Cell City Analogy - Rochester Community Schools
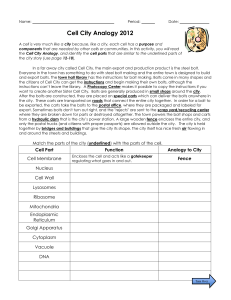
... A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city story (use page 12-18). ...
... A cell is very much like a city because, like a city, each cell has a purpose and components that are needed by other cells or communities. In this activity, you will read the Cell City Analogy, and identify the cell parts that are similar to the underlined parts of the city story (use page 12-18). ...
The Cell Membrane
... Controls what enters and leaves the cell Allows some things in and keeps others out ...
... Controls what enters and leaves the cell Allows some things in and keeps others out ...
Tour of Cell Organelles
... were able to see into cells with more detail. There were able to see that there are two main types of cells... PROKARYOTES and EUKARYOTES ...
... were able to see into cells with more detail. There were able to see that there are two main types of cells... PROKARYOTES and EUKARYOTES ...
What is the cell membrane?
... has chlorophyll, which helps a plant in the process of photosynthesis. ...
... has chlorophyll, which helps a plant in the process of photosynthesis. ...
Name
... Passive Transport -the movement of particles across a membrane. What do materials need to cross the plasma membrane? Transport proteins What is this process called? Facilitated diffusion Types of Transport Proteins Channel Proteins- form channels that allow specific molecules to flow through. (fig. ...
... Passive Transport -the movement of particles across a membrane. What do materials need to cross the plasma membrane? Transport proteins What is this process called? Facilitated diffusion Types of Transport Proteins Channel Proteins- form channels that allow specific molecules to flow through. (fig. ...
Sizing Up Cells - cloudfront.net
... Life Science: Grades 6 to 8 Structure and Function of Cells 3. Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles). Overview & Approximate Time Students analyze digital images of cells, mea ...
... Life Science: Grades 6 to 8 Structure and Function of Cells 3. Compare and contrast plant and animal cells, including major organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles). Overview & Approximate Time Students analyze digital images of cells, mea ...
Unit G Rev #2 - Mr. Lesiuk
... ___ 6. What is the required energy molecule for any method of Active Transport? ___ 7. What cell organelle do you think would be present in large numbers in cells that frequently perform lots of Active Transport? ___8. Which types of bodily cells contain high numbers of Na+/K+ Pumps? ___ 9. How is t ...
... ___ 6. What is the required energy molecule for any method of Active Transport? ___ 7. What cell organelle do you think would be present in large numbers in cells that frequently perform lots of Active Transport? ___8. Which types of bodily cells contain high numbers of Na+/K+ Pumps? ___ 9. How is t ...
1b. Induced pluripotent stem cells
... reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell–like state by being forced to express genes and factors important for maintaining the defining properties of embryonic stem cells. Although these cells meet the defining criteria for pluripotent stem cells, it is not known if iPSCs and embryonic stem cells diff ...
... reprogrammed to an embryonic stem cell–like state by being forced to express genes and factors important for maintaining the defining properties of embryonic stem cells. Although these cells meet the defining criteria for pluripotent stem cells, it is not known if iPSCs and embryonic stem cells diff ...
How Small Can You Go - Thunderbird High School
... Place the specimen on a slide, and cover with a cover slip. b. Examine the colored cells under low and high power. Notice the central vacuole. It is conspicuous because of the pigments present. c. Is the nucleus seen? If not, add a drop of iodine to the edge of the cover slip and allow the iodine to ...
... Place the specimen on a slide, and cover with a cover slip. b. Examine the colored cells under low and high power. Notice the central vacuole. It is conspicuous because of the pigments present. c. Is the nucleus seen? If not, add a drop of iodine to the edge of the cover slip and allow the iodine to ...
08_virology_frequently_asked_questions
... Yes, but specific rooms separated from other diagnostic laboratories should be dedicated to virology. If the laboratory receives samples from humans or samples containing highly infectious agents, a virology unit with all the necessary safety precautions should be used. ...
... Yes, but specific rooms separated from other diagnostic laboratories should be dedicated to virology. If the laboratory receives samples from humans or samples containing highly infectious agents, a virology unit with all the necessary safety precautions should be used. ...
Cell Organelles Worksheet
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life (Structure & function) 3. All Cells come from pre-existing cells In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? Mitochondria What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesi ...
... 1. All living organisms are composed of one or more cells 2. The cell is the most basic unit of life (Structure & function) 3. All Cells come from pre-existing cells In what organelle does cellular respiration take place? Mitochondria What is the list of organelles that take part in protein synthesi ...
1.2 Prokaryotic Eukaryotic
... cell is the smallest form of life ALL living organisms are made of cells ...
... cell is the smallest form of life ALL living organisms are made of cells ...
Introduction_to_Mitosis
... Cells that contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms ...
... Cells that contain organelles surrounded by membranes Most living organisms ...
Two important chemical molecules made by plant cells. What are
... and Virchow gave us this famous scientific idea. ...
... and Virchow gave us this famous scientific idea. ...
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION CHART
... Cilia, Pilli, and Flagella Structures used to enable movement of cells or sometimes to propel substances across outer surface of the cell. Predominantly protein in composition. ...
... Cilia, Pilli, and Flagella Structures used to enable movement of cells or sometimes to propel substances across outer surface of the cell. Predominantly protein in composition. ...
Mitosis
... metaphase plate with sister chromatids each facing opposite sides of cell Centrosomes at opposite sides of cell ...
... metaphase plate with sister chromatids each facing opposite sides of cell Centrosomes at opposite sides of cell ...
Date Per - Haiku Learning
... Cheek Cell Lab Problem: What are you made out of? Background: One main difference between plant cells and animal cells is that plant cells have a cell wall and animal cells do not. A good analogy to think of is an egg with a shell (plant cell) and an egg without a shell and just the membrane (animal ...
... Cheek Cell Lab Problem: What are you made out of? Background: One main difference between plant cells and animal cells is that plant cells have a cell wall and animal cells do not. A good analogy to think of is an egg with a shell (plant cell) and an egg without a shell and just the membrane (animal ...
Cell Structures
... 1. Free Ribosomes– These float “freely” in the cytoplasm of a cell. (They are found in ALL TYPES of cells.) a. These ribosomes make proteins that will stay inside the cell for use by the cell. 2. Bound Ribosomes – These are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum organelle (RER). (These are ONLY found ...
... 1. Free Ribosomes– These float “freely” in the cytoplasm of a cell. (They are found in ALL TYPES of cells.) a. These ribosomes make proteins that will stay inside the cell for use by the cell. 2. Bound Ribosomes – These are attached to the endoplasmic reticulum organelle (RER). (These are ONLY found ...
LAB ASSIGNMENT 1
... NAME: _____________________________ LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 Due at the start of Lab on July 8 ...
... NAME: _____________________________ LAB ASSIGNMENT 1 Due at the start of Lab on July 8 ...
Mitosis
... metaphase plate with sister chromatids each facing opposite sides of cell Centrosomes at opposite sides of cell ...
... metaphase plate with sister chromatids each facing opposite sides of cell Centrosomes at opposite sides of cell ...
Running A Flow Cytometry Facility
... What is Flow Cytometry • It is the technique used to measure properties of individual cells as they flow in a stream one by one past a sensing point • This ability to measure cellular parameters based on light scatter and fluorescence and to physically purify subpopulations has led to widespread us ...
... What is Flow Cytometry • It is the technique used to measure properties of individual cells as they flow in a stream one by one past a sensing point • This ability to measure cellular parameters based on light scatter and fluorescence and to physically purify subpopulations has led to widespread us ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).























