GCSE Cells Topic Learning Checklist
... Explain how to prepare an uncontaminated culture (biology only) B1.2 Cell division Recall that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each ...
... Explain how to prepare an uncontaminated culture (biology only) B1.2 Cell division Recall that the nucleus of a cell contains chromosomes made of DNA molecules. Each ...
Research into human body cell behaviour reveals
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
... allows us to have more complex functions than single cell organisms like yeast and bacteria. Cell specialization allows us to do things like hear, Provided by University of Western Australia pump blood and walk. "To make all of this work the human body has evolved protein messages that are used to c ...
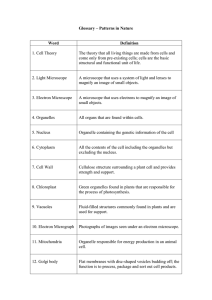
Glossary – Patterns in Nature
... Vascular tissue in plants that transports organic molecules (food) up and down the plant. ...
... Vascular tissue in plants that transports organic molecules (food) up and down the plant. ...
Biology Test 1 Study Guide – Things to know
... 21. Name the type of bond that forms between amino acids. 22. Describe the importance of CHNO. 23. Name the four organic compounds, the elements found in each, their primary functions, examples, and the subunits that make them up. 24. Describe the difference in a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid ...
... 21. Name the type of bond that forms between amino acids. 22. Describe the importance of CHNO. 23. Name the four organic compounds, the elements found in each, their primary functions, examples, and the subunits that make them up. 24. Describe the difference in a saturated and unsaturated fatty acid ...
Chapter 3
... The following terms are freely used in your textbook. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram desc ...
... The following terms are freely used in your textbook. Make sure you know what they mean, how they are used, and how to use them. When an example is given, make sure you can describe and recall it. If a picture is provided, know what the structure looks like and where it is located. If a diagram desc ...
Programmed Cell Death(Apoptosis)
... 2- limiting spread of virus through the host organism. DNA damage, programmed cell death may eliminate cells carrying potentially harmful mutations, including cells with mutations that might lead to the development of cancer. During development, programmed cell death plays a key role by eliminating ...
... 2- limiting spread of virus through the host organism. DNA damage, programmed cell death may eliminate cells carrying potentially harmful mutations, including cells with mutations that might lead to the development of cancer. During development, programmed cell death plays a key role by eliminating ...
Study Guide - Effingham County Schools
... 1. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound ____________________ that have a specific function to help the cell carry out life. 2. Any unicellular or multicellular organism that has a nucleus and other organelles within its cell or cells is called a ______________________. 3. __________ ...
... 1. Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and membrane-bound ____________________ that have a specific function to help the cell carry out life. 2. Any unicellular or multicellular organism that has a nucleus and other organelles within its cell or cells is called a ______________________. 3. __________ ...
Gross anatomy Microscopic anatomy Physiology Histology Organ
... organism and its parts The study of tissue ...
... organism and its parts The study of tissue ...
Document
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
... ___ 19.Chloroplasts are organelles that are found in the cells of a. animals. c. mitochondria. b. plants and algae. d. all eukaryotic cells. ___ 20.Which process happens inside a chloroplast? a. production of ATP c. photosynthesis b. production of DNA d. formation of animal cells ___ 21.Chloroplasts ...
Notes on Unit 7A Cells
... We are made up from organs. Organs might work together in an organ system, such as the digestive system. Organs are made up from special tissues. Tissues are made from cells, which do special things. We are multi-cellular because we are made from many, many cells. We use a microscope to look at cell ...
... We are made up from organs. Organs might work together in an organ system, such as the digestive system. Organs are made up from special tissues. Tissues are made from cells, which do special things. We are multi-cellular because we are made from many, many cells. We use a microscope to look at cell ...
Cells
... • A. Cells are the basic unit of life. • B. All organisms are made of one or more cells. • C. All cells come from existing cells. ...
... • A. Cells are the basic unit of life. • B. All organisms are made of one or more cells. • C. All cells come from existing cells. ...
DNA and Chromosomes
... Why is cell division important anyway?? We are very different than other species. BUT what we do have in common with them is that almost all multicellular organisms are made of trillions of cells. ...
... Why is cell division important anyway?? We are very different than other species. BUT what we do have in common with them is that almost all multicellular organisms are made of trillions of cells. ...
Wet Mount
... threads. At other times, only small branches will be seen. Yeast normally live in the vagina, but only in very small numbers. If you visualize any yeast in your sample, it is considered significant. Trichomonas is best seen on the Normal Saline slide. These protozoans are about the same size as a wh ...
... threads. At other times, only small branches will be seen. Yeast normally live in the vagina, but only in very small numbers. If you visualize any yeast in your sample, it is considered significant. Trichomonas is best seen on the Normal Saline slide. These protozoans are about the same size as a wh ...
Prokaryotic Cells Eukaryotic Cells
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
... -‐Be able to label at least 10 organelles in a Eukaryotic cell -‐Know how eukaryotic cells obtain energy -‐Be able to compare and contrast Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells (size, age, complexity, struc ...
Cells Alive- Internet Lesson
... Part A: Animal Cell Model – Go to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, Click on CELL MODELS. For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. ...
... Part A: Animal Cell Model – Go to the "Cell Biology" link to access this page, Click on CELL MODELS. For this model, you will need to click on the various parts of the cell to go to a screen that tells you about the parts. Answers to the following questions are found there. ...
5.5 Multicellular Life • How does an organism benefit by being able
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
... • Tissues are groups of cells that perform a similar function. • Organs are groups of tissues that perform a specific or related function. • Organ systems are groups of organs that carry out similar functions. ...
Cell Membrane Nucleus Cytoplasm Cell Wall Ribosome Reticulum
... membrane, tubes, can be smooth or rough ...
... membrane, tubes, can be smooth or rough ...
CELLS: What are they?
... Here are the parts you need to know: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, and chloroplasts. The cell membrane protects the cell and controls what substances enter and leave it. The nucleus is the cell’s control center. Genetic information is stored in the nucleus. The cell wall gives the pl ...
... Here are the parts you need to know: cell membrane, cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, and chloroplasts. The cell membrane protects the cell and controls what substances enter and leave it. The nucleus is the cell’s control center. Genetic information is stored in the nucleus. The cell wall gives the pl ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.