Read PDF
... induced stem cells (iSC) could obviate the need for exogenous stem cells with their attendant problems.5,19 Thus, there are many more questions than answers available at present regarding utility of stem cell in kidney diseases. Kidney is a complex, solid organ with a multitude of cells forming diff ...
... induced stem cells (iSC) could obviate the need for exogenous stem cells with their attendant problems.5,19 Thus, there are many more questions than answers available at present regarding utility of stem cell in kidney diseases. Kidney is a complex, solid organ with a multitude of cells forming diff ...
File
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/photosynthesis_1/graphics/chloroplast.GIF ...
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/photosynthesis_1/graphics/chloroplast.GIF ...
1.2 Ultrastructure of Cells 2016
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/photosynthesis_1/graphics/chloroplast.GIF ...
... http://www.biology.arizona.edu/biochemistry/problem_sets/photosynthesis_1/graphics/chloroplast.GIF ...
chromosomes - sandsbiochem
... series of events that cells go through as they grow and develop cells alive cell cycle ...
... series of events that cells go through as they grow and develop cells alive cell cycle ...
Cancer Stem Cells: Controversial or Just Misunderstood?
... CSCs may present a range of antigens commonly associated with primitive cells, but the specific expression pattern may vary from patient to patient. If so, then the properties of CSCs must be empirically determined for each patient. Notably, this exact scenario has been observed in leukemia studies ...
... CSCs may present a range of antigens commonly associated with primitive cells, but the specific expression pattern may vary from patient to patient. If so, then the properties of CSCs must be empirically determined for each patient. Notably, this exact scenario has been observed in leukemia studies ...
The 6 Kingdom`s
... not contain chlorophyll (nonphotosynthetic) Important decomposers Most are multi-cellular eukaryotes, but some are unicellular like yeast Cell walls are made of chitin (a complex sugar) ...
... not contain chlorophyll (nonphotosynthetic) Important decomposers Most are multi-cellular eukaryotes, but some are unicellular like yeast Cell walls are made of chitin (a complex sugar) ...
Chlorogloeopsis PC C 69 12
... The detection of 6-O-methyl-~-mannoseand of 3-0-methyl-mannose in ChZorogZoeopsis PCC 69 12 is reminiscent of previous findings of sugar 0-methyl ethers in (1ipo)polysaccharides from a number of other phototrophic prokaryotes (Weckesser et al., 1979). In the Chlorogloeopsis PCC 69 12 heteropolysacch ...
... The detection of 6-O-methyl-~-mannoseand of 3-0-methyl-mannose in ChZorogZoeopsis PCC 69 12 is reminiscent of previous findings of sugar 0-methyl ethers in (1ipo)polysaccharides from a number of other phototrophic prokaryotes (Weckesser et al., 1979). In the Chlorogloeopsis PCC 69 12 heteropolysacch ...
Plant Cell
... PLANT • Function: Gives the cell most of its support and structure • A thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell • Bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant ...
... PLANT • Function: Gives the cell most of its support and structure • A thick, rigid membrane that surrounds a plant cell • Bonds with other cell walls to form the structure of the plant ...
Juxtaglomerular cells
... The capsule consists of two layers of epithelium. The visceral layer fits like a glove over the glomerulus. This can not be seen with light microscope. Outer layer the parietal layer can be seen with light microscope. ...
... The capsule consists of two layers of epithelium. The visceral layer fits like a glove over the glomerulus. This can not be seen with light microscope. Outer layer the parietal layer can be seen with light microscope. ...
CELL PARTS Chapter 4 - local.brookings.k12.sd.us
... (… role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code define homeostasis; ...
... (… role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code define homeostasis; ...
CELL PARTS Chapter 4 - Brookings School District
... (… role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code define homeostasis; ...
... (… role of enzymes) recognize that different structures perform different functions identify DNA as the structure that carries the genetic code define homeostasis; ...
plasma membrane
... its structure and activities The cytoskeleton is composed of three kinds of fibers. 1. Microfilaments (actin filaments) support the cell’s shape and are involved in motility. 2. Intermediate filaments reinforce cell shape and anchor organelles. 3. Microtubules (made of tubulin) give the cell rigid ...
... its structure and activities The cytoskeleton is composed of three kinds of fibers. 1. Microfilaments (actin filaments) support the cell’s shape and are involved in motility. 2. Intermediate filaments reinforce cell shape and anchor organelles. 3. Microtubules (made of tubulin) give the cell rigid ...
Membrane Practice Test
... 33. Large amoeboid-type cells, called macrophages, remove bacteria and worn-out red blood cells by a process called (1.) facilitated diffusion (2.) osmosis (3.) exocytosis (4.) phagocytosis (5.) pinocytosis 34. The process by which a vesicle is formed at the plasma membrane to bring substances into ...
... 33. Large amoeboid-type cells, called macrophages, remove bacteria and worn-out red blood cells by a process called (1.) facilitated diffusion (2.) osmosis (3.) exocytosis (4.) phagocytosis (5.) pinocytosis 34. The process by which a vesicle is formed at the plasma membrane to bring substances into ...
Cells2ForAandP
... origins—separate cell interior from environment as cell membrane • Mammals and other vertebrates—long-term energy storage • Role in diet=big controversy! Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. ...
... origins—separate cell interior from environment as cell membrane • Mammals and other vertebrates—long-term energy storage • Role in diet=big controversy! Larry M. Frolich, Ph.D. ...
Communication
... Produced in a region of plant structure by unspecialised cells Some are active at the site of production Not specific – can have different effects on different tissues ...
... Produced in a region of plant structure by unspecialised cells Some are active at the site of production Not specific – can have different effects on different tissues ...
23.3_Stems
... Explain How does the arrangement of vascular bundles in monocot stems differ from dicot stems Apply Concepts How do the functions of a stem relate to the functions of the roots and leaves of a ...
... Explain How does the arrangement of vascular bundles in monocot stems differ from dicot stems Apply Concepts How do the functions of a stem relate to the functions of the roots and leaves of a ...
Document
... The Plasma Membrane • Because of the distribution of lipids and the proteins embedded in it, the membrane allows some substances across but not others; this is called Selective permeability – Rule of thumb: small, neutrally-charged, lipidsoluble substances can freely pass. Water is a special case - ...
... The Plasma Membrane • Because of the distribution of lipids and the proteins embedded in it, the membrane allows some substances across but not others; this is called Selective permeability – Rule of thumb: small, neutrally-charged, lipidsoluble substances can freely pass. Water is a special case - ...
Anatomy and Physiology Unit 2 Review
... 1. Endocytosis and exocytosis 2. Diffusion and phagocytosis 3. Osmosis and facilitated diffusion 4. Active and passive transport ...
... 1. Endocytosis and exocytosis 2. Diffusion and phagocytosis 3. Osmosis and facilitated diffusion 4. Active and passive transport ...
B2 checklist NEW
... B2.1 – CELLS AND SIMPLE TRANSPORT Label an animal cell and a plant cell. Give the functions of each of the part of a cell. Label a bacterial cell and a yeast cell. Give examples of specialised cells and explain how they are adapted to their function. Define diffusion. Give a factor that affects the ...
... B2.1 – CELLS AND SIMPLE TRANSPORT Label an animal cell and a plant cell. Give the functions of each of the part of a cell. Label a bacterial cell and a yeast cell. Give examples of specialised cells and explain how they are adapted to their function. Define diffusion. Give a factor that affects the ...
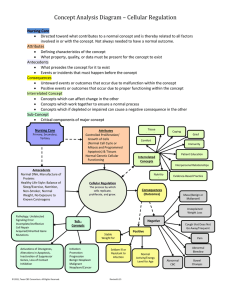
Concept Analysis Diagram * Cellular Regulation
... Concept Analysis Diagram – Cellular Regulation Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, h ...
... Concept Analysis Diagram – Cellular Regulation Explanation of Cellular Regulation Diagram Cellular Regulation is the process by which cells replicate, proliferate, and grow. In order for Cellular Regulation to occur the following antecedents should be present: normal DNA, manufacture of proteins, h ...
PhD position in Plant-Microbe Interaction Biology / Fungal effector
... The department headed by Prof. Volker Lipka is interested in the molecular analysis of plant microbe interactions. The proposed research will focus on the interaction of vascular fungal pathogens of the genus Verticillium with the model plant Arabidopsis . In preliminary work we found Verticillium i ...
... The department headed by Prof. Volker Lipka is interested in the molecular analysis of plant microbe interactions. The proposed research will focus on the interaction of vascular fungal pathogens of the genus Verticillium with the model plant Arabidopsis . In preliminary work we found Verticillium i ...
Extracellular matrix

In biology, the extracellular matrix (ECM) is a collection of extracellular molecules secreted by cells that provides structural and biochemical support to the surrounding cells. Because multicellularity evolved independently in different multicellular lineages, the composition of ECM varies between multicellular structures; however, cell adhesion, cell-to-cell communication and differentiation are common functions of the ECM.The animal extracellular matrix includes the interstitial matrix and the basement membrane. Interstitial matrix is present between various animal cells (i.e., in the intercellular spaces). Gels of polysaccharides and fibrous proteins fill the interstitial space and act as a compression buffer against the stress placed on the ECM. Basement membranes are sheet-like depositions of ECM on which various epithelial cells rest.The plant ECM includes cell wall components, like cellulose, in addition to more complex signaling molecules. Some single-celled organisms adopt multicelluar biofilms in which the cells are embedded in an ECM composed primarily of extracellular polymeric substances (EPS).