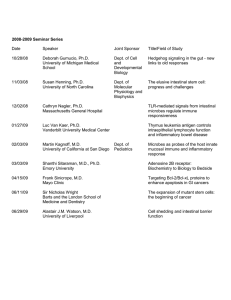
10 E all qs
... Q2: What is facilitated diffusion? A2: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration with the help of channel protein. Q3: What is simple diffusion? A3: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration through the selectively permeable membrane. Q4: What is a ...
... Q2: What is facilitated diffusion? A2: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration with the help of channel protein. Q3: What is simple diffusion? A3: The movement of molecules from an area of high to low concentration through the selectively permeable membrane. Q4: What is a ...
Review Guide Ch. 7 CP
... These are topics and vocabulary terms covered in this chapter which may appear on the chapter test. See chapter guide, warm-ups, quick reviews, and text chapter 7 parts 1 and 2 ...
... These are topics and vocabulary terms covered in this chapter which may appear on the chapter test. See chapter guide, warm-ups, quick reviews, and text chapter 7 parts 1 and 2 ...
biology terms cells mixed
... 2. A ___________________________ is a unicellular organism such as bacteria which is composed of a prokaryotic cell that lack internal membrane-bound structures. 3. ___________________________ means having or consisting of many cells. 4. ___________________________ means having or consisting of a si ...
... 2. A ___________________________ is a unicellular organism such as bacteria which is composed of a prokaryotic cell that lack internal membrane-bound structures. 3. ___________________________ means having or consisting of many cells. 4. ___________________________ means having or consisting of a si ...
Normal Haemopoiesis
... – Gradual replacement of active (red) marrow by inactive (fatty) tissue – Expansion can occur during increased need for cell production ...
... – Gradual replacement of active (red) marrow by inactive (fatty) tissue – Expansion can occur during increased need for cell production ...
Topic Vocabulary Test A
... Organ system - several organs may work together to perform one of the life processes Organelle - specialized structures found in cells that have specific life maintenance functions Organic - Molecules that contain BOTH carbon and hydrogen Receptor molecule - proteins found in the cell membrane that ...
... Organ system - several organs may work together to perform one of the life processes Organelle - specialized structures found in cells that have specific life maintenance functions Organic - Molecules that contain BOTH carbon and hydrogen Receptor molecule - proteins found in the cell membrane that ...
Cells and Homeostasis - Mrs. Blevins` Science
... When Linnaeus developed his system of classification, there were only two kingdoms, Plants and Animals. But the use of the microscope led to the discovery of new organisms and the identification of differences in cells. A two-kingdom ...
... When Linnaeus developed his system of classification, there were only two kingdoms, Plants and Animals. But the use of the microscope led to the discovery of new organisms and the identification of differences in cells. A two-kingdom ...
Developmental Biology I
... …………. instigates & orchestrates cell re-arrangements …………….to give a 3 layered, patterned embryo ...
... …………. instigates & orchestrates cell re-arrangements …………….to give a 3 layered, patterned embryo ...
Completed KWL Chart
... The endoplasmic reticulum can be either smooth or rough and consists of a network of tube-like passageways for proteins made from (grain-like) ribosomes travel to get to the Gogli apparatus. The mitochondria are bean-shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. They su ...
... The endoplasmic reticulum can be either smooth or rough and consists of a network of tube-like passageways for proteins made from (grain-like) ribosomes travel to get to the Gogli apparatus. The mitochondria are bean-shaped structures with a smooth outer membrane and a folded inner membrane. They su ...
Chapter 2 “Cells” Section 1: “Cell Structure
... found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle ...
... found on a hereditary material called DNA Usually the largest organelle ...
Cellular organisation
... Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialise throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. ...
... Unlike animals, many plant cells retain the ability to differentiate and specialise throughout their life. These cells are found in tissues called meristems. ...
Cancer Guided Notes
... • any disease caused by cells that do not have a regulated cell cycle • characterized by _______________________________ • caused by _____________________ that control cell division • some behaviors (smoking, sunlight exposure) can increase risks for developing certain cancers ______________: abnorm ...
... • any disease caused by cells that do not have a regulated cell cycle • characterized by _______________________________ • caused by _____________________ that control cell division • some behaviors (smoking, sunlight exposure) can increase risks for developing certain cancers ______________: abnorm ...
KINGDOM PROTISTA Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena
... KINGDOM PROTISTA Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Volvox, protozoa, and some algae Microscopic but larger than Monerans Eukaryotic – Inside the cell, there are specialised structures called organelles which are surrounded by membranes, such as nucleus (containing DNA), chloroplasts (for photos ...
... KINGDOM PROTISTA Examples: Amoeba, Paramecium, Euglena, Volvox, protozoa, and some algae Microscopic but larger than Monerans Eukaryotic – Inside the cell, there are specialised structures called organelles which are surrounded by membranes, such as nucleus (containing DNA), chloroplasts (for photos ...
Second Meyenburg Lecture at DKFZ: Thea Tlsty to speak on the
... in Preneoplastic Human Cells“ Those of you who attended the Meyenburg lecture in March will already appreciate the excellence of the speakers and the topical themes of the lectures in this series and won’t want to miss the next one. On 17 June 2002, again at 1600 hours in the lecture hall at DKFZ, T ...
... in Preneoplastic Human Cells“ Those of you who attended the Meyenburg lecture in March will already appreciate the excellence of the speakers and the topical themes of the lectures in this series and won’t want to miss the next one. On 17 June 2002, again at 1600 hours in the lecture hall at DKFZ, T ...
Mor-ganelles - JhaveriChemBioWiki
... Cell Wall The cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is on the outside of the cell, outside the cell membrane. It gives support and structure to plant cells. *Notice- plant cells are usually rectangular because of the cell wall ...
... Cell Wall The cell wall is only found in plant cells. It is on the outside of the cell, outside the cell membrane. It gives support and structure to plant cells. *Notice- plant cells are usually rectangular because of the cell wall ...
Overview of Cell Structure
... Outline the major concepts of the cell theory. What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? Describe the function of the nucleus. What are chromosomes and genes? Describe the function of the cell membrane. Describe the structure and function of centrioles. Why would muscle tissu ...
... Outline the major concepts of the cell theory. What is the difference between a prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell? Describe the function of the nucleus. What are chromosomes and genes? Describe the function of the cell membrane. Describe the structure and function of centrioles. Why would muscle tissu ...
Functions of Cell Structures
... Functions of Cell Structures page. Contains chlorophyll that changes sunlight into food Collects and stores food, water, and waste Produces the cells energy – “power plant” Directs materials inside the cell where to go Stiff wall that protects the cell membrane ...
... Functions of Cell Structures page. Contains chlorophyll that changes sunlight into food Collects and stores food, water, and waste Produces the cells energy – “power plant” Directs materials inside the cell where to go Stiff wall that protects the cell membrane ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.