2-3 eukaryotes
... The Cell membrane is the boundary of the cell. •It acts as a “gatekeeper”, preventing the entry or exit of some molecules and facilitating the movement of others. •It is a phospholipid bilayer •It is permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide •It is impermeable to water and charged particles, they must ...
... The Cell membrane is the boundary of the cell. •It acts as a “gatekeeper”, preventing the entry or exit of some molecules and facilitating the movement of others. •It is a phospholipid bilayer •It is permeable to oxygen and carbon dioxide •It is impermeable to water and charged particles, they must ...
Chapter 4 - selu moodle
... Use pili for attachment and to exchange genetic information Cell walls made of peptidoglycan (specific to bacteria) antibiotics stop formation of peptidoglycan. When you get sick you probably have about 1million cells infecting your body. Some of these cells double every 20min. Antibiotics don’t all ...
... Use pili for attachment and to exchange genetic information Cell walls made of peptidoglycan (specific to bacteria) antibiotics stop formation of peptidoglycan. When you get sick you probably have about 1million cells infecting your body. Some of these cells double every 20min. Antibiotics don’t all ...
Plant Cell
... meaning that they are combatable with water both within the cytosol and outside of the cell • Is made more complex by the presence of numerous proteins that are crucial to cell ...
... meaning that they are combatable with water both within the cytosol and outside of the cell • Is made more complex by the presence of numerous proteins that are crucial to cell ...
Chapter 4: Tissue Level of Organization
... of functions. Histology: the study of tissues Interstitial Fluid: the fluid found between cells, within a tissue, or between tissues ...
... of functions. Histology: the study of tissues Interstitial Fluid: the fluid found between cells, within a tissue, or between tissues ...
Document
... – Passive transport pores and channels – Active transport pumps and carriers – Membrane-linked enzymes, receptors and ...
... – Passive transport pores and channels – Active transport pumps and carriers – Membrane-linked enzymes, receptors and ...
Cell Organelles Graphic Organizer
... Structure: Jelly-like material found inside cell membrane Function: Supports and protects cell’s organelles. Contains some nutrients for cell. ...
... Structure: Jelly-like material found inside cell membrane Function: Supports and protects cell’s organelles. Contains some nutrients for cell. ...
the cell theory - Fredericksburg City Schools
... science of biology is the one known as the cell theory. Scientists use the term “theory” to indicate something that is more than just a hypothesis. A theory is a statement that has been proven true after many experiments. The cell theory was developed over many centuries by hundreds of scientists. I ...
... science of biology is the one known as the cell theory. Scientists use the term “theory” to indicate something that is more than just a hypothesis. A theory is a statement that has been proven true after many experiments. The cell theory was developed over many centuries by hundreds of scientists. I ...
File - need help with revision notes?
... modifies them, perhaps adding sugar, folds them into enzymes, and sorts them according to their destination. Enzymes are pinched off into secretary vesicles which can then travel to the plasma membrane to be secreted outside of the cell, or to other organelles inside the cell itself. The mitochondri ...
... modifies them, perhaps adding sugar, folds them into enzymes, and sorts them according to their destination. Enzymes are pinched off into secretary vesicles which can then travel to the plasma membrane to be secreted outside of the cell, or to other organelles inside the cell itself. The mitochondri ...
Cellular Transport
... from passive? Complete the chart. 2. What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? 3. How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? 4. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? ...
... from passive? Complete the chart. 2. What part of the cell is used to bring in particles? 3. How does a cell (including white blood cells) take in LARGE particles? 4. How does a cell take in small or liquid particles? ...
Steps for completing this study guide I Have, Who Has Matching
... is made, or shaped, affects what it is able to do. (For example, the Cell Wall is made of thick fibers so it can protect the cell.) Write down one more example of Structure Function within the cell. ...
... is made, or shaped, affects what it is able to do. (For example, the Cell Wall is made of thick fibers so it can protect the cell.) Write down one more example of Structure Function within the cell. ...
Mend a broken heart - Adam J. Engler
... reinforce. Heart wall stiffness only slightly decreased and cardiac function improved only marginally. It’s now thought that the needle used to inject the stem cells actually poked holes into scarred heart muscle, making it slightly softer instead of regenerating the tissue. Worse, the stem cells th ...
... reinforce. Heart wall stiffness only slightly decreased and cardiac function improved only marginally. It’s now thought that the needle used to inject the stem cells actually poked holes into scarred heart muscle, making it slightly softer instead of regenerating the tissue. Worse, the stem cells th ...
Cytoplasm
... “cell skeleton” network of protein rods thru cytosol supports cell structure allows cell movement Types: 1. Microfilaments 2. Intermediate Filaments 3. Microtubules ...
... “cell skeleton” network of protein rods thru cytosol supports cell structure allows cell movement Types: 1. Microfilaments 2. Intermediate Filaments 3. Microtubules ...
Growth and multiplication in bacteria
... Characterized by a period during which there is no increase in the number of cells. Cells enlarge ,as enzymes and metabolic intermediates are built up Duration of Lag phase varies with the Spp., size of the inoculum, nature of the culture medium and environmental factors . ...
... Characterized by a period during which there is no increase in the number of cells. Cells enlarge ,as enzymes and metabolic intermediates are built up Duration of Lag phase varies with the Spp., size of the inoculum, nature of the culture medium and environmental factors . ...
Review Sheet for Lecture Exam 2 Chapter Five Structure and
... Enzyme structure and function (substrate, active site, induced fit) What is activation energy? How are enzymes inhibited? (competitive and noncompetitive inhibition) Cofactors and coenzymes ...
... Enzyme structure and function (substrate, active site, induced fit) What is activation energy? How are enzymes inhibited? (competitive and noncompetitive inhibition) Cofactors and coenzymes ...
MT-0.6081 Microfluidics and BioMEMS Organs on a chip
... (non neuron support cells of CNS). - In vitro studies: brain slices or primary neurons and glial cells are commonly used. - Immortal cell lines with neuron like properties also exist, but are less common - In future, patient derived induced pluripotent cells differentiated into neurons? ...
... (non neuron support cells of CNS). - In vitro studies: brain slices or primary neurons and glial cells are commonly used. - Immortal cell lines with neuron like properties also exist, but are less common - In future, patient derived induced pluripotent cells differentiated into neurons? ...
Can EVERY molecule pass through the cell membrane freely? Why
... Materials move across membranes because of concentration differences. ...
... Materials move across membranes because of concentration differences. ...
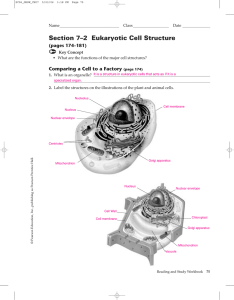
Section 7–2 Eukaryotic Cell Structure
... © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. ...
... © Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Prentice Hall. ...
The yellow structure represents the hydrophillic or water loving
... draw a picture of the cell membrane 2. Make sure you include phospholipids, all kinds of proteins, and cholesterol. 3. Color and label all parts properly. 4. Finish and turn in. ...
... draw a picture of the cell membrane 2. Make sure you include phospholipids, all kinds of proteins, and cholesterol. 3. Color and label all parts properly. 4. Finish and turn in. ...
Cell Structure and Function
... __________ are small structures in the cytoplasm that perform specific functions. 12. What surrounds the outside of all cells? 13. What 2 things make up all cell membranes? 14. Cell membranes only allow certain materials into & out of the cell so they are said to be ________________ _____________. ...
... __________ are small structures in the cytoplasm that perform specific functions. 12. What surrounds the outside of all cells? 13. What 2 things make up all cell membranes? 14. Cell membranes only allow certain materials into & out of the cell so they are said to be ________________ _____________. ...
(3) - cloudfront.net
... 12. Cell theory states that all organisms: A. Are composed of cells B. Reproduce asexually ...
... 12. Cell theory states that all organisms: A. Are composed of cells B. Reproduce asexually ...
End of the Year Test Review 1. What plant cell organelle changes
... 12. Cell theory states that all organisms: A. Are composed of cells B. Reproduce asexually ...
... 12. Cell theory states that all organisms: A. Are composed of cells B. Reproduce asexually ...
The Cell - Biology Mad
... A chromosome is a ‘condensed chromatin’ thread only visible during mitosis and meiosis. Haploid nuclei (n) have one set of chromosomes i.e. one of each kind of chromosome. Diploid nuclei (2n) have two sets of chromosomes i.e. two of each chromosome. The nuclei of human somatic (= body) cells are dip ...
... A chromosome is a ‘condensed chromatin’ thread only visible during mitosis and meiosis. Haploid nuclei (n) have one set of chromosomes i.e. one of each kind of chromosome. Diploid nuclei (2n) have two sets of chromosomes i.e. two of each chromosome. The nuclei of human somatic (= body) cells are dip ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).