How has animal multicellularity evolved? The quest for the origin of
... phyla. Cadherin’s role in the protists is not clear but may be involved with capturing bacteria for food. Cadherin adhesion complexes may have been a pre-adaptation that facilitated the later evolution of multicellular animals. Cell-cell communication: gap junctions are the main method in animals, w ...
... phyla. Cadherin’s role in the protists is not clear but may be involved with capturing bacteria for food. Cadherin adhesion complexes may have been a pre-adaptation that facilitated the later evolution of multicellular animals. Cell-cell communication: gap junctions are the main method in animals, w ...
Levels of Organization of Life
... –Metabolism: the sum of all chemical activities in an organism. • Stimulus. All living things respond to a stimulus. ...
... –Metabolism: the sum of all chemical activities in an organism. • Stimulus. All living things respond to a stimulus. ...
Mitosis Matching Worksheet
... _______ 10. Some cells can spend almost their entire life cycle in this phase (even 60 YEARS). _______ 11. The centromeres that joins the sister chromatids split, allowing the sister chromatids to separate and become individual chromosomes. _______ 12. The cell membrane is drawn inward until the cyt ...
... _______ 10. Some cells can spend almost their entire life cycle in this phase (even 60 YEARS). _______ 11. The centromeres that joins the sister chromatids split, allowing the sister chromatids to separate and become individual chromosomes. _______ 12. The cell membrane is drawn inward until the cyt ...
9 Weeks Assessment Review (You can use your notebook, green
... 1. Explain where cells come from and how two cells share the same traits. (Example: Two skin cells and each one has 46 chromosomes.) 2. How big are cells? And how does using a model help us understand cells? 3. What is the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell? 4. What does the nucle ...
... 1. Explain where cells come from and how two cells share the same traits. (Example: Two skin cells and each one has 46 chromosomes.) 2. How big are cells? And how does using a model help us understand cells? 3. What is the difference between the plant cell and the animal cell? 4. What does the nucle ...
Key Stage 3 biology lesson plan - plant and animal cells
... Get students to name particular organs within a certain system (for example, the small intestine). Explain how an organ is made up of different types of tissues, which are made up of different types of cells (see the image below). ...
... Get students to name particular organs within a certain system (for example, the small intestine). Explain how an organ is made up of different types of tissues, which are made up of different types of cells (see the image below). ...
Cells and Internal Structures
... *Cells are the smallest unit of life. *All cells come from pre-existing cells. These are the main facts of ...
... *Cells are the smallest unit of life. *All cells come from pre-existing cells. These are the main facts of ...
The Process of Cell Division
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
... Name the main events of the cell cycle. Describe what happens during the four stages of mitosis. Describe the process of cytokinesis. ...
Unit A, Chapter 1, Lesson 1
... All plants and animals have what in common? They are all made up of cells Name three different types of cells. 1.White blood cells 2.Red blood cells 3.Muscle cells Parts of a Cell Even smaller structures in cells are called organelles. Define these plant and animal cell organelles: Cell Membrane – a ...
... All plants and animals have what in common? They are all made up of cells Name three different types of cells. 1.White blood cells 2.Red blood cells 3.Muscle cells Parts of a Cell Even smaller structures in cells are called organelles. Define these plant and animal cell organelles: Cell Membrane – a ...
Cell Cycle and Mitosis Objectives (Chapter 12)
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
... After reading this chapter and attending class, you should be able to: ...
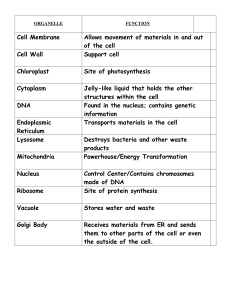
ANSWERS Cell Part or Organelle Is It Found In An Animal Cell? Is It
... 7. Why do Plant cells have cell walls and Animal cells do not? because animal cells use the cell membrane to hold the cell together. this in turn gives the animal cell more flexibility and gives it the ability to use specialized procedures. Also the plants cell wall protects the cell from damage (th ...
... 7. Why do Plant cells have cell walls and Animal cells do not? because animal cells use the cell membrane to hold the cell together. this in turn gives the animal cell more flexibility and gives it the ability to use specialized procedures. Also the plants cell wall protects the cell from damage (th ...
Cell Structure and Function
... All About Cells! Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
... All About Cells! Cells are the most basic unit of life. What are some ways that cells carry out life processes? ...
Cellular Biology Crossword
... solute relative to another solution (cell swells) 3 - This controls the movement (cellular traffic) in and out the cell 5 - Made of one cell 7 - These are the structural and functional units of all living organisms 9 - Composed of microtubules -Supports cell and provides shape 10 - These type of cel ...
... solute relative to another solution (cell swells) 3 - This controls the movement (cellular traffic) in and out the cell 5 - Made of one cell 7 - These are the structural and functional units of all living organisms 9 - Composed of microtubules -Supports cell and provides shape 10 - These type of cel ...
The Cell Cycle
... MAKES MORE ORGANELLES S – A SECOND COPY OF THE CELL’S DNA IS SYNTHESIZED G2 – THE CELL GETS READY FOR DIVISION ...
... MAKES MORE ORGANELLES S – A SECOND COPY OF THE CELL’S DNA IS SYNTHESIZED G2 – THE CELL GETS READY FOR DIVISION ...
Learning Outcomes
... Vesicles and Vacuoles Have Varied Functions 6. Describe the structure and function of lysosomes and peroxisomes. 7. Describe the varied functions of vacuoles and/or vesicles in protists, plants, and animals. A Cell Carries Out Energy Transformations 8. Compare and contrast the structure and function ...
... Vesicles and Vacuoles Have Varied Functions 6. Describe the structure and function of lysosomes and peroxisomes. 7. Describe the varied functions of vacuoles and/or vesicles in protists, plants, and animals. A Cell Carries Out Energy Transformations 8. Compare and contrast the structure and function ...
The Cell Theory
... 1. All living things are made up of 1 or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of function. 3. New cells come from preexisting cells. ...
... 1. All living things are made up of 1 or more cells. 2. The cell is the basic unit of function. 3. New cells come from preexisting cells. ...
Northeast High School GHSGT Junior Academy
... Assessment of this domain focuses on the following: Describing the roles of cell organelles in the following: ...
... Assessment of this domain focuses on the following: Describing the roles of cell organelles in the following: ...
Plant and Animal Cell Lab
... 1. Punch a cork borer through a potato to obtain a cylinder full of potato. 2. Slice a thin piece of potato from the cylinder and make a wet mount slide using iodine. ...
... 1. Punch a cork borer through a potato to obtain a cylinder full of potato. 2. Slice a thin piece of potato from the cylinder and make a wet mount slide using iodine. ...
doc 3.2.1.1 eukaryotes checklist
... The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: •• cell-surface membrane ...
... The structure of eukaryotic cells, restricted to the structure and function of: •• cell-surface membrane ...
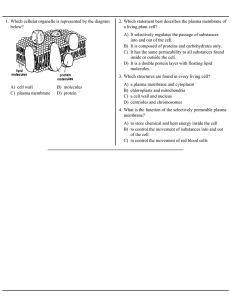
A) cell wall B) molecules C) plasma membrane D) protein 1. Which
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
... 2. Which statement best describes the plasma membrane of a living plant cell? A) It selectively regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. B) It is composed of proteins and carbohydrates only. C) It has the same permeability to all substances found inside or outside the cell. D) I ...
Cell & Tissue Renewal and Cell Death
... a. The rate that cells cycle and divide b. The fraction of cells in the cell cycle (vs. G0 or out of cycle) c. The rate of cell death In multicellular animals, once the periods of embryonic and fetal development and growth are completed, most cells withdraw from the cell cycle. Adult cells can be di ...
... a. The rate that cells cycle and divide b. The fraction of cells in the cell cycle (vs. G0 or out of cycle) c. The rate of cell death In multicellular animals, once the periods of embryonic and fetal development and growth are completed, most cells withdraw from the cell cycle. Adult cells can be di ...
Name Date Class
... 7. _______________ Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not. 8. _______________ The cell’s nucleus is filled with a substance called protein. 9. _______________ The specialized cells in a unicellular organism perform specialized jobs. 10. _______________ Ribosomes are made in a special ...
... 7. _______________ Plant cells have chloroplasts, but animal cells do not. 8. _______________ The cell’s nucleus is filled with a substance called protein. 9. _______________ The specialized cells in a unicellular organism perform specialized jobs. 10. _______________ Ribosomes are made in a special ...
The Diversity of Cells
... - Matthias Schleiden concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that animal tissues were composed of cells. - Rudolf Virchow stated that cells could form only from other cells. - The Cell Theory was created by Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow based off everyone’s obse ...
... - Matthias Schleiden concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that animal tissues were composed of cells. - Rudolf Virchow stated that cells could form only from other cells. - The Cell Theory was created by Schleiden, Schwann, & Virchow based off everyone’s obse ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.