Technology Integration for Analysis of High Throughput Cellular
... Cytomics will become a major field of study. Every cell is different. By studying each cell's unique function, that cell type can be further modeled for subsequent analysis using statistical techniques. As the field of tissue engineering explodes, it will not be long before cellular engineering will ...
... Cytomics will become a major field of study. Every cell is different. By studying each cell's unique function, that cell type can be further modeled for subsequent analysis using statistical techniques. As the field of tissue engineering explodes, it will not be long before cellular engineering will ...
Microbial Cell Surfaces and Secretion Systems
... Integral OM proteins (OMPs) structurally deviate from other membrane proteins. The membrane-spanning segments are not α-helices but β-strands, which form a βbarrel (Fig. 6.1). These β-strands are amphipathic with hydrophobic residues facing the lipids and hydrophilic ones directed toward the interio ...
... Integral OM proteins (OMPs) structurally deviate from other membrane proteins. The membrane-spanning segments are not α-helices but β-strands, which form a βbarrel (Fig. 6.1). These β-strands are amphipathic with hydrophobic residues facing the lipids and hydrophilic ones directed toward the interio ...
Science Monday 1/11/16
... List the levels of organization in multicellular organisms and give examples of each level. Explain the purpose of stem cells and specialized cells in a developing organism. Identify key organelles in a cell and explain their role in the cell’s survival. Name the organelles ONLY found in plant cells ...
... List the levels of organization in multicellular organisms and give examples of each level. Explain the purpose of stem cells and specialized cells in a developing organism. Identify key organelles in a cell and explain their role in the cell’s survival. Name the organelles ONLY found in plant cells ...
Class26 2-15 Win17 Proliferation, Apoptosis
... opening in fruit fly development. Based on what you see in this video, which of these are needed for dorsal closure? ...
... opening in fruit fly development. Based on what you see in this video, which of these are needed for dorsal closure? ...
ID number: S423100806M (王中峰)
... conditions, including glaucoma. Accompanying the enhanced expression of glial ...
... conditions, including glaucoma. Accompanying the enhanced expression of glial ...
Passivated Emitter Rear Locally Diffused Solar Cells
... saturation current density and improvement of the cell open-circuit voltage to above 700-mV are two major advantages of this technology. This method was not only used to improve the quality of this SiO2 layer but also used to maintain the high carrier lifetime through the cell processing [5]. In ord ...
... saturation current density and improvement of the cell open-circuit voltage to above 700-mV are two major advantages of this technology. This method was not only used to improve the quality of this SiO2 layer but also used to maintain the high carrier lifetime through the cell processing [5]. In ord ...
Membranes - OnCourse
... Exocytosis: movement of material out of a cell by means of a vesicle. During exocytosis a vesicles inside the cell fuse with the cell membrane. The contents of the vesicle are then release outside of the cell through the cell membrane. Exocytosis is used to transport proteins modified by the Golgi a ...
... Exocytosis: movement of material out of a cell by means of a vesicle. During exocytosis a vesicles inside the cell fuse with the cell membrane. The contents of the vesicle are then release outside of the cell through the cell membrane. Exocytosis is used to transport proteins modified by the Golgi a ...
`response to x` terms?
... 3. SourceForge Request Jesintha Maniraja • The GO definition for ‘response to stimulus’ is “A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a specified stimulus.” ...
... 3. SourceForge Request Jesintha Maniraja • The GO definition for ‘response to stimulus’ is “A change in state or activity of a cell or an organism (in terms of movement, secretion, enzyme production, gene expression, etc.) as a result of a specified stimulus.” ...
EDIBLE ANIMAL CELL
... into an additional plastic bag for extra protection. Fill in the attached key (page 4) to explain the description and function of each organelle. For example, Organelle: nucleus Description: Little blue bouncy ball. Function: The "brain" of the cell. Stores DNA (genetic information). ...
... into an additional plastic bag for extra protection. Fill in the attached key (page 4) to explain the description and function of each organelle. For example, Organelle: nucleus Description: Little blue bouncy ball. Function: The "brain" of the cell. Stores DNA (genetic information). ...
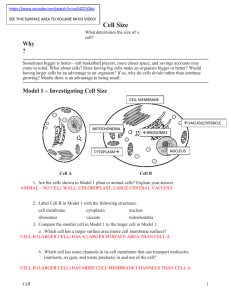
Model 1 – Investigating Cell Size
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
... a. Which cell has more mitochondria? CELL B (LARGER CELL) HAS MORE MITOCHONDRIA THAN CELL A. b. Propose an explanation for why the cell in part a would need more mitochondria for proper functioning of the cell. SINCE THE CELL IS LARGER, IT WILL NEED MORE ATP TO RUN CELL PROCESSES. 5. What would be t ...
File - fiserscience.com
... alterations that progressively release the cell from the normal controls on cell proliferation and malignancy © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
... alterations that progressively release the cell from the normal controls on cell proliferation and malignancy © 2012 Pearson Education, Inc. ...
Muscle Types
... (T tubules), tubes that extend inward and pass all the way through the cell. Each tube opens to the outside ...
... (T tubules), tubes that extend inward and pass all the way through the cell. Each tube opens to the outside ...
Notch 1 and pre-T-cell Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia (T
... causes over proliferation and accumulation of pre-T-cells (T lymphoblasts) • These pre-T-cells are nonfunctional and over proliferate without differentiating into T cells • Normal T-cells (T lymphocytes) are white blood cells that function in cell immunity ...
... causes over proliferation and accumulation of pre-T-cells (T lymphoblasts) • These pre-T-cells are nonfunctional and over proliferate without differentiating into T cells • Normal T-cells (T lymphocytes) are white blood cells that function in cell immunity ...
Transport across cell membranes
... • Cells must maintain enough water for cellular processes • Osmotic pressure: force of osmosis – Hypotonic: solution with the higher concentration versus the cell – Isotonic: solution with equal osmotic concentration to inner cell – Hypertonic: solution with the lower concentration versus the cell W ...
... • Cells must maintain enough water for cellular processes • Osmotic pressure: force of osmosis – Hypotonic: solution with the higher concentration versus the cell – Isotonic: solution with equal osmotic concentration to inner cell – Hypertonic: solution with the lower concentration versus the cell W ...
Exploring Animal and Plant Cells Desired Outcomes
... S5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, singlecelled, multi-celled). a. Use magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses to observe cells and their structure. b. Identify parts of a plant cell (cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell ( ...
... S5L3. Students will diagram and label parts of various cells (plant, animal, singlecelled, multi-celled). a. Use magnifiers such as microscopes or hand lenses to observe cells and their structure. b. Identify parts of a plant cell (cell wall, cytoplasm, nucleus, chloroplasts) and of an animal cell ( ...
fundamental unit of life
... Nucleus determine the way the cell will develop and what form it will exhibit at maturity, by directing the chemical activities of the cell. Nucleoid: In some organisms like bacteria, the nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane. Such an undefined nu ...
... Nucleus determine the way the cell will develop and what form it will exhibit at maturity, by directing the chemical activities of the cell. Nucleoid: In some organisms like bacteria, the nuclear region of the cell may be poorly defined due to the absence of a nuclear membrane. Such an undefined nu ...
WEEK 12 CP Cell_Transport_Bio
... Tuesday • What is the difference between active and passive transport? • Name the 3 types of passive transport. ...
... Tuesday • What is the difference between active and passive transport? • Name the 3 types of passive transport. ...
Six Instructional Shifts
... Under the microscope, a cell looks a lot like a fried egg: It has a white (the cytoplasm) that’s full of water and proteins to keep it fed, and a yolk (the nucleus) that holds all the genetic information that makes you you. The cytoplasm buzzes like a New York City street. It’s crammed full of molec ...
... Under the microscope, a cell looks a lot like a fried egg: It has a white (the cytoplasm) that’s full of water and proteins to keep it fed, and a yolk (the nucleus) that holds all the genetic information that makes you you. The cytoplasm buzzes like a New York City street. It’s crammed full of molec ...
07-2010C
... is tendency of molecules to spread out spontaneously from area of high concentration to area of low concentration ...
... is tendency of molecules to spread out spontaneously from area of high concentration to area of low concentration ...
Human Physiology: Cell Structure and Function
... -possess a membrane-bound nucleus -are more complex than prokaryotic cells -compartmentalize many cellular functions within organelles and the endomembrane system -possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure ...
... -possess a membrane-bound nucleus -are more complex than prokaryotic cells -compartmentalize many cellular functions within organelles and the endomembrane system -possess a cytoskeleton for support and to maintain cellular structure ...
monera - Sumber Belajar
... Cell walls with peptidoglycan Ribosom contain one kind of RNA Polymerase Plasma membrane contain lipid with ester bound Most bacteria in this kingdom Come in 3 basic shapes --- cocci (spheres), bacilli ...
... Cell walls with peptidoglycan Ribosom contain one kind of RNA Polymerase Plasma membrane contain lipid with ester bound Most bacteria in this kingdom Come in 3 basic shapes --- cocci (spheres), bacilli ...
File - Science for all
... Population A group of the same type of organisms all living together in the same place. ...
... Population A group of the same type of organisms all living together in the same place. ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).