Cosmological principle and the Cosmic microwave
... Recovered spectrum shows an infra-red cut-off on Horizon scale !!! Is it cosmic topology ? Signature of pre-inflationary phase ? Trans-Planckian physics ? …. ...
... Recovered spectrum shows an infra-red cut-off on Horizon scale !!! Is it cosmic topology ? Signature of pre-inflationary phase ? Trans-Planckian physics ? …. ...
PowerPoint Presentation - E/PO at LHEA
... Unchanging situations need not be static New matter can be created spontaneously as the universe expands (a few hundred atoms per year per galaxy) Expansion of universe and creation of new matter balanced via a negative energy. The universe is constant in its overall density ...
... Unchanging situations need not be static New matter can be created spontaneously as the universe expands (a few hundred atoms per year per galaxy) Expansion of universe and creation of new matter balanced via a negative energy. The universe is constant in its overall density ...
Cool Cosmology ppt pics
... particles – Particle accelerators are used to study quarks and what happened in the Big Bang. – Bombard subatomic particles w/ other subatomic particles and look @ what gets ejected as they collide ...
... particles – Particle accelerators are used to study quarks and what happened in the Big Bang. – Bombard subatomic particles w/ other subatomic particles and look @ what gets ejected as they collide ...
Exam 4 Study Guide
... and the strong force. Based on supernovae data the Universe will keep expanding at a faster rate. We have about 120 meteorites from Mars. Of the soil samples studied by Viking, 3 of 4 showed compatibility with the presence of life. The moons of Jupiter that might host life are Europa, Ganymede ...
... and the strong force. Based on supernovae data the Universe will keep expanding at a faster rate. We have about 120 meteorites from Mars. Of the soil samples studied by Viking, 3 of 4 showed compatibility with the presence of life. The moons of Jupiter that might host life are Europa, Ganymede ...
AY5 Homework for Quiz 4: Spring 2015
... __F__ the total star formation rate in the Universe has been relatively steady since about 1 billion years after the Big Bang __T__ Quasars were much more common in the period between 1 and 3 b ...
... __F__ the total star formation rate in the Universe has been relatively steady since about 1 billion years after the Big Bang __T__ Quasars were much more common in the period between 1 and 3 b ...
Big Bang Theory
... stars (much bigger than our sun) explode and immense energy is released (equal to a ...
... stars (much bigger than our sun) explode and immense energy is released (equal to a ...
Test string theory with primordial gravitational wave
... 1、Inflation is the paradigm of early universe. 2、The higher-order derivative terms in superstring theory is significant. ...
... 1、Inflation is the paradigm of early universe. 2、The higher-order derivative terms in superstring theory is significant. ...
Big Bang Theory
... • Hubble found that most galaxies had redshifted (meaning…) • They are moving away from the observer • This means that the universe is expanding • In honour of this discovery: the first large space telescope was named after Hubble ...
... • Hubble found that most galaxies had redshifted (meaning…) • They are moving away from the observer • This means that the universe is expanding • In honour of this discovery: the first large space telescope was named after Hubble ...
8.8A describe components of the universe, including stars, nebulae
... Seeing Stars with X Ray vision! ...
... Seeing Stars with X Ray vision! ...
1Ctauber.pdf
... The CMB is not exhausted We need an experiment which: • Has a sensitivity at least 10x better than WMAP • Has an angular resolution at least 2x better than WMAP • Can map the polarization of the CMB over the whole sky • Can cope with systematics and local signals Such an experiment is ~1000x more p ...
... The CMB is not exhausted We need an experiment which: • Has a sensitivity at least 10x better than WMAP • Has an angular resolution at least 2x better than WMAP • Can map the polarization of the CMB over the whole sky • Can cope with systematics and local signals Such an experiment is ~1000x more p ...
Unit D Test Review Electromagnetic Spectrum: Which
... Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the shortest wavelength? What is the connection between wavelength of the radiation its energy? List the colors of visible light in order from shortest wavelength to longest. Complete the table: Type of Radiation ...
... Which type of electromagnetic radiation has the shortest wavelength? What is the connection between wavelength of the radiation its energy? List the colors of visible light in order from shortest wavelength to longest. Complete the table: Type of Radiation ...
Our place in the Universe
... Milky Way, looks like. The Sun is about ½ way from the center on a galactic arm ...
... Milky Way, looks like. The Sun is about ½ way from the center on a galactic arm ...
The Life of the Universe - University of Minnesota
... • Inflation takes things that were very close together and spreads them out a lot – Universe was all close together, so everything was uniform, then inflation spread it out ...
... • Inflation takes things that were very close together and spreads them out a lot – Universe was all close together, so everything was uniform, then inflation spread it out ...
The Big Bang
... Expansion of the Universe • In 1929 Edwin Hubble found link between distances to galaxies and their radial velocities • Plot Hubble's data ...
... Expansion of the Universe • In 1929 Edwin Hubble found link between distances to galaxies and their radial velocities • Plot Hubble's data ...
Beginning With a Bang
... supported Hubble’s theory Four basic forces control the Universe: gravity, electromagnetism, strong nuclear ...
... supported Hubble’s theory Four basic forces control the Universe: gravity, electromagnetism, strong nuclear ...
Vocabulary Part Two
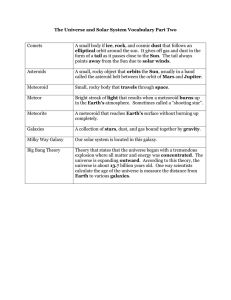
... A small body if ice, rock, and cosmic dust that follows an elliptical orbit around the sun. It gives off gas and dust in the form of a tail as it passes close to the Sun. The tail always points away from the Sun due to solar winds. ...
... A small body if ice, rock, and cosmic dust that follows an elliptical orbit around the sun. It gives off gas and dust in the form of a tail as it passes close to the Sun. The tail always points away from the Sun due to solar winds. ...
2.5.8 the future of the universe
... then, instead of something trying to escape the confines of the Earths gravitational well, but the gravitational well of a galaxy and all surrounding galaxies. In order to do so, the Ep of a galaxy would have to equal the Ek of the same galaxy. Substituting H0 in (v = H0r) into the equations, we ...
... then, instead of something trying to escape the confines of the Earths gravitational well, but the gravitational well of a galaxy and all surrounding galaxies. In order to do so, the Ep of a galaxy would have to equal the Ek of the same galaxy. Substituting H0 in (v = H0r) into the equations, we ...
Big Bang - schoolphysics
... The temperature in that explosion was unbelievably large – astrophysicists think it may have been as high as 1000 million million oC! (Compare that with the surface of our Sun at only 6000 oC.) Moments after the Big Bang (and we are talking here of times less than a million millionth of a second) so ...
... The temperature in that explosion was unbelievably large – astrophysicists think it may have been as high as 1000 million million oC! (Compare that with the surface of our Sun at only 6000 oC.) Moments after the Big Bang (and we are talking here of times less than a million millionth of a second) so ...
Image Credit - Northwestern University
... time, we can see the last scattering surface (opaque boundary). Doppler shift: observed radiation will be highly redshifted because of universe expansion. ...
... time, we can see the last scattering surface (opaque boundary). Doppler shift: observed radiation will be highly redshifted because of universe expansion. ...
BBN + Inflation
... If duration of inflation era is long compared to Hubble time, 1/H, during inflation, then universe exponentially expands and is driven exponentially towards flatness. ...
... If duration of inflation era is long compared to Hubble time, 1/H, during inflation, then universe exponentially expands and is driven exponentially towards flatness. ...
Cosmic microwave background
The cosmic microwave background (CMB) is the thermal radiation left over from the time of recombination in Big Bang cosmology. In older literature, the CMB is also variously known as cosmic microwave background radiation (CMBR) or ""relic radiation."" The CMB is a cosmic background radiation that is fundamental to observational cosmology because it is the oldest light in the universe, dating to the epoch of recombination. With a traditional optical telescope, the space between stars and galaxies (the background) is completely dark. However, a sufficiently sensitive radio telescope shows a faint background glow, almost exactly the same in all directions, that is not associated with any star, galaxy, or other object. This glow is strongest in the microwave region of the radio spectrum. The accidental discovery of CMB in 1964 by American radio astronomers Arno Penzias and Robert Wilson was the culmination of work initiated in the 1940s, and earned the discoverers the 1978 Nobel Prize.The CMB is a snapshot of the oldest light in our Universe, imprinted on the sky when the Universe was just 380,000 years old. It shows tiny temperature fluctuations that correspond to regions of slightly different densities, representing the seeds of all future structure: the stars and galaxies of today.The CMB is well explained as radiation left over from an early stage in the development of the universe, and its discovery is considered a landmark test of the Big Bang model of the universe. When the universe was young, before the formation of stars and planets, it was denser, much hotter, and filled with a uniform glow from a white-hot fog of hydrogen plasma. As the universe expanded, both the plasma and the radiation filling it grew cooler. When the universe cooled enough, protons and electrons combined to form neutral atoms. These atoms could no longer absorb the thermal radiation, and so the universe became transparent instead of being an opaque fog. Cosmologists refer to the time period when neutral atoms first formed as the recombination epoch, and the event shortly afterwards when photons started to travel freely through space rather than constantly being scattered by electrons and protons in plasma is referred to as photon decoupling. The photons that existed at the time of photon decoupling have been propagating ever since, though growing fainter and less energetic, since the expansion of space causes their wavelength to increase over time (and wavelength is inversely proportional to energy according to Planck's relation). This is the source of the alternative term relic radiation. The surface of last scattering refers to the set of points in space at the right distance from us so that we are now receiving photons originally emitted from those points at the time of photon decoupling.Precise measurements of the CMB are critical to cosmology, since any proposed model of the universe must explain this radiation. The CMB has a thermal black body spectrum at a temperature of 7000272548000000000♠2.72548±0.00057 K. The spectral radiance dEν/dν peaks at 160.2 GHz, in the microwave range of frequencies. (Alternatively if spectral radiance is defined as dEλ/dλ then the peak wavelength is 1.063 mm.) The glow is very nearly uniform in all directions, but the tiny residual variations show a very specific pattern, the same as that expected of a fairly uniformly distributed hot gas that has expanded to the current size of the universe. In particular, the spectral radiance at different angles of observation in the sky contains small anisotropies, or irregularities, which vary with the size of the region examined. They have been measured in detail, and match what would be expected if small thermal variations, generated by quantum fluctuations of matter in a very tiny space, had expanded to the size of the observable universe we see today. This is a very active field of study, with scientists seeking both better data (for example, the Planck spacecraft) and better interpretations of the initial conditions of expansion. Although many different processes might produce the general form of a black body spectrum, no model other than the Big Bang has yet explained the fluctuations. As a result, most cosmologists consider the Big Bang model of the universe to be the best explanation for the CMB.The high degree of uniformity throughout the observable universe and its faint but measured anisotropy lend strong support for the Big Bang model in general and the ΛCDM (""Lambda Cold Dark Matter"") model in particular. Moreover, the fluctuations are coherent on angular scales that are larger than the apparent cosmological horizon at recombination. Either such coherence is acausally fine-tuned, or cosmic inflation occurred.