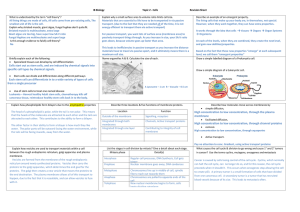
Connective Tissue - Seattle Central College
... 1. Connect epithelia to the rest of the body: secretes reticular lamina which binds to basal lamina 2. Provide structure (bone) 3. Store energy (fat) 4. Transport materials (blood) • Has no contact with environment ...
... 1. Connect epithelia to the rest of the body: secretes reticular lamina which binds to basal lamina 2. Provide structure (bone) 3. Store energy (fat) 4. Transport materials (blood) • Has no contact with environment ...
Cell Structure & Function
... • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes. • Most living organisms. Plant ...
... • Contain organelles surrounded by membranes. • Most living organisms. Plant ...
year-8-cells-task-2
... 3) Does it contain any special organelles? (E.g. cells of a plant’s leaf contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.) 4) What tissue and organ (if any) is formed by your chosen cell? (E.g. muscle cells form muscle tissue and certain muscle tissue forms the heart.) 5) What is the function of the tissue ...
... 3) Does it contain any special organelles? (E.g. cells of a plant’s leaf contain chloroplasts for photosynthesis.) 4) What tissue and organ (if any) is formed by your chosen cell? (E.g. muscle cells form muscle tissue and certain muscle tissue forms the heart.) 5) What is the function of the tissue ...
Cell Model Checklist
... Use any interesting materials you may have around your house that are good representations of the cell organelles. For example, plastic wrap may represent the cell membrane which surrounds the cell, or a small AAA battery may represent a mitochondria which produces energy for the cell. Some potentia ...
... Use any interesting materials you may have around your house that are good representations of the cell organelles. For example, plastic wrap may represent the cell membrane which surrounds the cell, or a small AAA battery may represent a mitochondria which produces energy for the cell. Some potentia ...
Cells as Molecular Factories
... The damaged protein is brought to a _________________ where enzymes digest the protein into amino acids which can be used to synthesize new proteins. A new protein to replace the damaged protein is synthesized by a ___________________ . The instructions for making the replacement protein are provide ...
... The damaged protein is brought to a _________________ where enzymes digest the protein into amino acids which can be used to synthesize new proteins. A new protein to replace the damaged protein is synthesized by a ___________________ . The instructions for making the replacement protein are provide ...
Life Science vocabulary quiz
... A structure in the cell that receives proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic recticulum packages them, and distributes them to the parts of the cell. A process in which an animals body undergoes dramatic changes in form during its life cycle. Thick gel-like fluid between the cell membrane ...
... A structure in the cell that receives proteins and other materials from the endoplasmic recticulum packages them, and distributes them to the parts of the cell. A process in which an animals body undergoes dramatic changes in form during its life cycle. Thick gel-like fluid between the cell membrane ...
Levels of Organization - Warren County Schools
... Levels of Organization Cells are the simplest level of organization. However … what makes up cells? ...
... Levels of Organization Cells are the simplest level of organization. However … what makes up cells? ...
Poor Primitive Prokaryotes
... Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or any internal membrane-bound structures. Within these cells, membranes do not separate different areas from one another. Bacteria in the Kingdom Monera are prokaryotes. There are some universal structures that all bacteria have. Like every living organism, t ...
... Prokaryotic cells do not have a nucleus or any internal membrane-bound structures. Within these cells, membranes do not separate different areas from one another. Bacteria in the Kingdom Monera are prokaryotes. There are some universal structures that all bacteria have. Like every living organism, t ...
Review Sheet Answers
... A cell is the basic unit of structure and function. Unicellular organisms are singlecelled organisms. Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells. 3. What are the three parts of cell theory? All living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living ...
... A cell is the basic unit of structure and function. Unicellular organisms are singlecelled organisms. Multicellular organisms are composed of many cells. 3. What are the three parts of cell theory? All living things are composed of cells, cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living ...
The Diversity of Cells
... protists, which he called animalcules, and bacteria. - Matthias Schleiden concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that animal tissues were composed of cells. - Rudolf Virchow stated that cells could form only from other cells. - The Cell Theory was created by Sc ...
... protists, which he called animalcules, and bacteria. - Matthias Schleiden concluded that plant parts were composed of cells. - Thedor Schwann concluded that animal tissues were composed of cells. - Rudolf Virchow stated that cells could form only from other cells. - The Cell Theory was created by Sc ...
Plant and Animal Cell Assessment
... 1. Based on your understand of the characteristics of Plant and Animal cells, list two ways that Plant & Animal cell are different. ...
... 1. Based on your understand of the characteristics of Plant and Animal cells, list two ways that Plant & Animal cell are different. ...
Life is Cellular
... 1. TEMs – (transmission electron microscopes) used to study cell structures & protein molecules. 2. SEMs – (scanning electron microscopes) scan surfaces of specimens & make 3-D images. 3. Scanning probe microscopes – trace surfaces of samples with a fine probe. Great for surfaces; can view single at ...
... 1. TEMs – (transmission electron microscopes) used to study cell structures & protein molecules. 2. SEMs – (scanning electron microscopes) scan surfaces of specimens & make 3-D images. 3. Scanning probe microscopes – trace surfaces of samples with a fine probe. Great for surfaces; can view single at ...
IB Biology Topic 2 - Cells Revision Sheet What is understood by the
... What causes the cell cycle & division to go wrong and cause 1° and 2° tumors in cancer? Use the terms cyclins, mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis Cancer is caused by cells losing control of the cell cycle. Cyclins, which normally can halt the cell cycle, can no longer do so, and for this reason, the ...
... What causes the cell cycle & division to go wrong and cause 1° and 2° tumors in cancer? Use the terms cyclins, mutagens, oncogenes and metastasis Cancer is caused by cells losing control of the cell cycle. Cyclins, which normally can halt the cell cycle, can no longer do so, and for this reason, the ...
GAMETE FORMATION IN ANIMALS
... 3. Following Meiosis II, each cell develops into a mature sperm. Head nucleus and molecules required by cell Midsection holds many mitochondria (Energy source) Tail flagellum for locomotion ...
... 3. Following Meiosis II, each cell develops into a mature sperm. Head nucleus and molecules required by cell Midsection holds many mitochondria (Energy source) Tail flagellum for locomotion ...
Cell Trafficking
... Integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are cell surface receptors mediating biological functions such as cell survival, proliferation and cell migration. Integrins, through direct binding to extracellular molecules, provide a physical link between the cell cytoskeleton and the surrounding en ...
... Integrins and receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) are cell surface receptors mediating biological functions such as cell survival, proliferation and cell migration. Integrins, through direct binding to extracellular molecules, provide a physical link between the cell cytoskeleton and the surrounding en ...
Patterns in Nature/Life on Earth Revision Quiz
... molecules on Earth 7. These animals appeared as the dinosaurs were dying out. 9. Life on earth appeared in this order: organic molecules, ________, procaryotes, colonial organisms, eucaryotes, multicellular organisms. 11. These are common examples of procaryotic organisms. 14. Carl ________ discover ...
... molecules on Earth 7. These animals appeared as the dinosaurs were dying out. 9. Life on earth appeared in this order: organic molecules, ________, procaryotes, colonial organisms, eucaryotes, multicellular organisms. 11. These are common examples of procaryotic organisms. 14. Carl ________ discover ...
Cell Parts and Functions
... All cells except bacteria Have a nucleus Have many different organelles in the cytoplasm About 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells more complex than prokaryotic cells DNA in the nucleus and linear Plant and fungi have a cell wall, other eukaryotic cells do not First appeared on Ea ...
... All cells except bacteria Have a nucleus Have many different organelles in the cytoplasm About 10 times larger than prokaryotic cells more complex than prokaryotic cells DNA in the nucleus and linear Plant and fungi have a cell wall, other eukaryotic cells do not First appeared on Ea ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).