Learning Guide: Origins of Life
... o Membrane carbohydrates are important in cell-cell recognition. What are two examples of this? o Distinguish between glycolipids and glycoproteins. 2nd Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s 015 Cell Membranes Video. Take notes in your bill. o In the context of cell membranes, explain why Mr. Andersen uses ...
... o Membrane carbohydrates are important in cell-cell recognition. What are two examples of this? o Distinguish between glycolipids and glycoproteins. 2nd Interact: Watch Mr. Andersen’s 015 Cell Membranes Video. Take notes in your bill. o In the context of cell membranes, explain why Mr. Andersen uses ...
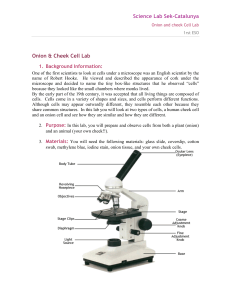
Onion and cheek Cell Lab
... because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living things are composed of cells. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and cells perform different functions. Although cells may appear outwardly different, they ...
... because they looked like the small chambers where monks lived. By the early part of the 19th century, it was accepted that all living things are composed of cells. Cells come in a variety of shapes and sizes, and cells perform different functions. Although cells may appear outwardly different, they ...
3.1 Notes
... • Janssen – given credit for inventing first compound microscope (2 or more lenses) ...
... • Janssen – given credit for inventing first compound microscope (2 or more lenses) ...
CELL TRANSPORT
... do not extend through the membrane. They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. ...
... do not extend through the membrane. They bond and drag molecules through the lipid bilayer and release them on the opposite side. ...
Prokaryotic and Eukaryotic Cells
... There are many different types of cells. For example, in you there are blood cells and skin cells and bone cells and even bacteria. Here we have drawings of bacteria and human cells. Can you tell which depicts various types of bacteria? All cells - whether from bacteria, human, or any other organism ...
... There are many different types of cells. For example, in you there are blood cells and skin cells and bone cells and even bacteria. Here we have drawings of bacteria and human cells. Can you tell which depicts various types of bacteria? All cells - whether from bacteria, human, or any other organism ...
cell model rubric
... As you work through the activity use the rubric below as a guide to earning your grade. TURN THIS PAPER IN WITH YOUR PROJECT Procedure 1. Use materials to build a plant or animal cell model. Your model should be three dimensional , not flat. Follow the materials guidelines below. 2. Your model must ...
... As you work through the activity use the rubric below as a guide to earning your grade. TURN THIS PAPER IN WITH YOUR PROJECT Procedure 1. Use materials to build a plant or animal cell model. Your model should be three dimensional , not flat. Follow the materials guidelines below. 2. Your model must ...
Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic Cells
... transporter protein for each substance • Group translocation – Occurs only in prokaryotes – Substance being transported is altered during transport (often phosphorylation) – Membrane is impermeable to the new product ...
... transporter protein for each substance • Group translocation – Occurs only in prokaryotes – Substance being transported is altered during transport (often phosphorylation) – Membrane is impermeable to the new product ...
BIOLOGY 12 UNIT 1b – The Cell Membrane
... c. Plasmolysis: Contraction of the cell contents as the cell shrinks due to the loss of water when placed in a hypertonic solution. d. Tonicity: The strength of a solution in relationship to osmosis or the degree to which the concentration of solute versus solvent causes fluids to move into or out o ...
... c. Plasmolysis: Contraction of the cell contents as the cell shrinks due to the loss of water when placed in a hypertonic solution. d. Tonicity: The strength of a solution in relationship to osmosis or the degree to which the concentration of solute versus solvent causes fluids to move into or out o ...
2106lecture 2a powerpoint
... acids from fat digestion and amino acids from proteins - is this really representative of energy metabolism? -catabolism-energy-producing reactions that occur as the result of breakdown of energy yielding nutrients-eg glucose from carbohydrates, glycerol and fatty acids from fat digestion and amino ...
... acids from fat digestion and amino acids from proteins - is this really representative of energy metabolism? -catabolism-energy-producing reactions that occur as the result of breakdown of energy yielding nutrients-eg glucose from carbohydrates, glycerol and fatty acids from fat digestion and amino ...
(not through inheritance). What is the origin of vacuole?
... membrane. What are the differences between the two membranes? ...
... membrane. What are the differences between the two membranes? ...
Marine Natural Products with Potential as Treatments for Pancreatic
... Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute at FAU ...
... Harbor Branch Oceanographic Institute at FAU ...
CellTransport
... plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell. ...
... plasma membrane allows it to function as a regulatory structure and/or protective barrier for a cell. ...
Cell Reproduction
... its organelles are equally separated into two daughter cells • Completes the process of cell division • the new cells are now in interphase ...
... its organelles are equally separated into two daughter cells • Completes the process of cell division • the new cells are now in interphase ...
Cell City Analogy
... A. City Limits- controls what goes into and out of a city. B. Road/Highway system- allows for movement throughout the city. C. City Hall- controls the activities of the city. D. City Auditor - stores all of the records of the city and passes them on as the city grows. E. City Planning Office- a plac ...
... A. City Limits- controls what goes into and out of a city. B. Road/Highway system- allows for movement throughout the city. C. City Hall- controls the activities of the city. D. City Auditor - stores all of the records of the city and passes them on as the city grows. E. City Planning Office- a plac ...
HUMAN-CTNND1_isform 2ABC(Y174) Antibody
... prostate, but lost in several tumor tissues derived from these organs. ...
... prostate, but lost in several tumor tissues derived from these organs. ...
AP Biology - ReicheltScience.com
... wall- protects and maintains shape Primary cell wall- thin flexible wall (young plant) Secondary cell wall- hardened structure between the plasma membrane and primary wall Middle lamella- Thin layer with sticky polysaccharides (pectins) glues cells together Plasmodesmatacommunicating channel ...
... wall- protects and maintains shape Primary cell wall- thin flexible wall (young plant) Secondary cell wall- hardened structure between the plasma membrane and primary wall Middle lamella- Thin layer with sticky polysaccharides (pectins) glues cells together Plasmodesmatacommunicating channel ...
Author - Princeton ISD
... o All living things are composed of cells (bacteria, Protista, fungi, plants, and animals) o Basic unit of life is the cell o Cells come from pre-existing cells (biogenesis) Cells are grouped into two categories, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, based on their structure. Organelles carry out specialized ...
... o All living things are composed of cells (bacteria, Protista, fungi, plants, and animals) o Basic unit of life is the cell o Cells come from pre-existing cells (biogenesis) Cells are grouped into two categories, prokaryotic and eukaryotic, based on their structure. Organelles carry out specialized ...
Cell Membrane Tutorial
... notebook: write a 1–2 paragraph summary about the cell membrane. It should include: a. Description and brief sketch of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane b. Function of the cell membrane c. What molecules can easily diffuse through the membrane, and how larger molecules get through the membrane? ...
... notebook: write a 1–2 paragraph summary about the cell membrane. It should include: a. Description and brief sketch of the lipid bilayer of the cell membrane b. Function of the cell membrane c. What molecules can easily diffuse through the membrane, and how larger molecules get through the membrane? ...
Chapter 3 Observing Microorganisms Through a Microscope
... • Gram positive cells have thick cell walls. They hold on to the primary stain. • Gram negative cells have thin cell wall. • One or two layers of peptidoglycan. They also have an outer membrane – lipids. • Alcohol causes damage to the lipids. Primary stain leaks out. ...
... • Gram positive cells have thick cell walls. They hold on to the primary stain. • Gram negative cells have thin cell wall. • One or two layers of peptidoglycan. They also have an outer membrane – lipids. • Alcohol causes damage to the lipids. Primary stain leaks out. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).