Chapter 4 Test - Nutley Public Schools
... o All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular. o The cell is the basic unit of life. o All cells come from pre-existing cells. Some ...
... o All living organisms are composed of cells. They may be unicellular or multicellular. o The cell is the basic unit of life. o All cells come from pre-existing cells. Some ...
Laboratory 1 - Vascular Plant Anatomy One of the major distinctions
... Collenchyma and sclerenchyma form the two major support tissues. Collenchyma is living cell type with thick, pearlly cell walls. It is located near the periphery of the plant and remains living during function, depending on turgor pressure to remain strongly supportive. Re-examine the celery section ...
... Collenchyma and sclerenchyma form the two major support tissues. Collenchyma is living cell type with thick, pearlly cell walls. It is located near the periphery of the plant and remains living during function, depending on turgor pressure to remain strongly supportive. Re-examine the celery section ...
Lec.14 Dr:Buthaina Al-Sabawi Date:21/12/2016 Mitosis
... Kinetochore microtubules: each sister chromatid is attached to a kinetochore microtubule; in cell division during anaphase the microtubules hold onto the kinetochore and pull the two sister chromatids apart to opposite poles. Polar microtubules: microtubules that connect to each other from opposite ...
... Kinetochore microtubules: each sister chromatid is attached to a kinetochore microtubule; in cell division during anaphase the microtubules hold onto the kinetochore and pull the two sister chromatids apart to opposite poles. Polar microtubules: microtubules that connect to each other from opposite ...
Cells Pretest - Warren County Schools
... Learning Target 2: I can describe the functions of the cell's organelles. 6. What structure allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosomes c. Cell membrane d. Golgi body 7. What is made of folded membranes that move materials around inside the cell a. Nucleus b ...
... Learning Target 2: I can describe the functions of the cell's organelles. 6. What structure allows only certain things to pass in and out of the cell? a. Cytoplasm b. Ribosomes c. Cell membrane d. Golgi body 7. What is made of folded membranes that move materials around inside the cell a. Nucleus b ...
Biology 1Pre-AP/GT - 2012 Unit 3: Cells/ Cell Processes Chapters 7
... 7. Complete the analogy assignment on the cellular organelles. (we will discuss this in class) Cell membrane Mitochondria Cytoplasm Chloroplast Ribosomes Lysosomes Nucleus Cytoskeleton Rough and smooth Centrioles (p.246) endoplasmic reticulum Flagella (p. 473) Golgi apparatus ...
... 7. Complete the analogy assignment on the cellular organelles. (we will discuss this in class) Cell membrane Mitochondria Cytoplasm Chloroplast Ribosomes Lysosomes Nucleus Cytoskeleton Rough and smooth Centrioles (p.246) endoplasmic reticulum Flagella (p. 473) Golgi apparatus ...
Cell Factory Analogy
... o Using most of the poster to draw your cell factory analogy. o Using colored pencils, draw in the organelles that represent your cell parts o Label them with both their factory analogy name and in parenthesis-their cell part name. Example: -Office of Manager (nucleus) ...
... o Using most of the poster to draw your cell factory analogy. o Using colored pencils, draw in the organelles that represent your cell parts o Label them with both their factory analogy name and in parenthesis-their cell part name. Example: -Office of Manager (nucleus) ...
Bacterial growth
... They live in aquatic environments including oceans, ponds, lakes, tidal flats, and moist soil. ...
... They live in aquatic environments including oceans, ponds, lakes, tidal flats, and moist soil. ...
SESSION 2: CELLS - THE BASIC UNITS OF LIFE
... 1. Unicellular organisms - one cell only Examples: amoeba, bacteria 2. Multi-cellular organisms - many cells Examples: plants, animals Different types of cells form parts of a plant or animal. Cells with similar structure and function group together to form tissues Cells tissue organs systems ...
... 1. Unicellular organisms - one cell only Examples: amoeba, bacteria 2. Multi-cellular organisms - many cells Examples: plants, animals Different types of cells form parts of a plant or animal. Cells with similar structure and function group together to form tissues Cells tissue organs systems ...
worksheet prokaryotic and eukaryotic cell structure
... Cell membrane, cytoplasm and various organelles________________________________ Have ribosomes and make proteins____________________________________________ ...
... Cell membrane, cytoplasm and various organelles________________________________ Have ribosomes and make proteins____________________________________________ ...
Document
... cysteine-containing aspartate-specific proteases normally inactive as zymogen (harmless to cell) zymogen form activated by proteolysis active caspases target other proteins for destruction ...
... cysteine-containing aspartate-specific proteases normally inactive as zymogen (harmless to cell) zymogen form activated by proteolysis active caspases target other proteins for destruction ...
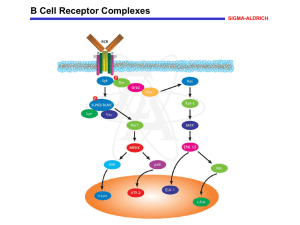
B Cell Receptor Complexes - Sigma
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
... family are activated initially and phosphorylate CD79 and CD79ß, thereby creating phosphotyrosine motifs that recruit downstream signaling molecules. In particular, phosphorylation of the BCR complex leads to the recruitment and activation of the protein tyrosine kinase Syk, which, in turn, promote ...
Yr-7-Science-Project-1-Oct-2011-Model
... cell, cell membrane, chloroplast, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole controls the cell, lets some substances in and out of the cell, does photosynthesis, stores cell sap, place where chemical reactions take place To get level ...
... cell, cell membrane, chloroplast, cytoplasm, nucleus, vacuole controls the cell, lets some substances in and out of the cell, does photosynthesis, stores cell sap, place where chemical reactions take place To get level ...
File - Classes with Mrs. Sheetz
... • Classified by their structure • Structure: see figure 24.2.1 on page 508 • Organelles: see figure 24.2.2 on page 508 ...
... • Classified by their structure • Structure: see figure 24.2.1 on page 508 • Organelles: see figure 24.2.2 on page 508 ...
File - Science with Snyder
... The Cell theory has three principles. 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the most basic unit of structure of all living things. • unicellular organisms- one cell • Multicellular – specialized regions called tissues. 3. All existing cells are come from previously ...
... The Cell theory has three principles. 1. All living things are composed of one or more cells. 2. The cell is the most basic unit of structure of all living things. • unicellular organisms- one cell • Multicellular – specialized regions called tissues. 3. All existing cells are come from previously ...
Prokaryotic Cells
... outside environment and the inside of the cell. The cytoplasm is the region of the cell within the cell membrane. The cytoplasm includes the fluid inside the cell called the cytosol. A ribosome is a cellular organ that makes proteins. The DNA of a cell provides instructions for making proteins, regu ...
... outside environment and the inside of the cell. The cytoplasm is the region of the cell within the cell membrane. The cytoplasm includes the fluid inside the cell called the cytosol. A ribosome is a cellular organ that makes proteins. The DNA of a cell provides instructions for making proteins, regu ...
Biological Membranes
... Uses energy in the form of ATP Pumps two K+ ions into the cell for every three Na+ ions it pumps out This causes an electrical as well as chemical gradient across the cell membrane – an ...
... Uses energy in the form of ATP Pumps two K+ ions into the cell for every three Na+ ions it pumps out This causes an electrical as well as chemical gradient across the cell membrane – an ...
Cells: form fits function - Science-Hinz
... from the soil. Describe the shape of these cells and explain how its shape would help it to do its job. ...
... from the soil. Describe the shape of these cells and explain how its shape would help it to do its job. ...
The 6 Kingdoms - Cloudfront.net
... 2. Aggregations—a temporary collection of cells that come together for a short time and then separate. Plasmodial slime mold—when starved they come together to produce spores which can be dispersed to distant locations. ...
... 2. Aggregations—a temporary collection of cells that come together for a short time and then separate. Plasmodial slime mold—when starved they come together to produce spores which can be dispersed to distant locations. ...
ch7_1 v2
... The Cell Theory 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is the unit of structure & function of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (No spontaneous generation ). ...
... The Cell Theory 1. All known living things are made up of cells. 2. The cell is the unit of structure & function of all living things. 3. All cells come from pre-existing cells by division. (No spontaneous generation ). ...
Chapter 3 Cell Structure - Shelbyville Central Schools
... •Small cells function more efficiently than large cells •If cell’s surface area–to-volume ratio is too low, subs can’t enter/leave cell well enough to meet cell’s needs ...
... •Small cells function more efficiently than large cells •If cell’s surface area–to-volume ratio is too low, subs can’t enter/leave cell well enough to meet cell’s needs ...
Cells and Cell Organelles
... Organisms made of these cells include protists, fungi, plants, and animals (including humans). 2.Organelles allow many activities to take place within the same cell other reactions take place on membrane surfaces and eukaryotic cells have much more internal membrane surface that prokaryotic cells ...
... Organisms made of these cells include protists, fungi, plants, and animals (including humans). 2.Organelles allow many activities to take place within the same cell other reactions take place on membrane surfaces and eukaryotic cells have much more internal membrane surface that prokaryotic cells ...
Angiosperms III - University of Nebraska Omaha
... primarily in herbaceous stems • Cells walls have extra cellulose thickenings in the corners (strong ...
... primarily in herbaceous stems • Cells walls have extra cellulose thickenings in the corners (strong ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).