Specialised cells worksheet.
... • Large surface area, for ________ to pass through. • Contains haemoglobin, which joins with oxygen. • Has no _________. ...
... • Large surface area, for ________ to pass through. • Contains haemoglobin, which joins with oxygen. • Has no _________. ...
MAIN IDEAS
... June 15th, 2017. object into view; moves the tube up and down Phases of matter MATTER ...
... June 15th, 2017. object into view; moves the tube up and down Phases of matter MATTER ...
Cell Organelles - Taran D. Thompson
... cell and maintain its shape • It is made up of microtubules and microfilaments. ...
... cell and maintain its shape • It is made up of microtubules and microfilaments. ...
Cell Organelles
... Large central vacuole usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. ...
... Large central vacuole usually in plant cells Many smaller vacuoles in animal cells Storage container for water, food, enzymes, wastes, pigments, etc. ...
Biology_Review_2012
... 26. During ____________________ the nucleus of the cell divides 27. Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called __________________________ 28. _________________________ is the longest stage of cell division 29. A ______________________ is a test in which a sample of living cells is remov ...
... 26. During ____________________ the nucleus of the cell divides 27. Water moves through a cell membrane by a process called __________________________ 28. _________________________ is the longest stage of cell division 29. A ______________________ is a test in which a sample of living cells is remov ...
of the cell - MrMsciences
... cell; 7nm wide •Selective permeability - allows some molecules to pass through while keeping others out. •Transport proteins- special tunnels or doors that only let in specific molecules ...
... cell; 7nm wide •Selective permeability - allows some molecules to pass through while keeping others out. •Transport proteins- special tunnels or doors that only let in specific molecules ...
Venn Diagram Organelles sgi_cell_ss_4
... On the second screen of the simulation you will see a column with 12 cell organelles and structures. Roll your mouse over each cell organelle or structure to read some information about it. Your task is to build a typical animal cell and a typical plant cell. To build each type of cell, drag the app ...
... On the second screen of the simulation you will see a column with 12 cell organelles and structures. Roll your mouse over each cell organelle or structure to read some information about it. Your task is to build a typical animal cell and a typical plant cell. To build each type of cell, drag the app ...
CELLS
... Cells have different sizes, shapes and parts. Their appearance will reflect their function. ...
... Cells have different sizes, shapes and parts. Their appearance will reflect their function. ...
Answers to Cell Lab
... 6. In what ways are Elodea cells different from onion cells? What organelle does Elodea have that the onion does not? Why might this be so? The Elodea has chloroplasts and the onion cells did not. The onion cells that we were looking at are found below ground where the sun doesn’t shine; therefore, ...
... 6. In what ways are Elodea cells different from onion cells? What organelle does Elodea have that the onion does not? Why might this be so? The Elodea has chloroplasts and the onion cells did not. The onion cells that we were looking at are found below ground where the sun doesn’t shine; therefore, ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells Guiding Questions: What are the
... Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells (prokaryotes) ...
... Characteristics of Prokaryotic Cells (prokaryotes) ...
Microscopy Lab: Prokaryotes vs. Eukaryotes Study Guide Prokaryotes
... Please Note!!: These images are provided to assist your studying for the PostLab quiz since you are not able to bring a microscope home with you. However, you are also still responsible for the information about these cells contained in the Lab Sheets that you used to guide you through the lab AND t ...
... Please Note!!: These images are provided to assist your studying for the PostLab quiz since you are not able to bring a microscope home with you. However, you are also still responsible for the information about these cells contained in the Lab Sheets that you used to guide you through the lab AND t ...
Powerpoint Presentation: Extra
... Mechanical, they give tissues strength and elasticity Protection against extracellular change and retention of water Control of cell behaviour by binding of growth factors and interaction with cellsurface receptors ...
... Mechanical, they give tissues strength and elasticity Protection against extracellular change and retention of water Control of cell behaviour by binding of growth factors and interaction with cellsurface receptors ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cell Venn Diagram
... BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. BI2. b. Students know only certain cells in a multicellular organism undergo meios ...
... BI2. a. Students know meiosis is an early step in sexual reproduction in which the pairs of chromosomes separate and segregate randomly during cell division to produce gametes containing one chromosome of each type. BI2. b. Students know only certain cells in a multicellular organism undergo meios ...
prokaryote and eukaryote
... Can be unicellular or multi-cellular organisms. Some have cilia -hair-like structures that protrude from their cells. – helps some cells move through their environment. – On other cells helps move substances across their surfaces. ...
... Can be unicellular or multi-cellular organisms. Some have cilia -hair-like structures that protrude from their cells. – helps some cells move through their environment. – On other cells helps move substances across their surfaces. ...
Cells and Cell Processes Final Review
... Which diagram below represents one type of human tissue? (The diagrams are not drawn to scale.) ...
... Which diagram below represents one type of human tissue? (The diagrams are not drawn to scale.) ...
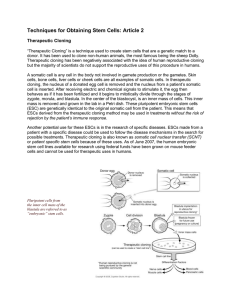
Techniques for Obtaining Stem Cells: Article 2 Therapeutic Cloning
... Therapeutic cloning has been negatively associated with the idea of human reproductive cloning but the majority of scientists do not support the reproductive uses of this procedure in humans. A somatic cell is any cell in the body not involved in gamete production or the gametes. Skin cells, bone ce ...
... Therapeutic cloning has been negatively associated with the idea of human reproductive cloning but the majority of scientists do not support the reproductive uses of this procedure in humans. A somatic cell is any cell in the body not involved in gamete production or the gametes. Skin cells, bone ce ...
Cells and organelles 1. Name the type of cell below Animal cell 2
... 18.Which tissue contracts to make parts move? 19.Which tissue makes covering layers? 20.Describe the function of the muscular tissue in the stomach 21.Describe the function of the epithelial tissue in the stomach ...
... 18.Which tissue contracts to make parts move? 19.Which tissue makes covering layers? 20.Describe the function of the muscular tissue in the stomach 21.Describe the function of the epithelial tissue in the stomach ...
CELLS LESSON
... Enduring Understanding: Cells have distinct and separate organelles which perform all the life functions for their survival. ...
... Enduring Understanding: Cells have distinct and separate organelles which perform all the life functions for their survival. ...
Cell
... • Name means “small room” • Basic structural, functional and biological unit of all KNOWN living organisms • Smallest unit of life that can replicate independently ...
... • Name means “small room” • Basic structural, functional and biological unit of all KNOWN living organisms • Smallest unit of life that can replicate independently ...
Active Transport Small particles such as water, carbon dioxide and
... Small particles such as water, carbon dioxide and oxygen diffuse freely through the cell membrane yet there are other larger particles that the cell needs that cannot be obtained through diffusion. For example cells need glucose for energy. The glucose is present in low concentrations in your blood ...
... Small particles such as water, carbon dioxide and oxygen diffuse freely through the cell membrane yet there are other larger particles that the cell needs that cannot be obtained through diffusion. For example cells need glucose for energy. The glucose is present in low concentrations in your blood ...
Cell Structure Notes - Center Grove Schools
... – A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste out of the cell (semipermeable) ...
... – A cell membrane allows food and oxygen into the cell and waste out of the cell (semipermeable) ...
Ch 7.1 notes
... a. Images are produced by tracing surfaces of samples with a fine probe. C. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. 2. All cells: a. are surrounded by a barrier called a cell membrane. b. at some point contain DNA. 3. Cells are classified into two categories, depen ...
... a. Images are produced by tracing surfaces of samples with a fine probe. C. Prokaryotes and Eukaryotes 1. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes. 2. All cells: a. are surrounded by a barrier called a cell membrane. b. at some point contain DNA. 3. Cells are classified into two categories, depen ...
Cellular differentiation

In developmental biology, cellular differentiation isa cell changes from one cell type to another. Most commonly this is a less specialized type becoming a more specialized type, such as during cell growth. Differentiation occurs numerous times during the development of a multicellular organism as it changes from a simple zygote to a complex system of tissues and cell types. Differentiation continues in adulthood as adult stem cells divide and create fully differentiated daughter cells during tissue repair and during normal cell turnover. Some differentiation occurs in response to antigen exposure. Differentiation dramatically changes a cell's size, shape, membrane potential, metabolic activity, and responsiveness to signals. These changes are largely due to highly controlled modifications in gene expression and are the study of epigenetics. With a few exceptions, cellular differentiation almost never involves a change in the DNA sequence itself. Thus, different cells can have very different physical characteristics despite having the same genome.A cell that can differentiate into all cell types of the adult organism is known as pluripotent. Such cells are called embryonic stem cells in animals and meristematic cells in higher plants. A cell that can differentiate into all cell types, including the placental tissue, is known as totipotent. In mammals, only the zygote and subsequent blastomeres are totipotent, while in plants many differentiated cells can become totipotent with simple laboratory techniques. In cytopathology, the level of cellular differentiation is used as a measure of cancer progression. ""Grade"" is a marker of how differentiated a cell in a tumor is.