What structures of living things are cells involved?
... 1. What do fungus, a tree and a newt all have in common? 2. What is the basic unit of structure of living things? 3. What do cells form? 4. What structures of living things are cells involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
... 1. What do fungus, a tree and a newt all have in common? 2. What is the basic unit of structure of living things? 3. What do cells form? 4. What structures of living things are cells involved? 5. What functions of living things are cells involved? ...
Honors Biology Ch. 4 The Cell Organelle Functions Study Sheet
... *Capsule: sticky coating on outside of some prokaryotes that helps non-motile bacteria stick, may hide cell from host’s immune system. Cell Wall: rigid, provide structure, protection, back-pressure for turgidity. Cytoskeleton: used like tent poles to support structure, used as internal tracks on whi ...
... *Capsule: sticky coating on outside of some prokaryotes that helps non-motile bacteria stick, may hide cell from host’s immune system. Cell Wall: rigid, provide structure, protection, back-pressure for turgidity. Cytoskeleton: used like tent poles to support structure, used as internal tracks on whi ...
Biology Study Guide with answers 1. Name 2 things in common
... 1. Name 2 things in common between all 4 of the protists we studied. They can move, they can reproduce, they can obtain food, they can get rid of waste. 2. What is similar between the flagella and cilia in protists? It helps them move. 3. Name a similarity between a volvox and a euglena. They ...
... 1. Name 2 things in common between all 4 of the protists we studied. They can move, they can reproduce, they can obtain food, they can get rid of waste. 2. What is similar between the flagella and cilia in protists? It helps them move. 3. Name a similarity between a volvox and a euglena. They ...
MaxCyte, NIH NIAID Study Published in Science Translational
... Using MaxCyte’s patented Flow Electroporation™ Technology, researchers demonstrated that transfecting three molecules, a single-‐strand oligonucleotide correction template, along with messenger RNA encoding for ...
... Using MaxCyte’s patented Flow Electroporation™ Technology, researchers demonstrated that transfecting three molecules, a single-‐strand oligonucleotide correction template, along with messenger RNA encoding for ...
Cell Theory
... Red Blood Cells, normal and sickle cell Myocardial cells through a light microscope ...
... Red Blood Cells, normal and sickle cell Myocardial cells through a light microscope ...
CH 3 P2 Lecture
... The plasma membrane allows some material to pass while excluding other materials. This permeability includes movement into and out of the cell ...
... The plasma membrane allows some material to pass while excluding other materials. This permeability includes movement into and out of the cell ...
Checkpoints in Cell Cycle
... the cells invade other parts of the body (this process is called metastasis) Metastasis is responsible for 90% of cancer related deaths Metastasis ...
... the cells invade other parts of the body (this process is called metastasis) Metastasis is responsible for 90% of cancer related deaths Metastasis ...
Ribosomes (20-30nm)
... o Have no ribosomes attached and often appear more tubular than the rough ER o Necessary for steroid synthesis, metabolism and detoxification, lipid synthesis o Numerous in the liver ...
... o Have no ribosomes attached and often appear more tubular than the rough ER o Necessary for steroid synthesis, metabolism and detoxification, lipid synthesis o Numerous in the liver ...
Lecture 14
... Long chains (polymers) Chains with complex branching Close rings or networks of rings Carbon compounds dissolve readily in liquids, especially water ...
... Long chains (polymers) Chains with complex branching Close rings or networks of rings Carbon compounds dissolve readily in liquids, especially water ...
Cells: Organelles - Biology Courses Server
... Rough ER makes proteins and membrane • When ribosomes encounter an ER signal sequence on the mRNA they bind the surface of the ER • Makes and modifies proteins that are inserted in membranes • Makes and modifies proteins that are secreted (i.e. insulin) -most secreted proteins are glycoproteins, co ...
... Rough ER makes proteins and membrane • When ribosomes encounter an ER signal sequence on the mRNA they bind the surface of the ER • Makes and modifies proteins that are inserted in membranes • Makes and modifies proteins that are secreted (i.e. insulin) -most secreted proteins are glycoproteins, co ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
Chapter 7 A tour of the Cell
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
... “sort” proteins into different vesicles Adds and removes monomers of sugar (small subunits) from glycoproteins Dispatches vesicles w/glyco-proteins for shipping (trans side) ...
Science Benchmark # 1 STUDY GUIDE!!!!!!
... Cell wall nucleus circular Larger vacuole cytoplasm Rectangular endoplasmic reticulum Cell membrane 15. List the stages of mitosis in order: _prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PMAT)_ 16. The nucleus stores hereditary material and _controls the cell’s activities. 17. The cell _wall_ provides ...
... Cell wall nucleus circular Larger vacuole cytoplasm Rectangular endoplasmic reticulum Cell membrane 15. List the stages of mitosis in order: _prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase (PMAT)_ 16. The nucleus stores hereditary material and _controls the cell’s activities. 17. The cell _wall_ provides ...
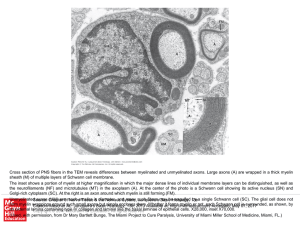
Slide ()
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
... The inset shows a portion of myelin at higher magnification in which the major dense lines of individual membrane layers can be distinguished, as well as the neurofilaments (NF) and microtubules (MT) in the axoplasm (A). At the center of the photo is a Schwann cell showing its active nucleus (SN) an ...
Unicellular and Multicellular
... Photosynthesis uses energy from the Sun to make carbohydrates. Folded membranes inside each chloroplast contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight. ...
... Photosynthesis uses energy from the Sun to make carbohydrates. Folded membranes inside each chloroplast contain the green pigment chlorophyll, which absorbs sunlight. ...
Keyword-list
... Eukaryotic- A cell which has a nucleus. Animal, plant, fungi and protoctista. Prokaryotic- A cell which has no nucleus, only a single loop of DNA found in the cytoplasm. Bacteria. Cell membrane- A part of the cell which controls what enters and exits the cell. Cytoplasm- A part of the cell where che ...
... Eukaryotic- A cell which has a nucleus. Animal, plant, fungi and protoctista. Prokaryotic- A cell which has no nucleus, only a single loop of DNA found in the cytoplasm. Bacteria. Cell membrane- A part of the cell which controls what enters and exits the cell. Cytoplasm- A part of the cell where che ...
Biology 12 Membrane Notes File
... o Selectively permeable = a living membrane that can use energy to select molecules (even if they are too big or the concentration gradient is going in the opposite direction) ...
... o Selectively permeable = a living membrane that can use energy to select molecules (even if they are too big or the concentration gradient is going in the opposite direction) ...
Cells
... Found mainly in plant cells, does the same job as lysosomes. As the vacuole grows with the addition of water the size of the cell grows. May be up to 90% of a plant cell volume. ...
... Found mainly in plant cells, does the same job as lysosomes. As the vacuole grows with the addition of water the size of the cell grows. May be up to 90% of a plant cell volume. ...
What are cells?
... – Holds “construction plan” for all parts of the cell – Duplicated and passed on to other cells ...
... – Holds “construction plan” for all parts of the cell – Duplicated and passed on to other cells ...
Cell Wall - Qld Science Teachers
... mitochondrion, and the inner membrane folded back and forth for large surface area for chemical reactions It is thought that mitochondria in eukaryotic cells may have evolved from ancient symbiotic prokaryotic bacteria that lived inside other larger prokaryotic cells. They have their own DNA and r ...
... mitochondrion, and the inner membrane folded back and forth for large surface area for chemical reactions It is thought that mitochondria in eukaryotic cells may have evolved from ancient symbiotic prokaryotic bacteria that lived inside other larger prokaryotic cells. They have their own DNA and r ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).