CELL ORGANELLES
... • Transports newly made proteins to other parts of the cell, or even out of the cell • Divides the cytoplasm into reaction areas • As it grows, it pushes out and inward to form the cell / nuclear membrane ...
... • Transports newly made proteins to other parts of the cell, or even out of the cell • Divides the cytoplasm into reaction areas • As it grows, it pushes out and inward to form the cell / nuclear membrane ...
Nobel Lecture December 7, 2013 Genes and proteins that organize
... Mutant sec23 complementation in vitro ...
... Mutant sec23 complementation in vitro ...
Notes
... oval, columnar, cuboidal and squamous cells. Some cells are spindle shaped; others are star shaped (stellate) with numerous cytoplasmic processes. Changes in activity are associated frequently with changes in shape (e.g., from squamous to cuboidal or cuboidal to columnar). Pronounced differences in ...
... oval, columnar, cuboidal and squamous cells. Some cells are spindle shaped; others are star shaped (stellate) with numerous cytoplasmic processes. Changes in activity are associated frequently with changes in shape (e.g., from squamous to cuboidal or cuboidal to columnar). Pronounced differences in ...
Section 7.2 Notes Name: Cell Structure A cell is like a . CELL
... 52. What are the functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria? A. ___________________capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into food that contains ___________________ energy in a process called photosynthesis. 53. ________________convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that ...
... 52. What are the functions of chloroplasts and mitochondria? A. ___________________capture the energy from sunlight and convert it into food that contains ___________________ energy in a process called photosynthesis. 53. ________________convert the chemical energy stored in food into compounds that ...
Cell Motility Learning Objectives Be able to define cell motility and
... wandering cells must get to sites of infections, cells must migrate during embryology and normal development, cell motility is involved in wound healing, and is involved in the spread of cancer throughout the body. 2. Be able to describe and relate the components and the process that enables a cell ...
... wandering cells must get to sites of infections, cells must migrate during embryology and normal development, cell motility is involved in wound healing, and is involved in the spread of cancer throughout the body. 2. Be able to describe and relate the components and the process that enables a cell ...
Genome-Scale Neoantigen Screening Using ATLAS™ Prioritizes
... Biosciences, 100 Acorn Park Drive, Cambridge, MA 02140; 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer center, 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065 ...
... Biosciences, 100 Acorn Park Drive, Cambridge, MA 02140; 2Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer center, 1275 York Avenue, New York, NY 10065 ...
Biol 115 DNA, the Thread of Life
... - Divide independent from nucleus. - Contain DNA that differs from nuclear DNA but similar to bacterial DNA. ...
... - Divide independent from nucleus. - Contain DNA that differs from nuclear DNA but similar to bacterial DNA. ...
Cells & The Cell Theory
... • Eukaryotic cells are more complex cells that contain a nucleus; where the genetic information is contained. ...
... • Eukaryotic cells are more complex cells that contain a nucleus; where the genetic information is contained. ...
Chapter 7 A view of the cell
... • Some are in all cells; membrane • Some are only found in either animal or plant cells ...
... • Some are in all cells; membrane • Some are only found in either animal or plant cells ...
Course Coordinator
... Membranes: Their structure, function and chemistry Transport across membranes: overcoming the permeability barrier The endomembrane system and peroxisomes Signal transduction mechanisms. III. Messengers and receptors ...
... Membranes: Their structure, function and chemistry Transport across membranes: overcoming the permeability barrier The endomembrane system and peroxisomes Signal transduction mechanisms. III. Messengers and receptors ...
Root hairs
... When a cell’s surface area to volume ratio is too small (the surface area and volume are too close in number), the efficiency of the cell’s functioning decreases. An efficient cell has the highest surface area to volume ratio possible! That’s from the previous section. ...
... When a cell’s surface area to volume ratio is too small (the surface area and volume are too close in number), the efficiency of the cell’s functioning decreases. An efficient cell has the highest surface area to volume ratio possible! That’s from the previous section. ...
File
... When a cell’s surface area to volume ratio is too small (the surface area and volume are too close in number), the efficiency of the cell’s functioning decreases. An efficient cell has the highest surface area to volume ratio possible! That’s from the previous section. ...
... When a cell’s surface area to volume ratio is too small (the surface area and volume are too close in number), the efficiency of the cell’s functioning decreases. An efficient cell has the highest surface area to volume ratio possible! That’s from the previous section. ...
Name: Pd.: ____ Chapter 10. Cell Growth and Division Section 10.1
... The formula for finding the surface area of a sphere, such as a baseball or basketball, is A=4πr2. where r is the radius. The formula for finding the volume of a sphere is V=4/3πr3 a. Calculate the surface area and the volume of a basketball that has a radius of 12.2 cm and a baseball that has a rad ...
... The formula for finding the surface area of a sphere, such as a baseball or basketball, is A=4πr2. where r is the radius. The formula for finding the volume of a sphere is V=4/3πr3 a. Calculate the surface area and the volume of a basketball that has a radius of 12.2 cm and a baseball that has a rad ...
Cell Division and Genetics
... Cytoplasm contains organelles, small structures that carry out the chemical activities of the cell, including mitochondria (which produce the cell’s energy) and vacuoles (which store food, water, or wastes). • Plant cells, unlike animal cells, have cell walls and chloroplasts. • Cells without nuclei ...
... Cytoplasm contains organelles, small structures that carry out the chemical activities of the cell, including mitochondria (which produce the cell’s energy) and vacuoles (which store food, water, or wastes). • Plant cells, unlike animal cells, have cell walls and chloroplasts. • Cells without nuclei ...
Cell Biology of Cancer
... o Most common site of distant metastases are lungs or liver o Some cancers show organ preference o Local concentrations of growth factors and hormones Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) & ECM Digestion Recently a lot of research has focused on matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) as targets for the develo ...
... o Most common site of distant metastases are lungs or liver o Some cancers show organ preference o Local concentrations of growth factors and hormones Matrix Metalloproteinases (MMPs) & ECM Digestion Recently a lot of research has focused on matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) as targets for the develo ...
Chapter 7 Cell Structure and Function I. 7.1 Life is Cellular A. Early
... proteins from food into particles that can be used by the rest of the cell (also break down organelles) • Vacuoles- __________________ structures that store materials like water, salts, proteins & carbohydrates • ___________________-found in plants -use energy from sunlight to make _________________ ...
... proteins from food into particles that can be used by the rest of the cell (also break down organelles) • Vacuoles- __________________ structures that store materials like water, salts, proteins & carbohydrates • ___________________-found in plants -use energy from sunlight to make _________________ ...
Study Guide Review
... Interphase: cell growth/development; DNA replication, prepares to be divided Mitosis: Cell division: a. Prophase b. Metaphase c. Anaphase and d. Telophase--------one copy of DNA is distributed into each of the two daughter cells. Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides and the organelles are distri ...
... Interphase: cell growth/development; DNA replication, prepares to be divided Mitosis: Cell division: a. Prophase b. Metaphase c. Anaphase and d. Telophase--------one copy of DNA is distributed into each of the two daughter cells. Cytokinesis: The cytoplasm divides and the organelles are distri ...
bio_ch05
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
Cells part 1 - Amanda Bohnert
... Most are stored nutrients or products from the cell Lipid drops in fat cells, glycogen abundant in liver and muscle cells, pigments such as melanin in skin and hair cells, mucus and other secreted products etc. Aggregate inside the cell and can be used sometimes as markers for ...
... Most are stored nutrients or products from the cell Lipid drops in fat cells, glycogen abundant in liver and muscle cells, pigments such as melanin in skin and hair cells, mucus and other secreted products etc. Aggregate inside the cell and can be used sometimes as markers for ...
Power Point
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
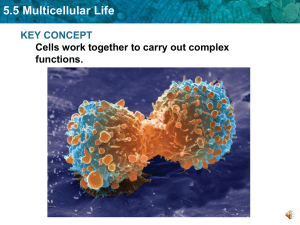
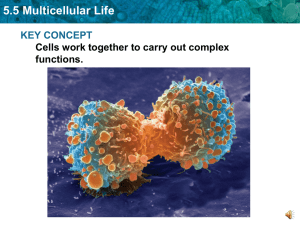
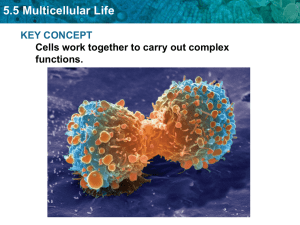
5.5 Multicellular Life KEY CONCEPT Cells work together to carry out complex functions.
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
... • Stem cells are classified into three types. – totipotent, or growing into any other cell type – pluripotent, or growing into any cell type but a totipotent cell – multipotent, or growing into cells of a closely related cell ...
CHAPTER 7 REVIEW
... 13. Create flash cards for the functions of the cellular organelles. 14. Draw a concept map for the chapter. Use different colors for different parts. Perhaps use the colors you choose for your flash cards as well. Include some detail on the map to help you remember specifics, but you should NOT att ...
... 13. Create flash cards for the functions of the cellular organelles. 14. Draw a concept map for the chapter. Use different colors for different parts. Perhaps use the colors you choose for your flash cards as well. Include some detail on the map to help you remember specifics, but you should NOT att ...
Characteristic Features of Epithelial Cells 3 rd lecture November 5
... • An extracellular basal lamina always lies at the interface of epithelial cells and connective tissue. The basal laminae to two neighboring epithelia can fuse or appear to fuse in places where there is no intervening connective tissue. Nutrients for epithelial cells must diffuse across the basal ...
... • An extracellular basal lamina always lies at the interface of epithelial cells and connective tissue. The basal laminae to two neighboring epithelia can fuse or appear to fuse in places where there is no intervening connective tissue. Nutrients for epithelial cells must diffuse across the basal ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).