that make them different than other organelles? ...
Homework Answers
... 1. Give 3 reasons why specialized systems are necessary in large multicellular organisms. Specialized systems are necessary in large multicellular organisms since 1. there is a division of labor between cells, 2. many individual cells cannot work together without coordination and 3. most of the cell ...
... 1. Give 3 reasons why specialized systems are necessary in large multicellular organisms. Specialized systems are necessary in large multicellular organisms since 1. there is a division of labor between cells, 2. many individual cells cannot work together without coordination and 3. most of the cell ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.