The Cell Theory - isgroeducationNSW
... structural unit (the building blocks) of all living things. They carry out various functions. Simple living things consist of only one cell. They are called prokaryotic organisms. Organisms that have more than one cell are called eukaryotic organisms ...
... structural unit (the building blocks) of all living things. They carry out various functions. Simple living things consist of only one cell. They are called prokaryotic organisms. Organisms that have more than one cell are called eukaryotic organisms ...
Cell Study Guide
... required to successfully clone certain cells using tissue culture. Three cell samples were placed in three different salt solutions and their change in mass was recorded in the data table shown below. ...
... required to successfully clone certain cells using tissue culture. Three cell samples were placed in three different salt solutions and their change in mass was recorded in the data table shown below. ...
Regulation of the Cell Cycle / Cancer
... Regulating Cell Division • Multicellular organisms must regulate cell division – Constantly replace skin and digestive cells – Brain cells (neurons) should not divide – Liver cells only divide to repair damage ...
... Regulating Cell Division • Multicellular organisms must regulate cell division – Constantly replace skin and digestive cells – Brain cells (neurons) should not divide – Liver cells only divide to repair damage ...
LS. 2 Notes
... IV. Cellular Transport A. In endocytosis, the cell engulfs some of its extracellular fluid, including material dissolved or suspended in it. A portion of the plasma membrane is invaginated and pinched off forming a membrane-bounded vesicle called an endosome. Endocytosis removes portions of the plas ...
... IV. Cellular Transport A. In endocytosis, the cell engulfs some of its extracellular fluid, including material dissolved or suspended in it. A portion of the plasma membrane is invaginated and pinched off forming a membrane-bounded vesicle called an endosome. Endocytosis removes portions of the plas ...
Cells - WordPress.com
... structure in cytoplasm. • Helps the cell maintain or change its shape. • Made of protein. ...
... structure in cytoplasm. • Helps the cell maintain or change its shape. • Made of protein. ...
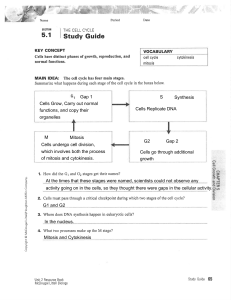
5.1 Study Guide KEY
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
... The rate of cell division is linked to the body's need for that type of cell. Skin cells are typically exposed to more damaging conditions and must be replaced more often than liver cells. ...
$doc.title
... Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? ...
... Create a model to illustrate how prokaryotic DNA is divided for cell reproduction. What is this process called? How are the two cells related to each other genetically? ...
Study Sheet for Chapter 4 Test
... 14. Trace path of protein-what happens at each position: In ROUGH ER by a bound ribosome-______________________________________ How does the protein change as it travels through the RER?___________________ Short chains of sugars added to the polypeptide change it into:_________________ How transport ...
... 14. Trace path of protein-what happens at each position: In ROUGH ER by a bound ribosome-______________________________________ How does the protein change as it travels through the RER?___________________ Short chains of sugars added to the polypeptide change it into:_________________ How transport ...
Standard
... communicate how natural life science context. (cell parts) systems work and interact. 2. Tissue, organs and organ systems are composed of cells and function to serve the needs of all cells for food, air and waste removal. ...
... communicate how natural life science context. (cell parts) systems work and interact. 2. Tissue, organs and organ systems are composed of cells and function to serve the needs of all cells for food, air and waste removal. ...
Honors Biology Review Chapter 4 Test
... 14. Trace path of protein-what happens at each position: In ROUGH ER by a bound ribosome-______________________________________ How does the protein change as it travels through the RER?___________________ Short chains of sugars added to the polypeptide change it into:_________________ How transport ...
... 14. Trace path of protein-what happens at each position: In ROUGH ER by a bound ribosome-______________________________________ How does the protein change as it travels through the RER?___________________ Short chains of sugars added to the polypeptide change it into:_________________ How transport ...
Name
... 26. _____________________: command center of cell 27. _____________________: transports proteins to golgi 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, ...
... 26. _____________________: command center of cell 27. _____________________: transports proteins to golgi 28. ______________________: makes proteins 29. ______________________: “powerhouse” of cell; makes energy 30. _____________________: garbage man; cleans up and digests proteins, viruses, lipids, ...
PDF
... (imprinted) expression of a subset of mammalian genes. For example, the paternally expressed imprinted long noncoding (lnc) RNA Airn initiates paternal-specific silencing of Igf2r, a gene that is essential for development. Airn initiation of Igf2r silencing is followed by gain of DNA methylation on ...
... (imprinted) expression of a subset of mammalian genes. For example, the paternally expressed imprinted long noncoding (lnc) RNA Airn initiates paternal-specific silencing of Igf2r, a gene that is essential for development. Airn initiation of Igf2r silencing is followed by gain of DNA methylation on ...
Structure and function of the cell
... Less flexible than cell membrane Gives plant cells the ability to stand up and grow into trees, flowers etc. Cell wall is thicker than cell membrane ...
... Less flexible than cell membrane Gives plant cells the ability to stand up and grow into trees, flowers etc. Cell wall is thicker than cell membrane ...
THE CELL
... Cell membrane The _____________ _____________ ______________ describes the structure of the plasma membrane. The membrane is seen as a ____________ of phospholipids in which protein molecules are embedded. Fluid = ______________. Mosaic = _____________ ______________. Ribosomes Found in the ________ ...
... Cell membrane The _____________ _____________ ______________ describes the structure of the plasma membrane. The membrane is seen as a ____________ of phospholipids in which protein molecules are embedded. Fluid = ______________. Mosaic = _____________ ______________. Ribosomes Found in the ________ ...
Unit 3: Cells Study Guide Write the correct letter in the blank provided
... _____ 3. This is the gel like material that holds all the other organelles in place inside the cell. _____ 4. This organelle surrounds plant cells, gives protection and shape to the cell. _____ 5. This organelle is responsible for processing, sorting and delivering proteins. _____ 6. This organelle ...
... _____ 3. This is the gel like material that holds all the other organelles in place inside the cell. _____ 4. This organelle surrounds plant cells, gives protection and shape to the cell. _____ 5. This organelle is responsible for processing, sorting and delivering proteins. _____ 6. This organelle ...
Cell Organelle Chart
... Suspends and supports the cell’s organelles Place where many of the cells most important chemical activities occur. ...
... Suspends and supports the cell’s organelles Place where many of the cells most important chemical activities occur. ...
Cells A cell is the basic unit of structure and function in all living
... The organelles in a cell have specific jobs, and their activities are coordinated to maintain homeostasis. Not all cells have all the same organelles. Example: Chloroplasts ...
... The organelles in a cell have specific jobs, and their activities are coordinated to maintain homeostasis. Not all cells have all the same organelles. Example: Chloroplasts ...
SPECIALIZED CELLS
... – Line organs like the stomach – Surround the outside of organs – Make the outer layer of skin ...
... – Line organs like the stomach – Surround the outside of organs – Make the outer layer of skin ...
Cell Theory and Viruses - Hicksville Public Schools / Homepage
... Can magnify up to a million times Subject must be dead and dry ...
... Can magnify up to a million times Subject must be dead and dry ...
cell wall - Johnston Community College
... permit the interaction of changes inside and outside the cell. ...
... permit the interaction of changes inside and outside the cell. ...
NAME DIABETES Energy our body needs comes from
... If a lump/tumor isn’t doing any harm, we call it a _________ ___________; meaning it’s ______________. If an abnormal cell grows like crazy and starts to infiltrate other tissue, and mutate more frequently, this group of cells are _______________ ______________. ...
... If a lump/tumor isn’t doing any harm, we call it a _________ ___________; meaning it’s ______________. If an abnormal cell grows like crazy and starts to infiltrate other tissue, and mutate more frequently, this group of cells are _______________ ______________. ...
Prokaryotic vs Eukaryotic cells Prokaryotes
... • No nuclear membrane: (genetic material dispersed throughout cytoplasm) the DNA is clumped in an area but there is no organized nucleus with a membrane. • Simple internal structure: Prokaryotes do not usually have any organelles. They will probably have ribosomes inside of their cells, but ribosom ...
... • No nuclear membrane: (genetic material dispersed throughout cytoplasm) the DNA is clumped in an area but there is no organized nucleus with a membrane. • Simple internal structure: Prokaryotes do not usually have any organelles. They will probably have ribosomes inside of their cells, but ribosom ...
1 - Evolving Sciences
... 2. Arrange the following in order from smallest to largest organelle Cell tissue Organ, organ system., Organism, , , 3. What is a tissue? ...
... 2. Arrange the following in order from smallest to largest organelle Cell tissue Organ, organ system., Organism, , , 3. What is a tissue? ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.