Comparing Plant And Animal Cells
... rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body for further processing and to the membranes. vacuole - a large, membrane-bound space within a plant cell that is filled with fluid, mostly water. Most plant cells have a single vacuole that takes up much of the cell. It helps main ...
... rough ER, moving the newly-made proteins and lipids to the Golgi body for further processing and to the membranes. vacuole - a large, membrane-bound space within a plant cell that is filled with fluid, mostly water. Most plant cells have a single vacuole that takes up much of the cell. It helps main ...
File
... completely from the parent cell. Budding also occurs in flatworms, which divide into two and then regenerate to form two new flatworms. ...
... completely from the parent cell. Budding also occurs in flatworms, which divide into two and then regenerate to form two new flatworms. ...
Name: ______ Pd ______ Date Foundations of Biology Mr
... less pure water. 23. Water tends to move towards the _________________ environment because the solute levels are higher but the water concentration is lower. 24. Hypotonic solutions have _________________dissolved solutes but a higher concentration of pure water. 25. Isotonic solutions have ________ ...
... less pure water. 23. Water tends to move towards the _________________ environment because the solute levels are higher but the water concentration is lower. 24. Hypotonic solutions have _________________dissolved solutes but a higher concentration of pure water. 25. Isotonic solutions have ________ ...
Cell Growth Section 10-1 pgs 241-243
... Understanding the relationship between a cell’s volume and its surface area is the key to understanding why cells must ______________________ as they grow. ...
... Understanding the relationship between a cell’s volume and its surface area is the key to understanding why cells must ______________________ as they grow. ...
Cell Analogy Project
... wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles). 4. Recognize that within cells, many of the basic functions of organisms (e.g., extracting energy from food and getting rid of waste) are carried out. The way in which cells function is similar in all living organisms. ...
... wall, nucleus, cytoplasm, chloroplasts, mitochondria, vacuoles). 4. Recognize that within cells, many of the basic functions of organisms (e.g., extracting energy from food and getting rid of waste) are carried out. The way in which cells function is similar in all living organisms. ...
Cells/Organelles Case
... inside cells and causes 1-2 week Q-fever. Infection occurs 23 weeks after inhalation of barnyard dust. Coxiella are often found in livestock and are excreted in milk, urine, and feces. ...
... inside cells and causes 1-2 week Q-fever. Infection occurs 23 weeks after inhalation of barnyard dust. Coxiella are often found in livestock and are excreted in milk, urine, and feces. ...
An Examination of Nunc Cell Factory System for Consistent Reliable
... systems are popular in fields where large quantities of cells are required and are a reliable tool for the production of vaccines, recombinant proteins, and for the generation of cell mass. Unlike single-layer systems, where the entire culture is easily visualized under a microscope, the middle laye ...
... systems are popular in fields where large quantities of cells are required and are a reliable tool for the production of vaccines, recombinant proteins, and for the generation of cell mass. Unlike single-layer systems, where the entire culture is easily visualized under a microscope, the middle laye ...
Principals of General Zoology (Zoo-103)
... Enzymes are important to metabolism because they act as catalysts to allow chemical reactions to proceed quickly and efficiently. ...
... Enzymes are important to metabolism because they act as catalysts to allow chemical reactions to proceed quickly and efficiently. ...
Epithelial and Connective Tissues
... and epithelia in place, and has a variety of proteinaceous fibers, including collagen and elastin. It is also important in inflammation. • Reticular connective tissue is a network of reticular fibers (fine collagen) that form a soft skeleton to support the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, ...
... and epithelia in place, and has a variety of proteinaceous fibers, including collagen and elastin. It is also important in inflammation. • Reticular connective tissue is a network of reticular fibers (fine collagen) that form a soft skeleton to support the lymphoid organs (lymph nodes, bone marrow, ...
Y - immunology.unideb.hu
... determine their specificities 3. In one individual a large B-cell repertoire is generated consisting of B-cell clones with different H- and L-chain variable domains 4. This potential B-cell repertoire is able to recognize a wide array of various antigens 5. Immature B-cells express IgM and IgD surfa ...
... determine their specificities 3. In one individual a large B-cell repertoire is generated consisting of B-cell clones with different H- and L-chain variable domains 4. This potential B-cell repertoire is able to recognize a wide array of various antigens 5. Immature B-cells express IgM and IgD surfa ...
Y - immunology.unideb.hu
... Due to clonal expansion of a single cell that contains a unique rearrangement the amount of cancer cells in blood or in bone marrow can be determined Can be used to monitor residual tumor cells upon treatment ...
... Due to clonal expansion of a single cell that contains a unique rearrangement the amount of cancer cells in blood or in bone marrow can be determined Can be used to monitor residual tumor cells upon treatment ...
cells - Fort Bend ISD
... lysosomal, and secretory proteins is called Rough ER. • Rough ER = ribosomes found on the surface of endoplasmic reticulum. • Newly made proteins leave ribosomes and are inserted into the ...
... lysosomal, and secretory proteins is called Rough ER. • Rough ER = ribosomes found on the surface of endoplasmic reticulum. • Newly made proteins leave ribosomes and are inserted into the ...
www.theallpapers.com
... answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should b ...
... answers A, B, C and D. Choose the one you consider correct and record your choice in soft pencil on the separate Answer Sheet. Read the instructions on the Answer Sheet very carefully. Each correct answer will score one mark. A mark will not be deducted for a wrong answer. Any rough working should b ...
5.5 Transport
... – against concentration gradient • LOW HIGH – uses a protein pump (requires ATP) ...
... – against concentration gradient • LOW HIGH – uses a protein pump (requires ATP) ...
Cell Structures - Manhasset Schools
... • The cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm and controls what enters and leaves the cell. • The cytoplasm helps the cell keep its shape. • Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and other organelles. They include the mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles, lysosomes, an ...
... • The cell membrane encloses the cytoplasm and controls what enters and leaves the cell. • The cytoplasm helps the cell keep its shape. • Eukaryotic cells contain a nucleus and other organelles. They include the mitochondrion, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, vesicles, vacuoles, lysosomes, an ...
12812 Describe eukaryotic cell structure and function
... Cellular transport processes are explained in terms of the properties of the substances transported. Range ...
... Cellular transport processes are explained in terms of the properties of the substances transported. Range ...
Galectin
... Many galectins have already been linked to immunity (Vasta, et al, 1999). Galectins regulate cytokine production (Cortegano et al, 19989; Vespa et al, 1999), stimulate thymocyte apoptosis (Galectin-1; Chung et al,2000; Pace et al 2000; Galectin9 - Wada et al, 1997), activate respiratory bursts of ne ...
... Many galectins have already been linked to immunity (Vasta, et al, 1999). Galectins regulate cytokine production (Cortegano et al, 19989; Vespa et al, 1999), stimulate thymocyte apoptosis (Galectin-1; Chung et al,2000; Pace et al 2000; Galectin9 - Wada et al, 1997), activate respiratory bursts of ne ...
Total marks available - Information for Parents
... (c) An investigation was carried out into the effects of mineral ion concentrations on the size of fibres produced by flax plants. Seedlings of flax plants were grown in different concentrations of mineral ions. A control group of plants was grown in a standard mineral ion concentration. This soluti ...
... (c) An investigation was carried out into the effects of mineral ion concentrations on the size of fibres produced by flax plants. Seedlings of flax plants were grown in different concentrations of mineral ions. A control group of plants was grown in a standard mineral ion concentration. This soluti ...
Chapters 4 and 5 Cell Structures, Functions and Transport
... smaller and less complex than eukaryotes Do not have membranes enclosing cell parts, therefore NO DISTINCT NUCLEUS DNA (genetic material) is on a circular loop in center of cell ...
... smaller and less complex than eukaryotes Do not have membranes enclosing cell parts, therefore NO DISTINCT NUCLEUS DNA (genetic material) is on a circular loop in center of cell ...
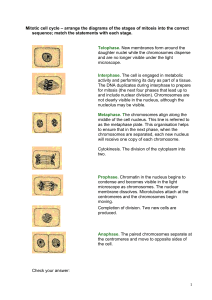
Mitotic cell cycle – arrange the diagrams of the stages of mitosis into
... Interphase. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleol ...
... Interphase. The cell is engaged in metabolic activity and performing its duty as part of a tissue. The DNA duplicates during interphase to prepare for mitosis (the next four phases that lead up to and include nuclear division). Chromosomes are not clearly visible in the nucleus, although the nucleol ...
HOC 1 - 8 The Cell
... When ova & sperm join, form a zygote (new cell) with 46 chromosomes (23 from ova & 23 from sperm) After zygote forms, rapid mitosis occurs 4-5 days, becomes blastocyst which contains embryonic stem cells – Stem cells have ability to transform into any specialized cell & perform functions – Contr ...
... When ova & sperm join, form a zygote (new cell) with 46 chromosomes (23 from ova & 23 from sperm) After zygote forms, rapid mitosis occurs 4-5 days, becomes blastocyst which contains embryonic stem cells – Stem cells have ability to transform into any specialized cell & perform functions – Contr ...
Transport Notes
... concentration with the help of a carrier protein – Molecules attach to a specific protein – The protein allows it to move through the membrane – Needed when molecules are too big or have an electrical charge (ions!!) • Glucose (large molecules), Na+, Ca+, K+, Cl- ...
... concentration with the help of a carrier protein – Molecules attach to a specific protein – The protein allows it to move through the membrane – Needed when molecules are too big or have an electrical charge (ions!!) • Glucose (large molecules), Na+, Ca+, K+, Cl- ...
Animal Cell - KerrBrookfield
... Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Cells are bathed in an aqueous solution called extracellular fluid. There are many different kinds of cells, which are specialized to carry out particular functions. In spite of this, cells have many common features. ...
... Cells are the basic structural and functional units of life. Cells are bathed in an aqueous solution called extracellular fluid. There are many different kinds of cells, which are specialized to carry out particular functions. In spite of this, cells have many common features. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).