Chapter 2 Study Guide - Conackamack Middle School
... Chapter Two Test – Review I – Format of test The exam will have different sections including: Multiple Choice, Matching, Fill-in-the-Blank, Diagramming, Short Answer (written in lists/sentences), Open-ended II – Topics of Study A. What is Life? (pages 34-40) a. Characteristics of life b. Basic needs ...
... Chapter Two Test – Review I – Format of test The exam will have different sections including: Multiple Choice, Matching, Fill-in-the-Blank, Diagramming, Short Answer (written in lists/sentences), Open-ended II – Topics of Study A. What is Life? (pages 34-40) a. Characteristics of life b. Basic needs ...
Unit 4 Cells Practice Exam
... 5. In all organisms, which microscopic structures carry out the major life functions? (1) chloroplasts (2) cells (3) cytoplasm (4) nucleus 6. What is the outermost structure in a plant cell? (1) cell membrane (2) cytoplasm ...
... 5. In all organisms, which microscopic structures carry out the major life functions? (1) chloroplasts (2) cells (3) cytoplasm (4) nucleus 6. What is the outermost structure in a plant cell? (1) cell membrane (2) cytoplasm ...
Kingdoms Of Life: Monerans
... They make up more matter than all other living things on earth combined ...
... They make up more matter than all other living things on earth combined ...
File
... Plants and animals cells have many of the same type of structures. These structures perform the same type of activities. Plants and animals cells have some structures that are not the same. These structures perform different activities, but necessary to it’s particular cell. ...
... Plants and animals cells have many of the same type of structures. These structures perform the same type of activities. Plants and animals cells have some structures that are not the same. These structures perform different activities, but necessary to it’s particular cell. ...
Ms - Mrs. Greyer`s 7th grade Life Science
... S7L2a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials. S7L2b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and mitochondria) to basic cell functions. S7L2c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, ...
... S7L2a. Explain that cells take in nutrients in order to grow and divide and to make needed materials. S7L2b. Relate cell structures (cell membrane, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, and mitochondria) to basic cell functions. S7L2c. Explain that cells are organized into tissues, tissues into organs, ...
Cell Theory Organelles Brain Cells Need a Tissue?
... These cells have a nucleus that contain DNA. ...
... These cells have a nucleus that contain DNA. ...
Chapter 3
... 6. Gram-positive cell walls contain a higher percentage of ___________ than those of Gramnegative cells. 7. Many bacteria have long, hair-like structures called ___________ projecting from the cell wall. These are used for ___________. 8. The DNA of eukaryotes is organised into chromosomes and assoc ...
... 6. Gram-positive cell walls contain a higher percentage of ___________ than those of Gramnegative cells. 7. Many bacteria have long, hair-like structures called ___________ projecting from the cell wall. These are used for ___________. 8. The DNA of eukaryotes is organised into chromosomes and assoc ...
Cell theory worksheet - science-teachers
... 1831, Robert Brown discovered a small, dark structure in each plant cell which he called a nucleus (after the Latin for ‘small nut’, which is what he thought it looked like). In 1838 the importance of cells became clearer, when Mattias Schleiden came to the conclusion that all plants were made of ce ...
... 1831, Robert Brown discovered a small, dark structure in each plant cell which he called a nucleus (after the Latin for ‘small nut’, which is what he thought it looked like). In 1838 the importance of cells became clearer, when Mattias Schleiden came to the conclusion that all plants were made of ce ...
Axon Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells: 1. Neurons ¾ transmit nerve impulses. 2. Neuroglial cells (glial cells) ¾ are non-conducting “support cells” of nervous tissue. Examples include astrocytes, attached to the outside of a capillary blood vessel in the brain, phagocytic microglial cells ...
... Nervous tissue is composed of two types of cells: 1. Neurons ¾ transmit nerve impulses. 2. Neuroglial cells (glial cells) ¾ are non-conducting “support cells” of nervous tissue. Examples include astrocytes, attached to the outside of a capillary blood vessel in the brain, phagocytic microglial cells ...
Cells - Haiku Learning
... • Conclusion – My hypothesis was ______ ___________________. I learned _____ _____________________. My observations were __________________ _____________________. I think this is because _______________________. I still wonder _______________________ ___________________________. ...
... • Conclusion – My hypothesis was ______ ___________________. I learned _____ _____________________. My observations were __________________ _____________________. I think this is because _______________________. I still wonder _______________________ ___________________________. ...
Photosynthesis-Cellular Respiration Study Guide
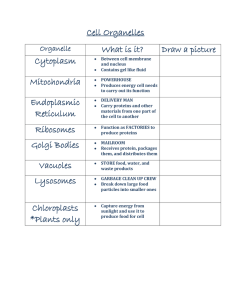
... Lysosomes – release chemicals that break down and get rid of old cell parts Mitochondria – this is where cellular respiration takes place and is where the energy (ATP) is made for the cells Vacuoles – storage tanks for water and other materials Cell Wall – protects and supports (found only in plant ...
... Lysosomes – release chemicals that break down and get rid of old cell parts Mitochondria – this is where cellular respiration takes place and is where the energy (ATP) is made for the cells Vacuoles – storage tanks for water and other materials Cell Wall – protects and supports (found only in plant ...
The Cell Cycle, Rate and Control
... Rate of Cell Division Different types of cells divide at different rates. Some types of cells like bone marrow reproduce rapidly (1 hour) Other extreme certain cells like nerve and muscle cells never reproduce once they mature (stay in interphase) Other cells divide only when needed for repair ...
... Rate of Cell Division Different types of cells divide at different rates. Some types of cells like bone marrow reproduce rapidly (1 hour) Other extreme certain cells like nerve and muscle cells never reproduce once they mature (stay in interphase) Other cells divide only when needed for repair ...
Abstract
... Received April 28, 2006; revision accepted August 5, 2006 The development of the suspensor in Sedum acre L. and S. hispanicum L. was investigated using cytochemical methods and light microscopy. After the first division of the zygote, two cells of unequal size are formed: the large basal cell (BC) a ...
... Received April 28, 2006; revision accepted August 5, 2006 The development of the suspensor in Sedum acre L. and S. hispanicum L. was investigated using cytochemical methods and light microscopy. After the first division of the zygote, two cells of unequal size are formed: the large basal cell (BC) a ...
Marine Biology Cell Assessment 1) Cyanide is a poison that
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
... 2) Use the information and the figure below to answer the following. The diagram below shows a colony of prokaryotes and a single-celled eukaryote. The eukaryote contains organelles that resemble the three types of bacteria found in the colony of prokaryotes. More than a billion years ago, bacteria ...
Toxicology: A Springboard for Stem Cell Scientists? - NAS
... treatment of diseases? Transplantation ...
... treatment of diseases? Transplantation ...
Cell Structure and Function
... stores and distributes proteins • Proteins from rough ER will be shipped to cell membrane for exocytosis • Produces lysosomes • Cis and trans face ...
... stores and distributes proteins • Proteins from rough ER will be shipped to cell membrane for exocytosis • Produces lysosomes • Cis and trans face ...
Ch. 3 Review - Cobb Learning
... c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs ______ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, long life, and cell specialization. b. generalized cells, longer life, and ability to prey on small animals. c. larger ...
... c. a group of tissues that work together to perform a specific job d. a body structure, such as muscles or lungs ______ 8. The benefits of being multicellular include a. small size, long life, and cell specialization. b. generalized cells, longer life, and ability to prey on small animals. c. larger ...
AQA B2 ESQ - Mitosis and Meiosis 1
... (2 mark) The diagram shows some types of cell division that happen during human reproduction. ...
... (2 mark) The diagram shows some types of cell division that happen during human reproduction. ...
Quiz- Cells/ Photosynthesis/ Respiration
... energy they need. 10. Smallopeningscalled allow carbondioxide to enter a leaf. IL ...
... energy they need. 10. Smallopeningscalled allow carbondioxide to enter a leaf. IL ...
Intro to Cells
... chemicals throughout the cytoplasm • Cytoplasm – all of the fluid in the cell ...
... chemicals throughout the cytoplasm • Cytoplasm – all of the fluid in the cell ...
Grade 11 Biology DP Assignment 3 Cells
... • allow a steady supply of glucose, amino acids, and lipids to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. • remove excess amounts of these nutrients when levels get so high that they are harmful. • allow waste and other products to leave the cell. ...
... • allow a steady supply of glucose, amino acids, and lipids to come into the cell no matter what the external conditions are. • remove excess amounts of these nutrients when levels get so high that they are harmful. • allow waste and other products to leave the cell. ...
Supplementary Materials and Methods
... Cell lines were treated with CPI203 for 4 d, and viability was assessed using resazurin (Sigma). GI50 values were calculated as the concentration at which fluorescence reached 50% of the DMSO control. Cell lines were classified as sensitive if they had a GI50 value of less than or equal to 0.25 M, ...
... Cell lines were treated with CPI203 for 4 d, and viability was assessed using resazurin (Sigma). GI50 values were calculated as the concentration at which fluorescence reached 50% of the DMSO control. Cell lines were classified as sensitive if they had a GI50 value of less than or equal to 0.25 M, ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.