Features of Cells and Prokaryotes: Worksheet 2
... g. peroxisomes h. plasma membrane 7. The ____Paladae’s pulse-chase experiment_____ was used to determine the pathway a protein takes through the endomembrane system by using radioactive amino acids Explanation of ‘pulse-chase’: researchers administered a pulse of radioactive amino acids to the cells ...
... g. peroxisomes h. plasma membrane 7. The ____Paladae’s pulse-chase experiment_____ was used to determine the pathway a protein takes through the endomembrane system by using radioactive amino acids Explanation of ‘pulse-chase’: researchers administered a pulse of radioactive amino acids to the cells ...
Cells—The Units of Life
... boundary of the cell and helps control what enters and exits the cell; some cells have a cell wall that helps support and protect the cell. ...
... boundary of the cell and helps control what enters and exits the cell; some cells have a cell wall that helps support and protect the cell. ...
Objectives Cell unit
... 10. label organelles on diagrams of typical plant and animal cells 11. work cooperatively with team members to develop and construct models of cells 12. distinguish between typical plant and animal cells 13. produce labeled drawings of each type of cell 14. list three differences between plant and a ...
... 10. label organelles on diagrams of typical plant and animal cells 11. work cooperatively with team members to develop and construct models of cells 12. distinguish between typical plant and animal cells 13. produce labeled drawings of each type of cell 14. list three differences between plant and a ...
Document
... a. Most cells are too small to be seen without a microscope. b. All organisms are made of one or more cells c. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. d. All cells come from existing cells. ...
... a. Most cells are too small to be seen without a microscope. b. All organisms are made of one or more cells c. The cell is the basic unit of all living things. d. All cells come from existing cells. ...
The Microscope
... • Observed living blood cells, and bacteria a few years later • Leeuwenhoek is called the “father of ...
... • Observed living blood cells, and bacteria a few years later • Leeuwenhoek is called the “father of ...
Apoptosis
... 488 nm with a broad emission centered around 600 nm. Since PI can also bind to doublestranded RNA, it is necessary to treat the cells with RNase for optimal DNA resolution. The excitation of PI at 488 nm facilitates its use on the benchtop cytomters. [PI can also be excited in the UV (351-364 nm lin ...
... 488 nm with a broad emission centered around 600 nm. Since PI can also bind to doublestranded RNA, it is necessary to treat the cells with RNase for optimal DNA resolution. The excitation of PI at 488 nm facilitates its use on the benchtop cytomters. [PI can also be excited in the UV (351-364 nm lin ...
cells - Biology I
... Pasteur definitively demonstrated that microorganisms are present in air but not created by air. This was critical for refutation of the concept of spontaneous generation and the for development of germ ...
... Pasteur definitively demonstrated that microorganisms are present in air but not created by air. This was critical for refutation of the concept of spontaneous generation and the for development of germ ...
Force Microscopy of Non-adherent Cells: A Comparison of
... • Used microfabricated wells to trap cells • Array of 8 – 20 µm diameter wells •Jurkat and HL60 cells trapped in 13.6 µm wells 50 µm ...
... • Used microfabricated wells to trap cells • Array of 8 – 20 µm diameter wells •Jurkat and HL60 cells trapped in 13.6 µm wells 50 µm ...
The Cell Theory
... Modern Cell Theory contains 4 statements, in addition to the original Cell Theory: ...
... Modern Cell Theory contains 4 statements, in addition to the original Cell Theory: ...
Onion Root Lab - Meester Martinez
... Onion, a garden plant of the lily family, closely related to the leek, garlic, chive, and shallot. The bulb of the onion plant, also called onion, is widely used as a seasoning and is eaten as a vegetable. Although onions have little food value, they impart a desirable flavor to stews, soups, ham ...
... Onion, a garden plant of the lily family, closely related to the leek, garlic, chive, and shallot. The bulb of the onion plant, also called onion, is widely used as a seasoning and is eaten as a vegetable. Although onions have little food value, they impart a desirable flavor to stews, soups, ham ...
Study Guide Review packet Lessons 1
... iii. The basic shape and size (compared to the field of view) are done carefully to be accurate. iv. Visible features are carefully drawn as seen (ex: structures and organelles) v. Label cellular features, such as nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane/cell wall OUTSIDE of the circle. The term is written ...
... iii. The basic shape and size (compared to the field of view) are done carefully to be accurate. iv. Visible features are carefully drawn as seen (ex: structures and organelles) v. Label cellular features, such as nucleus, cytoplasm, cell membrane/cell wall OUTSIDE of the circle. The term is written ...
Plant cells - Sackville School
... Cell structure and function • Cells are the ‘building blocks’ of living organisms. • Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. • All cells have the same overall structure (cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus) that allow them to carry out the basic life processes - but some are c ...
... Cell structure and function • Cells are the ‘building blocks’ of living organisms. • Cells are so small that you need a microscope to see them. • All cells have the same overall structure (cell membrane, cytoplasm and a nucleus) that allow them to carry out the basic life processes - but some are c ...
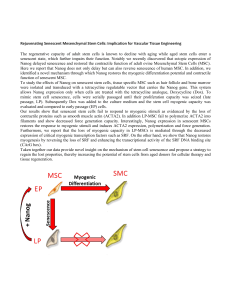
Rejuvenating Senescent Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implication for
... Rejuvenating Senescent Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implication for Vascular Tissue Engineering The regenerative capacity of adult stem cells is known to decline with aging while aged stem cells enter a senescent state, which further impairs their function. Notably we recently discovered that ectopic exp ...
... Rejuvenating Senescent Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Implication for Vascular Tissue Engineering The regenerative capacity of adult stem cells is known to decline with aging while aged stem cells enter a senescent state, which further impairs their function. Notably we recently discovered that ectopic exp ...
Cell Division and Reproduction
... _____________ cell division. __________ involves a complex series of ___________ in the _________ of body cells that produce ______________ (same) ______________ cells. o They have the __________ number and __________ of ___________________ as the _______________ cells. The Cell Cycle – Stages of ...
... _____________ cell division. __________ involves a complex series of ___________ in the _________ of body cells that produce ______________ (same) ______________ cells. o They have the __________ number and __________ of ___________________ as the _______________ cells. The Cell Cycle – Stages of ...
Cell City Analogy
... Organelle – is the small specialized structures found inside a cell that perform a specific function. The cell is a fabulous piece of machinery. All tiny intricate parts or organelles work together to make the cell function properly. We can compare cells to real-life structures that enable us to bet ...
... Organelle – is the small specialized structures found inside a cell that perform a specific function. The cell is a fabulous piece of machinery. All tiny intricate parts or organelles work together to make the cell function properly. We can compare cells to real-life structures that enable us to bet ...
Science Background Living Systems: Cells and the Five Kingdoms
... ¸ A cell is a microscopic, living structure. ¸ Even though they are very tiny, cells have identifiable parts and we can observe them with microscopes. ¸ Cells come in different sizes and shapes and behave in different ways. ...
... ¸ A cell is a microscopic, living structure. ¸ Even though they are very tiny, cells have identifiable parts and we can observe them with microscopes. ¸ Cells come in different sizes and shapes and behave in different ways. ...
APh/BE161: Physical Biology of the Cell Winter
... Figure 1 The photoperiodic response of long-day insects which are induced to enter diapause when the daylight hours falls below a certain level. The four species shown here, Laspeyresia molesta, Pieris brassicae, Acronycta rumicis, and Leptinotarsa decemlineata each leaves diapause when daylight is ...
... Figure 1 The photoperiodic response of long-day insects which are induced to enter diapause when the daylight hours falls below a certain level. The four species shown here, Laspeyresia molesta, Pieris brassicae, Acronycta rumicis, and Leptinotarsa decemlineata each leaves diapause when daylight is ...
Cells: The Basic Unit of Life - Warren County Public Schools
... The first cell of a chicken is the yolk with a tiny white dot in it. It is surrounded by a clear jellylike fluid called egg white. The white dot divides over and over again to become a chick. ...
... The first cell of a chicken is the yolk with a tiny white dot in it. It is surrounded by a clear jellylike fluid called egg white. The white dot divides over and over again to become a chick. ...
1590 Two Dutch eye glass makers, Zaccharias
... The father of microscopy, Anton Van Leeuwenhoek of Holland (1632-1723), started as an apprentice in a dry goods store where magnifying glasses were used to count the threads in cloth. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was inspired by the glasses used by drapers to inspect the quality of cloth. He taught himsel ...
... The father of microscopy, Anton Van Leeuwenhoek of Holland (1632-1723), started as an apprentice in a dry goods store where magnifying glasses were used to count the threads in cloth. Anton van Leeuwenhoek was inspired by the glasses used by drapers to inspect the quality of cloth. He taught himsel ...
Supplementary Material Supplementary Figure 1. HPLC purification
... Methods section and analyzed at the University of Western Ontario (UWO) Biological Mass Spectrometry Laboratory. ...
... Methods section and analyzed at the University of Western Ontario (UWO) Biological Mass Spectrometry Laboratory. ...
Human Structure and Function (HUMB1000) – UNIT NOTES
... - groups of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 5) Organ level : tissues of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 6) system level: one or more organs make up a system 7) Organism level: all the systems make up a organism ...
... - groups of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 5) Organ level : tissues of cells that are grouped together having the same goal 6) system level: one or more organs make up a system 7) Organism level: all the systems make up a organism ...
Cells
... • Plants’ cell walls are made of cellulose, a complex sugar. This is why celery crunches when you bite it. • Chloroplasts have their own membranes and DNA. They contain chlorophyll, which makes them green. This is also what traps the energy of sunlight. ...
... • Plants’ cell walls are made of cellulose, a complex sugar. This is why celery crunches when you bite it. • Chloroplasts have their own membranes and DNA. They contain chlorophyll, which makes them green. This is also what traps the energy of sunlight. ...
Cheek Observation
... Cheek Cell Slide Preparation Obtain a clean slide. Place 1 drop of stain in the middle of the slide. Scrape cells from the inside of your cheek. Stir them in the stain. Add a cover slip. Sketch (½ page) a cell on high power. Label all visible structures to the best of your abilities. ...
... Cheek Cell Slide Preparation Obtain a clean slide. Place 1 drop of stain in the middle of the slide. Scrape cells from the inside of your cheek. Stir them in the stain. Add a cover slip. Sketch (½ page) a cell on high power. Label all visible structures to the best of your abilities. ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.