Lecture 4 - Harford Community College
... • Route through which material is passed within the cell • Main components include: – Nuclear envelope – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Complex – Vesicles – Cell membrane ...
... • Route through which material is passed within the cell • Main components include: – Nuclear envelope – Endoplasmic Reticulum – Golgi Complex – Vesicles – Cell membrane ...
Parts of a Cell
... •The endoplasmic reticulum is similar to the system of hallways in a building. Proteins and other materials move throughout the cell by way of the endoplasmic reticulum. The spots on this organelle are ribosomes, which produce proteins. ...
... •The endoplasmic reticulum is similar to the system of hallways in a building. Proteins and other materials move throughout the cell by way of the endoplasmic reticulum. The spots on this organelle are ribosomes, which produce proteins. ...
Calling All Cells
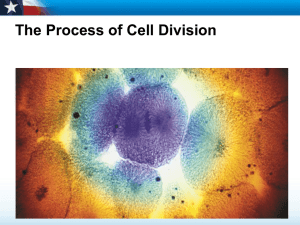
... Why is cells division important? Cell division is important because after an organism stop to grow. Cell division is the way on celled organism can reach a certain size it reproduce by dividing into two cells. For example everyday billions of your blood cells wear out get replaced. The cell divisi ...
... Why is cells division important? Cell division is important because after an organism stop to grow. Cell division is the way on celled organism can reach a certain size it reproduce by dividing into two cells. For example everyday billions of your blood cells wear out get replaced. The cell divisi ...
Anatomy of Plants
... Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes or very few. • Proteins produced by ribosomes are passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen, where they are sealed in vesicles for transport to the cell organelles ...
... Endoplasmic reticulum (ER) • Site of protein synthesis • Two types: Rough ER has ribosomes and Smooth ER does not have ribosomes or very few. • Proteins produced by ribosomes are passed through the ER membrane into the ER lumen, where they are sealed in vesicles for transport to the cell organelles ...
BIOLOGY CHAPTER 10
... take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. Metaphase: The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart. Telophase: The chromosome ...
... take up positions on opposite sides of the nucleus. Metaphase: The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome is connected to a spindle fiber at its centromere. Anaphase: The sister chromatids separate into individual chromosomes and are moved apart. Telophase: The chromosome ...
Tissues – Chapter 4 • A tissue is a group of cells having similar
... ----------and--------------are 2 types of fluid connective tissues. -------, -------,and -------- are 3 kinds of cells found in loose C.T. ---------------fibers are straight, long, unbranched strong but flexible. ------fibers are branched and wavy and contract back after extension -------- tissue is ...
... ----------and--------------are 2 types of fluid connective tissues. -------, -------,and -------- are 3 kinds of cells found in loose C.T. ---------------fibers are straight, long, unbranched strong but flexible. ------fibers are branched and wavy and contract back after extension -------- tissue is ...
Cell Project
... Due:____1/29/2016_______ Make a 3 dimensional model of either a plant or animal cell Cell model must contain the following organelles: o Nucleus o cytoplasm o mitochondria o vacuole o cell membrane o chloroplast (plant only) o Chlorophyll (plant only) o cell wall (plant only) Materials for the ...
... Due:____1/29/2016_______ Make a 3 dimensional model of either a plant or animal cell Cell model must contain the following organelles: o Nucleus o cytoplasm o mitochondria o vacuole o cell membrane o chloroplast (plant only) o Chlorophyll (plant only) o cell wall (plant only) Materials for the ...
Cell Biology - rci.rutgers.edu
... a. Act as guy wires to resist pulling forces on the cell b. Fix organelle position VI. Specialized Surface Structures and Functions A. Cell walls 1. Unique to plants 2. Basic design a. Cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of protein and polysaccharide b. Plasmodesmata i. Channels connecting neighbo ...
... a. Act as guy wires to resist pulling forces on the cell b. Fix organelle position VI. Specialized Surface Structures and Functions A. Cell walls 1. Unique to plants 2. Basic design a. Cellulose fibers embedded in a matrix of protein and polysaccharide b. Plasmodesmata i. Channels connecting neighbo ...
CELLS LESSON
... Enduring Understanding: Cells have distinct and separate organelles which perform all the life functions for their survival. ...
... Enduring Understanding: Cells have distinct and separate organelles which perform all the life functions for their survival. ...
7.2 Organelles
... protein and other molecules) Nuclear envelope-surrounds the nucleus Has pores to allow certain things to enter and leave ...
... protein and other molecules) Nuclear envelope-surrounds the nucleus Has pores to allow certain things to enter and leave ...
Chapter 40
... homologous structures c. Sympatric and Allopatric isolation can create homologies ...
... homologous structures c. Sympatric and Allopatric isolation can create homologies ...
The Discovery of Cells
... Microscope (SEM) Scans cells surface to provide scientist with its 3-D shape. ...
... Microscope (SEM) Scans cells surface to provide scientist with its 3-D shape. ...
POGIL Biology I – Introduction to life on earth
... function of the extracellular matrix of the animal cell (p. 67) with that of the cell wall of the plant cell (p. 68), and the cell wall of a bacterial cell (p. 321). ...
... function of the extracellular matrix of the animal cell (p. 67) with that of the cell wall of the plant cell (p. 68), and the cell wall of a bacterial cell (p. 321). ...
A View of the Cell
... “Tiny organs” of the Cell Objective: C2 - Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell and compare the structures of plant, animal, & bacteria cells recognizing ...
... “Tiny organs” of the Cell Objective: C2 - Identify the structure and function of the parts of a typical eukaryotic cell and compare the structures of plant, animal, & bacteria cells recognizing ...
Development - Cal State LA
... gastrulation + organ formation All three steps will make use of mitosis to produce new cells ...
... gastrulation + organ formation All three steps will make use of mitosis to produce new cells ...
common formative assessment planning template
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells; each cell carries on life-sustaining functions. Multi-cellular organisms need specialized structures and systems to perform basic life functions. 2. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and ...
... 1. All organisms are composed of one or more cells; each cell carries on life-sustaining functions. Multi-cellular organisms need specialized structures and systems to perform basic life functions. 2. All cells come from other cells and they hold the genetic information needed for cell division and ...
Life Science
... 18. _______________________-- when particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 19. ________________________________--when the concentration of a substance is the same inside and outside of the cell 20. __________________-- the diffusion of water through a se ...
... 18. _______________________-- when particles move from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration 19. ________________________________--when the concentration of a substance is the same inside and outside of the cell 20. __________________-- the diffusion of water through a se ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).