Properties of Enzymes
... Many competitive inhibitors are substrate analogs. Compound (b) designed as an inhibitor of the enzyme purine nucleoside phosphorylase, that utilizes guanosine (a) as a substrate. (b) is a possible drug for the treatment of arthritis. Figure 5.13 ...
... Many competitive inhibitors are substrate analogs. Compound (b) designed as an inhibitor of the enzyme purine nucleoside phosphorylase, that utilizes guanosine (a) as a substrate. (b) is a possible drug for the treatment of arthritis. Figure 5.13 ...
Enzymes - NVHSIntroBioPiper1
... molecule binds to another spot on the enzyme causing it to change shape and become inactive ...
... molecule binds to another spot on the enzyme causing it to change shape and become inactive ...
Access Slides - Science Signaling
... causes resistance to leptin signaling believed to occur in dietinduced obesity. Although leptin binds normally to its cell surface receptor (1) and phosphorylates Jak2 (2), the receptor complex comes into proximity with PTP1B on the ER (3). There, PTP1B dephosphorylates Jak2, blocking the phosphoryl ...
... causes resistance to leptin signaling believed to occur in dietinduced obesity. Although leptin binds normally to its cell surface receptor (1) and phosphorylates Jak2 (2), the receptor complex comes into proximity with PTP1B on the ER (3). There, PTP1B dephosphorylates Jak2, blocking the phosphoryl ...
Enzymes
... Why are enzymes important? •Without catalysts reactions would be too slow •Needed to sustain life ...
... Why are enzymes important? •Without catalysts reactions would be too slow •Needed to sustain life ...
L5 Metabolism Part2 Fa08
... • Necessary for some enzymatic reactions • E.g., iron, zinc, copper, many vitamins – Coenzyme – when the cofactor is an organic molecule ...
... • Necessary for some enzymatic reactions • E.g., iron, zinc, copper, many vitamins – Coenzyme – when the cofactor is an organic molecule ...
Multiple Choice Enzymes and Resp Answers
... Data Analysis Question At the start of glycolysis, glucose is phosphorylated to produce glucose 6-phosphate, which is converted into fructose 6-phosphate. A second phosphorylation reaction is then carried out, in which fructose 6-phosphate is converted into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. This reaction i ...
... Data Analysis Question At the start of glycolysis, glucose is phosphorylated to produce glucose 6-phosphate, which is converted into fructose 6-phosphate. A second phosphorylation reaction is then carried out, in which fructose 6-phosphate is converted into fructose 1,6-bisphosphate. This reaction i ...
7.6 Enzymes – summary of mark schemes
... end-product can inhibit enzyme needed for early / first step in metabolic pathway; negative feedback since increased level of product decreases rate of its own production; metabolic pathway regulated according to the requirement for its end-product; idea that inhibition is reversible; ...
... end-product can inhibit enzyme needed for early / first step in metabolic pathway; negative feedback since increased level of product decreases rate of its own production; metabolic pathway regulated according to the requirement for its end-product; idea that inhibition is reversible; ...
Gene Section RGS2 (regulator of G protein signaling 2, 24kDa) -
... mRNA variant is 1355bp long arising from 5 exons: 32bp 5' UTR, 636bp coding sequence, 687 bp 3' UTR. ...
... mRNA variant is 1355bp long arising from 5 exons: 32bp 5' UTR, 636bp coding sequence, 687 bp 3' UTR. ...
Review: Thermodynamics and Cell Respiration
... 20. Briefly describe the electron transport chain in terms of structure and function. Make specific reference to the organization of the membrane and the number of ATP made. ...
... 20. Briefly describe the electron transport chain in terms of structure and function. Make specific reference to the organization of the membrane and the number of ATP made. ...
Principles of Metabolic Regulation
... Regulation by Fructose 2,6Bisphosphate • Go glycolysis if F26BP is high • Go gluconeogenesis if F26BP is low ...
... Regulation by Fructose 2,6Bisphosphate • Go glycolysis if F26BP is high • Go gluconeogenesis if F26BP is low ...
printed handout sheet
... phospholipid PIP3 or phosphatidyl inositol 3,4,5 trisphosphate. This lipid indirectly activates protein kinase B, which converts glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) from the active to the non-active form. Phosphorylated GSK3 is not able to phosphorylate and inactivate glycogen synthase, leading to inc ...
... phospholipid PIP3 or phosphatidyl inositol 3,4,5 trisphosphate. This lipid indirectly activates protein kinase B, which converts glycogen synthase kinase 3 (GSK3) from the active to the non-active form. Phosphorylated GSK3 is not able to phosphorylate and inactivate glycogen synthase, leading to inc ...
1. dia
... 2.) steady state condition: [ES] is constant, so ES formation and degradation velocity are equal, appearance of P is linear in time, E is saturated with S 3.) slowest step is the formation of P, its rate constant is k2 4.) refers to initial velocity: [P] < 5% of [S], product does not compete with su ...
... 2.) steady state condition: [ES] is constant, so ES formation and degradation velocity are equal, appearance of P is linear in time, E is saturated with S 3.) slowest step is the formation of P, its rate constant is k2 4.) refers to initial velocity: [P] < 5% of [S], product does not compete with su ...
Gene Section MAPK4 (mitogen-activated protein kinase 4) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics
... DOI: 10.4267/2042/44379 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2009 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
... DOI: 10.4267/2042/44379 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-Noncommercial-No Derivative Works 2.0 France Licence. © 2009 Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology ...
Enzymes are specific? - The BioUpdate Foundation
... taught, and which I would like to challenge is the idea that enzymes are specific. I think this idea really is a self perpetuating myth. A biological activity is observed, an enzyme (a biological catalyst), typically a protein, is isolated and found to be responsible for that activity. This protein ...
... taught, and which I would like to challenge is the idea that enzymes are specific. I think this idea really is a self perpetuating myth. A biological activity is observed, an enzyme (a biological catalyst), typically a protein, is isolated and found to be responsible for that activity. This protein ...
Quiz (B) 1. Which of the following statements concerning enzyme
... a. Heterotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own product. b. Allosteric effectors always increase K0.5 c. induction or repression the enzyme synthesis, example insulin. d. Homotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own substrate. e. Covalent modification (phosphoryla ...
... a. Heterotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own product. b. Allosteric effectors always increase K0.5 c. induction or repression the enzyme synthesis, example insulin. d. Homotropic effectors; some enzymes are regulated by their own substrate. e. Covalent modification (phosphoryla ...
LEC 4
... recombines with βγ domains. This whole process results in amplification effect because binding of agonist to receptor causes activation of numerous G-protein, which in turn can each ,via association with effector ,produce many molecules of product. ...
... recombines with βγ domains. This whole process results in amplification effect because binding of agonist to receptor causes activation of numerous G-protein, which in turn can each ,via association with effector ,produce many molecules of product. ...
Enzymes lecture 2
... Inhibitors: Thiol blocking compounds, heavy metal ions, histidine, and certain amines. Tris should not be used as a buffer due to its inhibitory effect. Storage: Store at 2-8° C. ...
... Inhibitors: Thiol blocking compounds, heavy metal ions, histidine, and certain amines. Tris should not be used as a buffer due to its inhibitory effect. Storage: Store at 2-8° C. ...
lec1-introduction
... – Dehydrogenases catalyst the transfer of hydrogen from the substrate to a particular side of nicotinamide ring in NAD+ or NADP+ – Phenylalanine hydroxylase uses L-Phe not D-Phe ...
... – Dehydrogenases catalyst the transfer of hydrogen from the substrate to a particular side of nicotinamide ring in NAD+ or NADP+ – Phenylalanine hydroxylase uses L-Phe not D-Phe ...
TyrPhos12
... effects due to simultaneous activation of several signaling pathways that are often synergistic and enhanced survival and growth. • This is an important function of growth factors when they are located on dendritic spines or shafts or on nerve terminals. • Ser/Thr kinases can alter gene expression ...
... effects due to simultaneous activation of several signaling pathways that are often synergistic and enhanced survival and growth. • This is an important function of growth factors when they are located on dendritic spines or shafts or on nerve terminals. • Ser/Thr kinases can alter gene expression ...
Lecture 2
... Summary: important to remember 1) How does a target protein become polyubiquitinated through the sequential action of E1, E2 and E3 enzymes? 2) 26S Proteasome: structure/function. How does the proteasome detect and then degrade target proteins? 3) Where in the cell does the Ubiquitin/26S Proteasome ...
... Summary: important to remember 1) How does a target protein become polyubiquitinated through the sequential action of E1, E2 and E3 enzymes? 2) 26S Proteasome: structure/function. How does the proteasome detect and then degrade target proteins? 3) Where in the cell does the Ubiquitin/26S Proteasome ...
Enzymes - Solon City Schools
... An egg becomes hard boiled when placed in hot water. What is similar about these two events? ...
... An egg becomes hard boiled when placed in hot water. What is similar about these two events? ...
Questions
... 2. Based on results described in question 1, investigators used the technique of sitedirected mutagenesis to synthesize five mutant CK proteins in which the Cys278 residue was replaced with either a Gly, Ser, Ala , Asn or Asp residue. The mutants were called C278G, C278S, C278A, C278N and C278D, re ...
... 2. Based on results described in question 1, investigators used the technique of sitedirected mutagenesis to synthesize five mutant CK proteins in which the Cys278 residue was replaced with either a Gly, Ser, Ala , Asn or Asp residue. The mutants were called C278G, C278S, C278A, C278N and C278D, re ...
No Slide Title
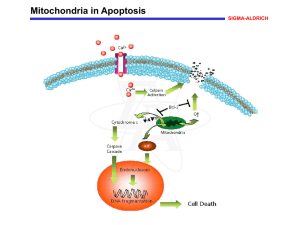
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
... Increases in cytosolic Ca2+ levels due to activation of ion channel-linked receptors, such as that for the excitatory amino acid neurotransmitter glutamic acid, can induce permeability transition (PT) of the mitochondrial membrane. PT constitutes the first rate-limiting event of the common pathway o ...
Ultrasensitivity

In molecular biology, ultrasensitivity describes an output response that is more sensitive to stimulus change than the hyperbolic Michaelis-Menten response. Ultrasensitivity is one of the biochemical switches in the cell cycle and has been implicated in a number of important cellular events, including exiting G2 cell cycle arrests in Xenopus laevis oocytes, a stage to which the cell or organism would not want to return.Ultrasensitivity is a cellular system which triggers entry into a different cellular state. Ultrasensitivity gives a small response to first input signal, but an increase in the input signal produces higher and higher levels of output. This acts to filter out noise, as small stimuli and threshold concentrations of the stimulus (input signal) is necessary for the trigger which allows the system to get activated quickly. Ultrasensitive responses are represented by sigmoidal graphs, which resemble cooperativity. Quantification of ultrasensitivity is often approximated by the Hill equation (biochemistry):Response= Stimulus^n/(EC50^n+Stimulus^n)Where Hill's coefficient (n) may represent quantitative measure of ultrasensitive response.