PDF
... epithelial morphogenesis and tissue maintenance, involves interactions between cortical polarity components and astral microtubules. The molecular machinery that regulates spindle apicobasal orientation during asymmetric cell division is well understood but what orientates the spindle along the epit ...
... epithelial morphogenesis and tissue maintenance, involves interactions between cortical polarity components and astral microtubules. The molecular machinery that regulates spindle apicobasal orientation during asymmetric cell division is well understood but what orientates the spindle along the epit ...
Cell Structure & Function
... No nuclear membrane or other membranebound organelles DNA is in a tangled loop Some prokaryotes have a second loop of DNA called a plasmid Cell walls vary but can be very “tough” to help the cell survive harsh environments ...
... No nuclear membrane or other membranebound organelles DNA is in a tangled loop Some prokaryotes have a second loop of DNA called a plasmid Cell walls vary but can be very “tough” to help the cell survive harsh environments ...
Virology
... must take over a host cell that provides these functions; therefore a virus is not considered "living." The structure of a virus is extremely simple . Structure: Viruses are the smallest infectious agents (ranging from about 20 nm to about 300 nm in diameter) and contain only one kind of nucleic aci ...
... must take over a host cell that provides these functions; therefore a virus is not considered "living." The structure of a virus is extremely simple . Structure: Viruses are the smallest infectious agents (ranging from about 20 nm to about 300 nm in diameter) and contain only one kind of nucleic aci ...
Chp 4 Notes
... 5. Flagella: long less numerous hair-like structures i. Both are composed of microtubules 6. Centriolies: located near the nucleus in animal cells to organize microtubules during cell division ...
... 5. Flagella: long less numerous hair-like structures i. Both are composed of microtubules 6. Centriolies: located near the nucleus in animal cells to organize microtubules during cell division ...
2 Cells flashcards
... What is cancer of the connective tissue called? What is cancer of the blood called? ...
... What is cancer of the connective tissue called? What is cancer of the blood called? ...
Cell Membranes Review
... 3. Water is a polar (charged) molecule. How does this impact the interactions of water with other molecules? How does water react with non-polar molecules, such as lipids or fats? Explain how water’s polarity results in a high surface tension and high heat capacity. What does this mean for living or ...
... 3. Water is a polar (charged) molecule. How does this impact the interactions of water with other molecules? How does water react with non-polar molecules, such as lipids or fats? Explain how water’s polarity results in a high surface tension and high heat capacity. What does this mean for living or ...
CELL STRUCTURE AND FUNCTION OVERVIEW Cells: the building
... So, they are larger cells than Prokaryotes and Archae So, smaller SA:V ratio Made up for by compartmentalized (membrane-bound) organelles Both Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes have Plasma (Cell) Membrane Plants, like Bacteria, have Cell Walls, but composed of a different material Cellulose vs. Peptidoglyc ...
... So, they are larger cells than Prokaryotes and Archae So, smaller SA:V ratio Made up for by compartmentalized (membrane-bound) organelles Both Eukaryotes and Prokaryotes have Plasma (Cell) Membrane Plants, like Bacteria, have Cell Walls, but composed of a different material Cellulose vs. Peptidoglyc ...
Cell Organelles
... support to plant cells • Found In – Plants cells only (Bacteria can have a cell wall but it is biochemically different from plant cell walls) ...
... support to plant cells • Found In – Plants cells only (Bacteria can have a cell wall but it is biochemically different from plant cell walls) ...
Datasheet TKE P2O5 Moisture Cell
... the count of water molecules. Two electrons are needed to split up one water molecule. Due to this simple principle a calibration of individual cells is not necessary. The gas flow does not need to be observed as long as it stays below the limit where all molecules can be absorbed (none are leaving ...
... the count of water molecules. Two electrons are needed to split up one water molecule. Due to this simple principle a calibration of individual cells is not necessary. The gas flow does not need to be observed as long as it stays below the limit where all molecules can be absorbed (none are leaving ...
INFECTIOUS BIOFE
... Water – To keep things moving in and out of cells. (Universal Solvent) Minerals- For proper chemical balance. NEW AREA OF FOCUS: CELLULAR BIOLOGY Form Follows Function: Parts of the cell are shaped to perform a particular job. ...
... Water – To keep things moving in and out of cells. (Universal Solvent) Minerals- For proper chemical balance. NEW AREA OF FOCUS: CELLULAR BIOLOGY Form Follows Function: Parts of the cell are shaped to perform a particular job. ...
View pdf
... Cells get the instructions what to do from their genes: recipes for making proteins, written in a chemical language on an incredibly thin thread called DNA. Without genes a cell wouldn’t know what to do. It would run out of fresh proteins and die. Almost all of our cells have the same complete set o ...
... Cells get the instructions what to do from their genes: recipes for making proteins, written in a chemical language on an incredibly thin thread called DNA. Without genes a cell wouldn’t know what to do. It would run out of fresh proteins and die. Almost all of our cells have the same complete set o ...
Cell History and Structure - Fort Thomas Independent Schools
... function in living things. b. All cells are produced from other cells. d. All living things are composed of cells. 4. What is the function of a cell wall? a. to protect and support the cell c. to prevent water from passing through it b. to perform different functions in each cell d. to prevent oxyge ...
... function in living things. b. All cells are produced from other cells. d. All living things are composed of cells. 4. What is the function of a cell wall? a. to protect and support the cell c. to prevent water from passing through it b. to perform different functions in each cell d. to prevent oxyge ...
BIOLOGY 1: FIRST SEMESTER FINAL EXAM
... 33. Know the organelles of the cell and what they do. 34. How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different? 35. Give an example of a prokaryotic cell? ...
... 33. Know the organelles of the cell and what they do. 34. How are prokaryotes and eukaryotes different? 35. Give an example of a prokaryotic cell? ...
Virtual Cell Tour Assignment
... Go to http://personal.tmlp.com/Jimr57/textbook/chapter3/chapter3.htm Scroll down to the table of contents and click on the structure you want. In this activity we are concerned with three main structures: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. 1. The Cell Membrane ...
... Go to http://personal.tmlp.com/Jimr57/textbook/chapter3/chapter3.htm Scroll down to the table of contents and click on the structure you want. In this activity we are concerned with three main structures: the cell membrane, the nucleus, and the cytoplasm. 1. The Cell Membrane ...
How is a Cell Like a Factory? (An Introduction to Cell Organelles
... In a factory, a lot of the work is set up in rows called assembly lines. Workers sit or stand along the line, and each worker does his or her part and then moves the work along. In cells, the endoplasmic reticulum is a series of pathways through the cell. It acts as a transport system, work system, ...
... In a factory, a lot of the work is set up in rows called assembly lines. Workers sit or stand along the line, and each worker does his or her part and then moves the work along. In cells, the endoplasmic reticulum is a series of pathways through the cell. It acts as a transport system, work system, ...
Lesson Overview - Midland Park School
... THINK ABOUT IT The human body contains hundreds of different cell types, and every one of them develops from the single cell that starts the process. How do the cells get to be so different from each other? ...
... THINK ABOUT IT The human body contains hundreds of different cell types, and every one of them develops from the single cell that starts the process. How do the cells get to be so different from each other? ...
CH 3 Part 2 - Catherine Huff`s Site
... •Are arranged in bundles and meshworks. •Provide tensional support like cables on a bridge •Composed of the contracticle protein actin and the motor protein myosin •Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. •Are assembled ...
... •Are arranged in bundles and meshworks. •Provide tensional support like cables on a bridge •Composed of the contracticle protein actin and the motor protein myosin •Play key role in cell’s ability to change shape, break apart during cell division and form outpouchings and involutions. •Are assembled ...
3 Bio Eukaryotic Cell Structure and Function (Ch 7.2)
... Small round membrane surrounded organelles filled with enzymes Found anywhere in the cytoplasm Digests or breaks down macromolecules so they can be used by the rest of the cell Eat worn out organelles Remove “junk” Cleanup Crew ...
... Small round membrane surrounded organelles filled with enzymes Found anywhere in the cytoplasm Digests or breaks down macromolecules so they can be used by the rest of the cell Eat worn out organelles Remove “junk” Cleanup Crew ...
S U M M A R Y
... Paclitaxel (taxol), for instance, are both isolated from plants while doxorubicin and bleomycin are derived from bacteria. As many tumors become resistent over time, new anticancer drugs are still needed. Therefore there is a large interest in the identification of small molecules that can be used a ...
... Paclitaxel (taxol), for instance, are both isolated from plants while doxorubicin and bleomycin are derived from bacteria. As many tumors become resistent over time, new anticancer drugs are still needed. Therefore there is a large interest in the identification of small molecules that can be used a ...
MCF7 Whole Cell Lysate: sc-2206
... Santa Cruz Biotechnology offers a variety of whole cell lysates for use in combination with our antibodies as Western Blotting controls. MCF7 Whole Cell Lysate is derived from the MCF7 cell line using a procedure that ensures protein integrity and lot-to-lot reproducibility. All lysates are tested b ...
... Santa Cruz Biotechnology offers a variety of whole cell lysates for use in combination with our antibodies as Western Blotting controls. MCF7 Whole Cell Lysate is derived from the MCF7 cell line using a procedure that ensures protein integrity and lot-to-lot reproducibility. All lysates are tested b ...
Tissue Notes
... 3. Because of the matrix – CT can bear weight, withstand tension d. Structure of CT i. Ground substance, fibers, cells ii. Arrangements vary in different types of tissues and locations iii. Ground substance 1. Unstructured material that fills the space between the cells 2. Contains fibers 3. Interst ...
... 3. Because of the matrix – CT can bear weight, withstand tension d. Structure of CT i. Ground substance, fibers, cells ii. Arrangements vary in different types of tissues and locations iii. Ground substance 1. Unstructured material that fills the space between the cells 2. Contains fibers 3. Interst ...
1 Cytology (Cells) Cells are the lowest level of organization that can
... b. “collage” of proteins embedded/attached to phospholipid bilayer; have pores or channels. 2 main types: 1) peripheral proteins—not embedded 2) integral proteins—penetrate through hydrophobic core—if all the way through, called transmembrane proteins c. six main functions of plasma membrane protein ...
... b. “collage” of proteins embedded/attached to phospholipid bilayer; have pores or channels. 2 main types: 1) peripheral proteins—not embedded 2) integral proteins—penetrate through hydrophobic core—if all the way through, called transmembrane proteins c. six main functions of plasma membrane protein ...
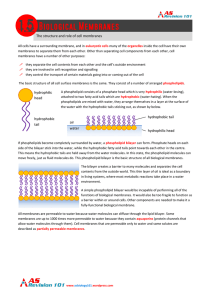
The structure and role of cell membranes hydrophilic head
... contents from the outside world. This thin layer of oil is ideal as a boundary in living systems, where most metabolic reactions take place in a water environment. A simple phospholipid bilayer would be incapable of performing all of the functions of biological membranes. It would also be too fragil ...
... contents from the outside world. This thin layer of oil is ideal as a boundary in living systems, where most metabolic reactions take place in a water environment. A simple phospholipid bilayer would be incapable of performing all of the functions of biological membranes. It would also be too fragil ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).